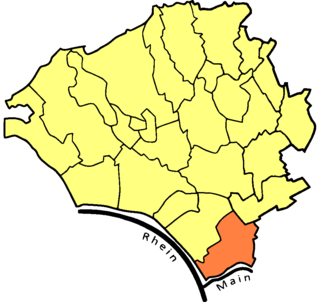
Main-Taunus is a Kreis (district) in the middle of Hessen, Germany and is part of the Frankfurt/Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region as well as the Frankfurt urban area. Neighboring districts are Hochtaunuskreis, district-free Frankfurt, Groß-Gerau, district-free Wiesbaden, Rheingau-Taunus. It is the second most densely populated rural district in Germany.
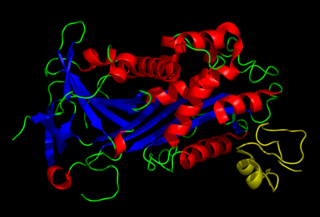
Vitronectin is a glycoprotein of the hemopexin family which is synthesized and excreted by the liver, and abundantly found in serum, the extracellular matrix and bone. In humans it is encoded by the VTN gene.

Frauenstein is the westernmost borough of the city of Wiesbaden, located in the Rhine Main Area near Frankfurt and capital of the federal state of Hesse, Germany. The borough has a population of approximately 2,400. The formerly independent village was incorporated into Wiesbaden in 1928.
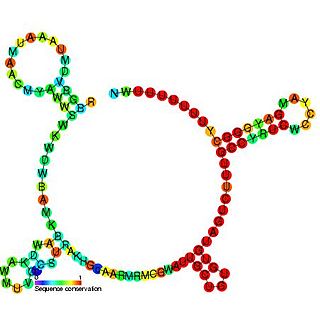
The RprA RNA gene encodes a 106 nucleotide regulatory non-coding RNA. Translational regulation of the stationary phase sigma factor RpoS is mediated by the formation of a double-stranded RNA stem-loop structure in the upstream region of the rpoS messenger RNA, occluding the translation initiation site.
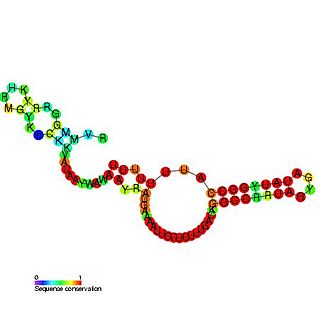
The sroB RNA is a non-coding RNA gene of 90 nucleotides in length. sroB is found in several Enterobacterial species but its function is unknown. SroB is found in the intergenic region on the opposite strand to the ybaK and ybaP genes. SroB is expressed in stationary phase. Experiments have shown that SroB is a Hfq binding sRNA.

The Hfq protein encoded by the hfq gene was discovered in 1968 as an Escherichia coli host factor that was essential for replication of the bacteriophage Qβ. It is now clear that Hfq is an abundant bacterial RNA binding protein which has many important physiological roles that are usually mediated by interacting with Hfq binding sRNA.
Mainz-Kostheim is a district administered by the city of Wiesbaden, Germany. Its population is 14,381. Mainz-Kostheim was formerly a district of the city of Mainz, until the public administration by the city of Wiesbaden was decided on 10 August 1945. The reason for this had been the easy control of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany, where the Rhine formed the border between the American sector and the French sector. Mainz-Kostheim faces the city of Mainz on the opposite shore of the Rhine river.

Wallau in Taunus is a quarter of Hofheim in Main-Taunus-Kreis in Hesse, Germany, and has a population of 4,442.

Schierstein is a southwestern borough of Wiesbaden, capital of state of Hesse, Germany. First mentioned in historical records in 860, Schierstein was incorporated into Wiesbaden in 1926. Today the borough has about 10,000 residents. Situated on the Rhine River, Schierstein is known as the "Gateway to the Rheingau."

Dotzheim is a western borough of Wiesbaden, capital of the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the second largest borough of the city by area and, with over 27,000 inhabitants the second-most populated of Wiesbaden's suburban boroughs. It was the largest village in the former Duchy of Nassau. The formerly independent village was incorporated into Wiesbaden in 1928.

The Ländches Railway (Ländchesbahn) is a single-track non-electrified branch railway line between Wiesbaden and Niedernhausen, in the German state of Hesse. The 19.6-kilometre (12.2 mi) long line was opened in 1879. It is now Deutsche Bahn route 627 and route 21 of the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund.
The Ländchen was a region east of Wiesbaden, Germany that comprised ten villages: Breckenheim, Delkenheim, Diedenbergen, Igstadt, Langenhain, Massenheim, Medenbach, Nordenstadt, Wallau, and Wildsachsen, plus Domäne Mechtildshausen.

Myosin-4 also known as myosin, heavy chain 4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MYH4 gene.

Nassauer Hof is a luxury five-star superior hotel in Wiesbaden, Germany, and member of the international association The Leading Hotels of the World as well as the German association Selektion Deutscher Luxushotels. The property was built in 1813 and is situated across from the Wiesbaden Kurhaus and at the end of Wiesbaden's luxury shopping avenue Wilhelmstrasse.
In molecular biology, the SR1 RNA is a small RNA (sRNA) produced by species of Bacillus and closely related bacteria. It is a dual-function RNA which acts both as a protein-coding RNA and as a regulatory sRNA.
In molecular biology, the FasX small RNA (fibronectin/fibrinogen-binding/haemolytic-activity/streptokinase-regulator-X) is a non-coding small RNA (sRNA) produced by all group A Streptococcus. FasX has also been found in species of group D and group G Streptococcus. FasX regulates expression of secreted virulence factor streptokinase (SKA), encoded by the ska gene. FasX base pairs to the 5' end of the ska mRNA, increasing the stability of the mRNA, resulting in elevated levels of streptokinase expression. FasX negatively regulates the expression of pili and fibronectin-binding proteins on the bacterial cell surface. It binds to the 5' untranslated region of genes in the FCT-region in a serotype-specific manner, reducing the stability of and inhibiting translation of the pilus biosynthesis operon mRNA by occluding the ribosome-binding site through a simple Watson-Crick base-pairing mechanism.
Cholest-4-en-3-one 26-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.141, CYP125, CYP125A1, cholest-4-en-3-one 27-monooxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name cholest-4-en-3-one,NADH:oxygen oxidoreductase (26-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ribonuclease E is a bacterial ribonuclease that participates in the processing of ribosomal RNA and the chemical degradation of bulk cellular RNA.
The gene rpoN encodes the sigma factor sigma-54, a protein in Escherichia coli and other species of bacteria. RpoN antagonizes RpoS sigma factors.

The Kulturzentrum Schlachthof in Wiesbaden, Hesse, Germany, is a cultural center in a complex which formerly housed the municipal slaughterhouse, approximately 500 meters southeast of the Wiesbaden Hauptbahnhof railway station. The cultural center, known as Schlachthof, was founded in 1994. It offers two concert halls for events from 300 to 2,000 people; the large concert hall has an area of about 1,200 square meters. The location is used for concert in rock, metal and punk, for music parties, poetry slams and readings. It is surrounded by a leisure park.













