
The John F. Kennedy Space Center, located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since 1968, KSC has been NASA's primary launch center of American spaceflight, research, and technology. Launch operations for the Apollo, Skylab and Space Shuttle programs were carried out from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 and managed by KSC. Located on the east coast of Florida, KSC is adjacent to Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS). The management of the two entities work very closely together, share resources, and operate facilities on each other's property.

The Aerobee rocket was one of the United States' most produced and productive sounding rockets. Developed by the Aerojet Corporation, the Aerobee was designed to combine the altitude and launching capability of the V-2 with the cost effectiveness and mass production of the WAC Corporal. More than 1000 Aerobees were launched between 1947 and 1985, returning vast amounts of astronomical, physical, aeronomical, and biomedical data.

A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km, such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. For certain purposes Sounding Rockets may be flown to altitudes as high as 3,000 kilometers to allow observing times of around 40 minutes to provide geophysical observations of the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere and mesosphere. Sounding rockets have been used for the examination of atmospheric nuclear tests by revealing the passage of the shock wave through the atmosphere. In more recent times Sounding Rockets have been used for other nuclear weapons research. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km.

White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established in 1941 as the Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range, where the Trinity test site lay at the northern end of the Range, in Socorro County near the towns of Carrizozo and San Antonio. It then became the White Sands Proving Ground on 9 July 1945.

Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
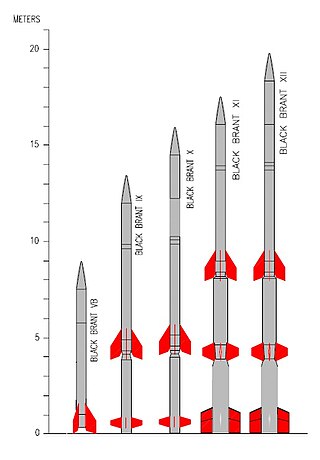
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is a network of American communications satellites and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets.

Little Joe II was an American rocket used from 1963 to 1966 for five uncrewed tests of the Apollo spacecraft launch escape system (LES), and to verify the performance of the command module parachute recovery system in abort mode. It was named after a similar rocket designed for the same function in Project Mercury. Launched from White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, it was the smallest of four launch rockets used in the Apollo program.

A mobile launcher platform (MLP), also known as mobile launch platform, is a structure used to support a large multistage space vehicle which is assembled (stacked) vertically in an integration facility and then transported by a crawler-transporter (CT) to a launch pad. This becomes the support structure for launch.
White Sands Test Facility (WSTF) is a NASA rocket engine test facility and a resource for testing and evaluating potentially hazardous materials, space flight components, and rocket propulsion systems. NASA established WSTF on the White Sands Missile Range in 1963. WSTF services are available to NASA, the United States Department of Defense, other federal agencies, universities and commercial industry. WSTF is managed by the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center. WSTF is located in the western foothills of the Organ Mountains, eleven miles east of Las Cruces, New Mexico.

The RTV-G-4 Bumper was a sounding rocket built by the United States. A combination of the German V-2 rocket and the WAC Corporal sounding rocket, it was used to study problems pertaining to two-stage high-speed rockets. The Bumper program launched eight rockets between May 13, 1948 and July 29, 1950. The first six flights were conducted at the White Sands Missile Range; the seventh launch, Bumper 8 on July 24, 1950, was the first rocket launched from Cape Canaveral.

A boilerplate spacecraft, also known as a mass simulator, is a nonfunctional craft or payload that is used to test various configurations and basic size, load, and handling characteristics of rocket launch vehicles. It is far less expensive to build multiple, full-scale, non-functional boilerplate spacecraft than it is to develop the full system. In this way, boilerplate spacecraft allow components and aspects of cutting-edge aerospace projects to be tested while detailed contracts for the final project are being negotiated. These tests may be used to develop procedures for mating a spacecraft to its launch vehicle, emergency access and egress, maintenance support activities, and various transportation processes.

Launch Complex 39B (LC-39B) is the second of Launch Complex 39's three launch pads, located at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida. The pad, along with Launch Complex 39A, was first designed for the Saturn V launch vehicle, which at the time was the United States' most powerful rocket. Typically used to launch NASA's crewed spaceflight missions since the late 1960s, the pad is currently configured for use by the agency's Space Launch System rocket, a Shuttle-derived launch vehicle which is currently used in the Artemis program and subsequent Moon to Mars campaigns. The pad had also been leased by NASA to aerospace company Northrop Grumman, for use as a launch site for their Shuttle-derived OmegA launch vehicle, for National Security Space Launch flights and commercial launches, before the OmegA program was cancelled.

White Sands Space Harbor (WSSH) is a spaceport in New Mexico that was formerly used as a Space Shuttle runway, a test site for rocket research, and the primary training area used by NASA for Space Shuttle pilots practicing approaches and landings in the Shuttle Training Aircraft and T-38 Talon aircraft. With its runways, navigational aids, runway lighting, and control facilities, it also served as a backup Shuttle landing site. WSSH is a part of the White Sands Test Facility, and is located approximately 30 miles west of Alamogordo, New Mexico, within the boundaries of the White Sands Missile Range.

Spaceflight as a practical endeavor began during World War II with the development of operational liquid-fueled rockets. Beginning life as a weapon, the V-2 was pressed into peaceful service after the war at the United States' White Sands Missile Range as well as the Soviet Union's Kapustin Yar. This led to a flourishing of missile designs setting the stage for the exploration of space. The small American WAC Corporal rocket was evolved into the Aerobee, a much more powerful sounding rocket. Exploration of space began in earnest in 1947 with the flight of the first Aerobee, 46 of which had flown by the end of 1950. These and other rockets, both Soviet and American, returned the first direct data on air density, temperature, charged particles and magnetic fields in the Earth's upper atmosphere.
A number of suborbital spaceflights were conducted during 2008. These consist mostly of sounding rocket missions and missile tests, and include other flights such as an ASAT firing. Between the start of the year and 16 July, at least 43 publicly announced suborbital spaceflights were conducted, the first of them on 11 January.

The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had three stages, and was powered by liquid fuel. Flown from 1967 to 1973, it was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station.

The NASA Sounding Rocket Program (NSRP) is a NASA run program of sounding rockets which has been operating since 1959. The missions carried out by this program are primarily used for scientific research, particularly low gravity and material based research. NASA's sounding rocket program is commonly used by colleges and universities for upper atmosphere research.
Rapid Acquisition Imaging Spectrograph Experiment or RAISE is a NASA funded series of sounding rocket missions to study the Sun in extreme ultraviolet. RAISE is supported by NASA's Sounding Rocket Program at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. NASA's Heliophysics Division manages the Sounding Rocket Program.
















