Related Research Articles

A sash is a large and usually colorful ribbon or band of material worn around the human body, either draping from one shoulder to the opposing hip and back up, or else encircling the waist. The sash around the waist may be worn in daily attire, but the sash from shoulder to hip is worn on ceremonial occasions only. Ceremonial sashes are also found in a V-shaped format, draping straight from both shoulders down, intersecting and forming an angle over the chest or abdomen.

Juan Evo Morales Ayma is a Bolivian politician, trade union organizer, and former cocalero activist who served as the 65th president of Bolivia from 2006 to 2019. Widely regarded as the country's first president to come from its indigenous population, his administration worked towards the implementation of left-wing policies, focusing on the legal protections and socioeconomic conditions of Bolivia's previously marginalized indigenous population and combating the political influence of the United States and resource-extracting multinational corporations. Ideologically a socialist, he has led the Movement for Socialism (MAS) party since 1998.

Leonel Antonio Fernández Reyna is a Dominican lawyer, academic, and was the 50th and 52nd President of the Dominican Republic from 1996 to 2000 and from 2004 to 2012. From 2016 until 2020, he was the President of the EU–LAC Foundation.
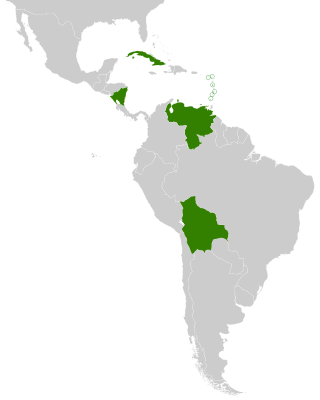
ALBA or ALBA–TCP, formally the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America or the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty, is an intergovernmental organization based on the idea of political and economic integration of Latin American and Caribbean countries.

Rafael Vicente Correa Delgado is an Ecuadorian politician and economist who served as President of Ecuador from 2007 to 2017. The leader of the PAIS Alliance political movement from its foundation until 2017, Correa is a democratic socialist and his administration focused on the implementation of left-wing policies. Internationally, he served as president pro tempore of the UNASUR.

Socialism of the 21st century is an interpretation of socialist principles first advocated by German sociologist and political analyst Heinz Dieterich and taken up by a number of Latin American leaders. Dieterich argued in 1996 that both free-market industrial capitalism and 20th-century socialism have failed to solve urgent problems of humanity such as poverty, hunger, exploitation of labour, economic oppression, sexism, racism, the destruction of natural resources and the absence of true democracy. Socialism of the 21st century has democratic socialist elements, but it also resembles Marxist revisionism.

The pink tide, or the turn to the left, is a political wave and turn towards left-wing governments in Latin America throughout the 21st century. As a term, both phrases are used in political analysis in the news media and elsewhere to refer to a move toward more economic progressive or social progressive policies in the region. Such governments have been referred to as "left-of-centre", "left-leaning", and "radical social-democratic". They are also members of the São Paulo Forum, a conference of left-wing political parties and other organizations from the Americas.

The foreign policy of the Evo Morales administration concerns the policy initiatives made towards other states by the former President of Bolivia, in difference to past, or future, Bolivian foreign policy. Morales' foreign policy can be roughly divided between that of the Americas and the rest of the world.

Jorge Gestoso is a Uruguayan journalist who was born in Montevideo.

The foreign policy of the Rafael Correa administration (2007-2017) was the policy initiatives towards other states by the former President of Ecuador, as differed to past, or future, Ecuadorian foreign policy. Correa's foreign policy was somewhat similar to that of the other leaders of the Bolivarian Alternative for the Americas (ALBA) such as Hugo Chavez and Evo Morales. This entailed a rough division between relations with other states of the Americas and the rest of the world.

The Presidency of Evo Morales began on January 22, 2006 when Evo Morales was inaugurated as the 80th President of Bolivia, following his victory in the 2005 general election, where he won 53.7% of the vote, defeating Jorge Quiroga, Samuel Doria Medina, and several other candidates. Morales increased taxation on the hydrocarbon industry to bolster social spending, emphasising projects to combat illiteracy, poverty, racism, and sexism. Vocally criticizing neoliberalism and reducing Bolivia's dependence on the World Bank and International Monetary Fund, his administration oversaw strong economic growth while following a policy termed "Evonomics" which sought to move from a liberal economic approach to a mixed economy. Scaling back U.S. influence in the country, he built relationships with leftist governments in the Latin American pink tide and signed Bolivia into the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas. Attempting to moderate the left-indigenous activist community, his administration also opposed the right-wing autonomist demands of Bolivia's eastern provinces. Winning a recall referendum in 2008, he instituted a new constitution that established Bolivia as a plurinational state and was re-elected in 2009. His second term witnessed the continuation of leftist policies and Bolivia's joining of the Bank of the South and Community of Latin American and Caribbean States; he was again reelected in the 2014 general election. Following the disputed 2019 general election and the ensuing unrest, Morales resigned and flew to Mexico where he had been granted political asylum.

Néstor Kirchner, former President of Argentina, died of heart failure on the morning of 27 October 2010 at the Jose Formenti hospital in El Calafate, Santa Cruz Province at the age of 60. Efforts to revive him were unsuccessful. His wife, President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, was present with him when he died. He was expected to run for president in 2011.

Aló Presidente was a long-running, unscripted talk show hosted by former Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez. It was broadcast on Venezuelan state television and radio channels, including Venezolana de Televisión, on Sundays from 11:00am until mid/late afternoon. The show was a powerful tool in promoting Chavista socialist ideals of the Bolivarian Revolution to supporters in Venezuela and beyond. Many editions were filmed outdoors before large audiences, commonly featuring a local farm, factory, school, hospital, housing project or other public investment. Although Chávez typically appeared on television several times a week, Aló Presidente was his opportunity to reach most families on their day off.

The foreign policy of the Ollanta Humala concerns the policy initiatives made towards other states by the former President of Peru, in difference to past, or future, Peruvian foreign policy as represented by his Foreign Minister Rafael Roncagliolo. Humala's foreign policy was based on relations with other states of the Americas.

Fernando Lugo, elected President of Paraguay in 2008, was impeached and removed from office by the Congress of Paraguay in June 2012. On 21 June the Chamber of Deputies voted 76 to 1 to impeach Lugo, and the Senate removed him from office the following day, by 39 votes to 4, resulting in Vice President Federico Franco, who had broken with Lugo, becoming President. Lugo contends he was denied due process because he did not have enough time to prepare a defense. A number of Latin American governments declared the proceeding was effectively a coup d'état. Lugo himself formally accepted the impeachment, but called it a "parliamentary coup".

On 1 July 2013, president Evo Morales of Bolivia, who had been attending a conference of gas-exporting countries in Russia, gave an interview to the RT television network in which he appeared predisposed to offer asylum to Edward Snowden. The day after his TV interview, Morales's Dassault Falcon 900 FAB-001, carrying him back to La Paz from Moscow, took off from Vnukovo Airport, flew uninterrupted over Poland and the Czech Republic, but then unexpectedly landed in Vienna, Austria.
Isla presidencial is an adult web animation page from Venezuela. The political satire follows the heads of state of Latin America and Spain who are stranded on an island. The three seasons amassed more than 50 million views on YouTube.
The following is a list of reactions to the 2019 Bolivian political crisis.

The People's Force is a political party in the Dominican Republic led by former President Leonel Fernández.

Bolivia-Venezuela Relations are the existing bilateral relations between the Plurinational State of Bolivia and the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. Both nations established their diplomatic relations on 14 September 1883, during the government of the President of Bolivia Narciso Campero Leyes and the government of the President of Venezuela Antonio Guzmán Blanco.
References
- 1 2 3 Lansberg-Rodriguez, Daniel (May 25, 2010). "Wiki-Constitutionalism. The strange phenomenon that's destroying Latin America". The New Republic .
- ↑ "More Recommended Reading". The New York Times . May 27, 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 Lansberg-Rodriguez, Daniel (May 26, 2010). "Wiki-Constitutionalism". CBS News .
- ↑ "Artículo de la cadena CBS califica al presidente Fernández de dictador". Panorama Diario (in Spanish). May 28, 2010. Archived from the original on March 8, 2012. Retrieved September 23, 2010.
- ↑ "La cadena CBS dice que Leonel Fernández,es un "Dictador Moderno" entre un puñado de ellos". Barahonero.com (in Spanish).
- ↑ "Cómo constituir un régimen dictatorial". Hoy.com (in Spanish).
- Eichler, Alex (June 1, 2010). "Latin American Constitutions = Wikipedia". The Atlantic Wire . Archived from the original on June 8, 2010. Retrieved September 23, 2010.