Related Research Articles

MIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
A signal generator is an electronic device that generates repeating or non-repeating electronic signals in either the analog or the digital domain. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well.

Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in hardware are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible.

Single Channel Ground and Airborne Radio System (SINCGARS) is a Combat Net Radio (CNR) currently used by U.S. and allied military forces. The radios, which handle voice and data communications, are designed to be reliable, secure, and easily maintained. Vehicle-mount, backpack, airborne, and handheld form factors are available.
Ultra-wideband is a radio technology that can use a very low energy level for short-range, high-bandwidth communications over a large portion of the radio spectrum. UWB has traditional applications in non-cooperative radar imaging. Most recent applications target sensor data collection, precision locating and tracking applications.

The Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS) aimed to replace existing radios in the American military with a single set of software-defined radios that could have new frequencies and modes (“waveforms”) added via upload, instead of requiring multiple radio types in ground vehicles, and using circuit board swaps in order to upgrade. JTRS has seen cost overruns and full program restructurings, along with cancellation of some parts of the program.
Link 16 is a military tactical data link network used by NATO and nations allowed by the MIDS International Program Office (IPO). Its specification is part of the family of Tactical Data Links.
Network-centric warfare, also called network-centric operations or net-centric warfare, is a military doctrine or theory of war pioneered by the United States Department of Defense in the 1990s.

The Mobile User Objective System is a narrowband military communications satellite system that supports a worldwide, multi-Service population of users in the ultra high frequency band. The system provides increased communications capabilities to newer, smaller terminals while still supporting interoperability with legacy terminals. MUOS is designed to support users who require greater mobility, higher bit rates and improved operational availability.
WNW may stand for:
The Software Communications Architecture (SCA) is an open architecture framework that defines a standard way for radios to instantiate, configure, and manage waveform applications running on their platform. The SCA separates waveform software from the underlying hardware platform, facilitating waveform software portability and re-use to avoid costs of redeveloping waveforms. The latest version is SCA 4.1.

The AN/PRC-148 Multiband Inter/Intra Team Radio (MBITR) is the most widely fielded handheld multiband, tactical software-defined radio, used by NATO forces around the world. The radio is built by Thales Communications, a subsidiary of the Thales Group. The designation AN/PRC translates to Army/Navy Portable Radio used for two way Communications, according to Joint Electronics Type Designation System guidelines.

The Wideband Global SATCOM system (WGS) is a high capacity satellite communications system planned for use in partnership by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) and the Australian Department of Defence. The system is composed of the Space Segment satellites, the Terminal Segment users and the Control Segment operators.
The AN/PRC-152 Multiband Handheld Radio is a portable, compact, tactical software-defined combat-net radio manufactured by Harris Corporation. It is compliant without waivers to the Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS) Software Communications Architecture (SCA). It has received NSA certification for the transmission of Top Secret data.

The AN/PRC-117 Multiband Manpack Radio, or Multiband Multi Mission Radio (MBMMR), is a man-portable, tactical software-defined combat-net radio, manufactured by Harris Corporation, in two different version:
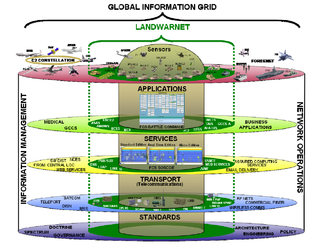
The FCS Network - Brigade Combat Team (BCT) Network consists of five layers that combine to provide seamless delivery of data to forward-deployed Army units.
The Software Communications Architecture Reference Implementation (SCARI) is an implementation of the US Military's Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS) Software Communications Architecture (SCA) Core Framework. It was developed mainly by the Canadian Communications Research Centre (CRC) under contract by the Software Defined Radio Forum.

The Global Broadcast Service (GBS) is a one-way broadcast capability supporting timely delivery of unclassified and classified video, large quantities of unclassified or classified digital data and other theater information transfer need for the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and its deployed and garrisoned units worldwide. GBS has become a critical piece of the DoD's intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance architecture. An advancement in satellite communications, GBS fills two key military communications requirements:
The Advanced Narrowband Digital Voice Terminal (ANDVT) is a secure voice terminal for low bandwidth secure voice communications throughout the U.S. Department of Defense. Devices in the ANDVT family include the AN/USC-43 Tactical Terminal (TACTERM), the KY-99A Miniaturized Terminal (MINTERM), and the KY-100 Airborne Terminal (AIRTERM). ANDVT uses LPC-10 voice compression.
Multifunctional Information Distribution System (MIDS) is the NATO name for the communication component of Link-16.
References
- 1 2 3 Joint Tactical Networking Center, USA Department of Defense. "OUR PRODUCTS". USDOD. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ↑ "Wideband Networking Waveform OFDM PHY" (PDF). Spectrum. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 March 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ↑ Defense Systems Staff (24 May 2012). "NSA certifies JTRS wideband networking waveform radio". defensesystems.com.
| This article related to telecommunications is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This mobile technology related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |