Western Pomerania is an area on the Baltic coast of Poland and Germany.
Western Pomerania may also refer to:
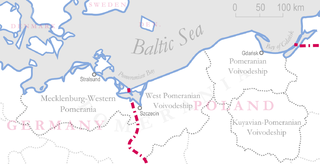
Pomerania is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg, while the eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland. Its historical border in the west is the Mecklenburg-Western Pomeranian border Urstromtal which now constitutes the border between the Mecklenburgian and Pomeranian part of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, while it is bounded by the Vistula River in the east. The easternmost part of Pomerania is alternatively known as Pomerelia, consisting of four sub-regions: Kashubia inhabited by ethnic Kashubians, Kociewie, Tuchola Forest and Chełmno Land.
Pommern is the German language name for Pomerania, a historical region divided between Germany and Poland.

The West Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as the West Pomerania Province, is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22 892.48 km², and in 2021, it was inhabited by 1 682 003 people.

Swedish Pomerania was a dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held extensive control over the lands on the southern Baltic coast, including Pomerania and parts of Livonia and Prussia.

The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and Poland. Its name comes from the Slavic po more, which means "land at the sea".
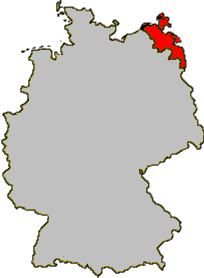
The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was a Protestant regional church in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, serving the citizens living in Hither Pomerania. The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was based on the teachings brought forward by Martin Luther and other Reformators during the Reformation. It combined Lutheran and Reformed traditions. The seat of the church was Greifswald, the bishop's preaching venue was the former Collegiate Church of St. Nicholas in Greifswald.
Starogard, Starogród, or Stargard means old fort or old city in Polish, Polabian and Pomeranian languages, and gard is Old Slavic, Old Germanic, Old Baltic, and Old Finnic for castle or fortification. Places with those names include:

Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania, is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Oder River in the West to Pomerelia in the East. Since 1945, Farther Pomerania has been part of Poland; the bulk of former Farther Pomerania is within the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, while its easternmost parts are within the Pomeranian Voivodeship. The Polish term Pomorze Zachodnie is colloquially used in contemporary Poland as a synonym for the West Pomeranian Voivodship whose borders do not match the historical ones; in Polish historical usage, it applied to all areas west of Pomerelia.
Kraków is a city in southern Poland.
Pomeranian is an adjective referring to the historical region of Pomerania, which is today divided between Poland and Germany.

The Province of Pomerania was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1945. Pomerania was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1815, an expansion of the older Brandenburg-Prussia province of Pomerania, and then became part of the German Empire in 1871. From 1918, Pomerania was a province of the Free State of Prussia until it was dissolved in 1945 following World War II, and its territory divided between Poland and Allied-occupied Germany. The city of Stettin was the provincial capital.
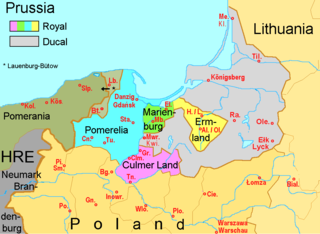
Lauenburg and Bütow Land formed a historical region in the western part of Pomerelia or in the eastern part of Farther Pomerania. It was composed of two districts centered on the towns of Lauenburg (Lębork) and Bütow (Bytów). The land is today part of the Polish Pomeranian Voivodeship.

This article is about the coat of arms of the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
Pomerania Province may refer to one of several provinces established in Pomerania, a region of Europe:

Pomerania during the Early Modern Age covers the history of Pomerania in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries.

The Province of Pomerania was a province of Brandenburg-Prussia, the later Kingdom of Prussia. After the Thirty Years' War, the province consisted of Farther Pomerania. Subsequently, the Lauenburg and Bütow Land, Draheim, and Swedish Pomerania south of the Peene river were joined into the province. The province was succeeded by the Province of Pomerania set up in 1815.

History of Pomerania (1806–1933) covers the history of Pomerania from the early 19th century until the rise of Nazi Germany.

Dobieszczyn is a settlement in the administrative district of Gmina Police, within Police County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland, close to the German border. It lies approximately 18 kilometres (11 mi) north-west of Police and 27 km (17 mi) north-west of the regional capital Szczecin.

Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania,Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania, is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Western Pomerania's boundaries have changed through the centuries as it belonged to various countries such as Poland, the Duchy of Pomerania, Sweden, Denmark, as well as Prussia which incorporated it as the Province of Pomerania.