Related Research Articles

Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol.
Hot flashes are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testicles or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estrogen as hypoestrogenism. These are responsible for the observed signs and symptoms in both males and females.
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), also known as bioidentical hormone therapy (BHT) or natural hormone therapy, is the use of hormones that are identical on a molecular level with endogenous hormones in hormone replacement therapy. It may also be combined with blood and saliva testing of hormone levels, and the use of pharmacy compounding to obtain hormones in an effort to reach a targeted level of hormones in the body. A number of claims by some proponents of BHT have not been confirmed through scientific testing. Specific hormones used in BHT include estrone, estradiol, progesterone, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and estriol.

Estradiol acetate (EA), sold under the brand names Femtrace, Femring, and Menoring, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. It is taken by mouth once daily or given as a vaginal ring once every three months.

Estradiol valerate (EV), sold for use by mouth under the brand name Progynova and for use by injection under the brand names Delestrogen and Progynon Depot among others, is an estrogen medication. It is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels, hormone therapy for transgender people, and in hormonal birth control. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The medication is taken by mouth or by injection into muscle or fat once every 1 to 4 weeks.
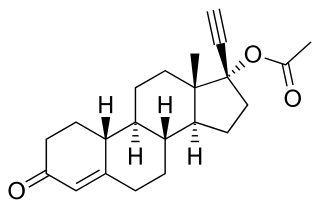
Norethisterone acetate (NETA), also known as norethindrone acetate and sold under the brand name Primolut-Nor among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and for the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication available in low-dose and high-dose formulations and is used alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is ingested orally.
Teresa S. Wiley is the author of Lights Out: Sleep, Sugar and Survival, and Sex, Lies and Menopause. She writes about women's health, particularly sleep and hormonal issues, hormone replacement therapy and bioidentical hormone replacement therapy. Wiley has developed her own version of BHRT known as the Wiley Protocol, though she has been strongly criticized for lacking the relevant credentials and potentially putting women at risk with an unproven, untested intervention that uses possibly dangerously high doses of hormones.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones that occur during menopause.

Estradiol benzoate (EB), sold under the brand name Progynon-B among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Estradiol benzoate is used in veterinary medicine as well. When used clinically, the medication is given by injection into muscle usually two to three times per week.

Trimegestone, sold under the brand names Ondeva and Totelle among others, is a progestin medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It was also under development for use in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, but ultimately was not marketed for this purpose. The medication is available alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Lawley Pharmaceuticals is a privately owned Australian pharmaceutical company established by pharmacist Michael Buckley in 1995.

Conjugated estrogens (CEs), or conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), sold under the brand name Premarin among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and for various other indications. It is a mixture of the sodium salts of estrogen conjugates found in horses, such as estrone sulfate and equilin sulfate. CEEs are available in the form of both natural preparations manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares and fully synthetic replications of the natural preparations. They are formulated both alone and in combination with progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate. CEEs are usually taken by mouth, but can also be given by application to the skin or vagina as a cream or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle.

Estradiol (E2) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is an estrogen and is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy and to treat low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in hormonal birth control for women, in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women, among other uses. Estradiol can be taken by mouth, held and dissolved under the tongue, as a gel or patch that is applied to the skin, in through the vagina, by injection into muscle or fat, or through the use of an implant that is placed into fat, among other routes.

High-dose estrogen therapy (HDE) is a type of hormone therapy in which high doses of estrogens are given. When given in combination with a high dose of progestogen, it has been referred to as pseudopregnancy. It is called this because the estrogen and progestogen levels achieved are in the range of the very high levels of these hormones that occur during pregnancy. HDE and pseudopregnancy have been used in medicine for a number of hormone-dependent indications, such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and endometriosis, among others. Both natural or bioidentical estrogens and synthetic estrogens have been used and both oral and parenteral routes may be used.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.
The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

The pharmacokinetics of progesterone, concerns the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration of progesterone.
The Estrogen in Venous Thromboembolism Trial (EVTET) was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) of menopausal hormone therapy in 140 postmenopausal women with previous history of venous thromboembolism (VTE). It was a double-blind RCT of the estrogen, oral estradiol 2 mg/day, plus the progestogen, norethisterone acetate (NETA) (n=71) 1 mg/day versus placebo (n=69). The results of the trial were published in 2000 and 2001. The incidence of VTE was 10.7% in the hormone therapy group and 2.3% in the placebo group, with all events occurring within 261 days after study inclusion. The difference did not reach statistical significance in the sequential analysis, but was statistically significant if the sequential design was ignored. Markers of coagulation were likewise increased by hormone therapy. As a result of the high incidence of VTE in the treatment group, the trial was terminated prematurely. The researchers concluded on the basis of their findings that menopausal hormone therapy should not be used in women with a previous history of VTE.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 T.S. Wiley (2007-01-03). "Hormone replacement composition and method". FreshPatents.com. Retrieved 2007-12-20.
- ↑ "Testimony of T.S. Wiley before the Special Committee on Aging United States Senate" (PDF). United States Senate Special Committee on Aging. 2007-04-19. Retrieved 2007-12-20.
- ↑ "Interview with T.S. Wiley". Personal Life Media.
- ↑ USpatent 7879830, T. S. Wiley,"Hormone replacement composition and method",issued 2011-02-01
- ↑ Feig SA, Hynote E, Speight N, Magaziner A, Miranda RA, Schachter MA (September 2005). "Summary of the American College for Advancement in Medicine May 2005 Conference: Menopause, Andropause: Power in Transition". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2 (3): 413–419. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh113. PMC 1193553 .
- 1 2 3 Rosenthal MS (2008). "The Wiley Protocol: an analysis of ethical issues". Menopause. 15 (5): 1014–1022. doi:10.1097/gme.0b013e318178862e. PMID 18551081. S2CID 196421747.
- ↑ Schwartz E, Schwarzbein D.; et al. (October 11, 2006). "Letter to Suzanne Somers". Dr Erika's blog. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ↑ Ellin, Abby (October 15, 2006). "A Battle Over 'Juice of Youth'". The New York Times . Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ↑ Rosenthal MS (2008). "Ethical problems with bioidentical hormone therapy". Int. J. Impot. Res. 20 (1): 45–52. doi:10.1038/sj.ijir.3901622. PMID 18075509. S2CID 2313626.