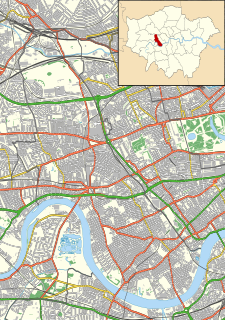
Fulham is an area of the London Borough of Hammersmith & Fulham in West London, England, 3.6 miles (5.8 km) southwest of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, bordering Hammersmith, Kensington and Chelsea. The area faces Wandsworth, Putney, Barn Elms and the London Wetland Centre in Barnes. on the far side of the river.

Whittington Hospital is a district general and teaching hospital of UCL Medical School and Middlesex University School of Health and Social Sciences. Located in Upper Holloway, it is managed by Whittington Health NHS Trust, operating as Whittington Health, an integrated care organisation providing hospital and community health services in the north London boroughs of Islington and Haringey. Its Jenner Building, a former smallpox hospital, is a Grade II listed building.

Rampton Secure Hospital is a high-security psychiatric hospital near the village of Woodbeck between Retford and Rampton in Nottinghamshire, England. It is one of three high-security psychiatric hospitals in England, alongside Ashworth Hospital in Merseyside and Broadmoor Hospital in Berkshire. It is managed by Nottinghamshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust.

The Royal Free Hospital is a major teaching hospital in the Hampstead area of the London Borough of Camden. The hospital is part of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, which also runs services at Barnet Hospital, Chase Farm Hospital and a number of other sites. The trust is a founder member of the UCLPartners academic health science centre.
The London Ambulance Service NHS Trust (LAS) is an NHS trust responsible for operating ambulances and answering and responding to urgent and emergency medical situations within the London region of England. The service responds to 999 phone calls across the region, and 111 phone calls from certain parts, providing triage and advice to enable an appropriate level of response.

The Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a specialist orthopaedic hospital located in the London Borough of Harrow, United Kingdom, and a part of Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust. It provides the most comprehensive range of neuro-musculoskeletal health care in the UK, including acute spinal injury, complex bone tumour treatment, orthopaedic medicine and specialist rehabilitation for chronic back pain. The RNOH is a major teaching centre and around 20% of orthopaedic surgeons in the UK receive training there.

The Royal Marsden Hospital (RM) is a specialist cancer treatment hospital in London based in Kensington and Chelsea, next to the Royal Brompton Hospital, in Fulham Road with a second site in Belmont, close to Sutton Hospital, High Down and Downview Prisons. It is managed by the Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust.
The Metropolitan Asylums Board (MAB) was established under Poor Law legislation to deal with London's sick and poor. It was established by the Metropolitan Poor Act 1867 and dissolved in 1930, when its functions were transferred to the London County Council.

Westminster Hospital was a hospital in London, England, founded in 1719. In 1834 a medical school attached to the hospital was formally founded. In 1939 a newly built hospital and medical school opened in Horseferry Road, Westminster. In 1994 the hospital closed, and its resources were moved to the new Chelsea and Westminster Hospital at the old St Stephen's Hospital site in Fulham Road.

St Ann's Hospital is a mixed healthcare campus in South Tottenham in the London Borough of Haringey, England, and is the headquarters for Barnet, Enfield and Haringey Mental Health NHS Trust. It also formerly housed the Haringey NHS primary care trust.

Hammersmith and Fulham London Borough Council is the local authority for the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in the United Kingdom capital of London. Hammersmith and Fulham is divided into 21 wards, electing a total of 50 councillors. The council was created by the London Government Act 1963 as the Hammersmith London Borough Council and replaced two local authorities: Hammersmith Metropolitan Borough Council and Fulham Metropolitan Borough Council. The council was renamed on 1 January 1980.

King's Cross Hospital, often shortened to King's Cross is a hospital in Dundee, Scotland. It is managed by NHS Tayside.
Healthcare in London, which consumes about a fifth of the NHS budget in England, is in many respects distinct from that in the rest of the United Kingdom, or England.
St James' Hospital was a healthcare facility in Balham, London that existed between 1910 and 1988. The hospital buildings occupied sites within the boundary of Ouseley Road, Sarsfield Road and St James's Drive Balham London SW12.

John Davy Rolleston FSA FRCP was an English physician and folklorist, who published extensively on infectious diseases and the history of medicine. Overshadowed by his brother, Sir Humphry Rolleston, he established himself as an epidemiologist, gave the Fitzpatrick Lecture at the Royal College of Physicians in 1935-1936 and became involved in numerous other learned societies and medical bodies, including The Royal Society of Medicine and the Society for the Study and Cure of Inebriety.
The South Middlesex Hospital was a hospital in Isleworth, London. Opened by the Duke of Cambridge as the Mogden Isolation Hospital in July 1898, it served its own borough and that of Richmond, retaining its name until 1938 when it was then renamed South Middlesex Fever Hospital but continued under local authority control.

New Cross Hospital was a hospital in the New Cross district of south east London, open from 1877 until around 1991.
Fulham Hospital was an English hospital in the west London district of Fulham from 1884 to 1973. From 1957 onwards it was merged with the Charing Cross Hospital and was gradually demolished. Charing Cross Hospital relocated from central London and now occupies the former Fulham Hospital site, south of St Dunstan's Road.

Coppetts Wood Hospital was an infectious diseases isolation hospital in Muswell Hill, North London. It was used to treat, amongst other things, patients suffering from Tuberculosis and Lassa fever.

A fever hospital or isolation hospital is a hospital for infectious diseases such as Scarlet fever, Tuberculosis, Lassa fever and Smallpox. Their purpose is to treat affected people while isolating them from the general population. Early examples included the Liverpool Fever Hospital (1801) and the London Fever Hospital (1802). Other examples occurred elsewhere in the British Isles and India.