
Nordic Semiconductor ASA was founded in 1983 and is a Norwegian fabless technology company with its headquarters in Trondheim, Norway. The company specializes in designing ultra-low-power wireless communication semiconductors and supporting software for engineers developing and manufacturing Internet of Things (IoT) products.
Synaptics, Inc. American neural network technologies and computer-to-human interface devices development company based in San Jose, California. It develops touchpads and fingerprint biometrics technology for computer laptops; touch, display driver, and fingerprint biometrics technology for smartphones; and touch, video and far-field voice, and wireless technology for smart home devices, wearables, and automobiles. Synaptics sells its products to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and display manufacturers.

Avery Dennison Corporation is a multinational manufacturer and distributor of pressure-sensitive adhesive materials, apparel branding labels and tags, RFID inlays, and specialty medical products. The company is a member of the Fortune 500 and is headquartered in Mentor, Ohio.
Crocus Technology, founded in 2004, was a venture-capital-backed semiconductor startup company developing and manufacturing integrated magnetic field sensors for a variety of applications: Automotive, consumer goods, industrial and medical IoT.

Silicon Laboratories, Inc., commonly referred to as Silicon Labs, is a fabless global technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors, other silicon devices and software, which it sells to electronics design engineers and manufacturers in Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure worldwide.
DexCom, Inc. is a company that develops, manufactures, produces, and distributes continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems for diabetes management. It operates internationally with headquarters in San Diego, California; and has manufacturing facilities in Mesa, Arizona; Batu Kawan, Malaysia; and Athenry, Ireland.

Jerusalem Venture Partners (JVP) is an international venture capital firm founded in 1993. The fund specializes in investments in startup companies, focusing on digital media, enterprise software, semiconductors, data storage and cyber security, having raised close to $1.4 billion USD across nine funds. JVP is headquartered in Margalit Startup City Jerusalem with offices in Be'er Sheva, New York City and Paris.

Redpine Signals was a fabless semiconductor company founded in 2001. The company made chipsets and system-level products for wireless networks. It served the Internet of Things and wireless embedded systems market, enabling all volume levels of chipsets and modules.

Local Motors was an American manufacturing company focused on low-volume production of open-source vehicles and other products using multiple microfactories. The company built a platform that combined online community co-creation with distributed digital manufacturing. It was co-founded in 2007 by John B. Rogers Jr. and had headquarters in Phoenix, Arizona. It produced the Rally Fighter, the Strati and Olli.

EVRYTHNG is an internet of things (IoT) software company based in London, with operations in Oregon, New York, Beijing, Minsk and Switzerland. The company delivers real-time data and actionable information about “smart products” featuring a digital identity in its EVRYTHNG Product Cloud, which connects consumer packaged goods to the web for business intelligence.
Sequans Communications is a fabless semiconductor company that designs, develops, and markets integrated circuits ("chips") and modules for 4G and 5G cellular IoT devices. The company is based in Paris, France with offices in the United States, United Kingdom, Israel, Hong Kong, Singapore, Taiwan, South Korea, Finland and China. The company was founded as a société anonyme in October 2003 by Georges Karam. It originally focused on the WiMAX market and expanded to the LTE market in 2009, dropping WiMAX altogether in 2011. Today the company develops and delivers only LTE chips and modules for the global 5G/4G cellular IoT market. Sequans was listed on the New York Stock Exchange in April 2011. Karam is the company's CEO.
Giatec Scientific Inc. is a Canadian-based company with headquarters located in Ottawa, Ontario. It is a developer and manufacturer of nondestructive testing quality control and condition assessment devices for the construction industry.
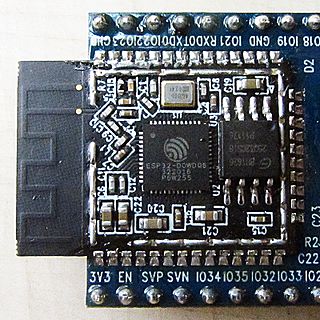
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system-on-chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, an Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor, or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. It is commonly found either on device-specific PCBs or on a range of development boards with GPIO pins and various connectors depending on the model and manufacturer of the board.
The Lenovo Z2 Plus is a smartphone manufactured by Lenovo. It is a part of Lenovo's premium smartphone line in 2017, and has two variants. Lenovo Z2 Plus is the Indian version of Lenovo Zuk Z2, that was launched in China in May, 2016.

The Nikon D5600 is a 24.2 megapixel upper-entry level, APS-C sensor DSLR announced by Nikon on November 10, 2016, as the successor of the D5500. The camera has an F-mount.

Puls is a San Francisco–based startup founded by Eyal Ronen and Itai Hirsch in 2015. The company provides in-home services such as repairs to all household appliances. The user books an appointment for a technician to visit the user's location to fix said problem.
Makita Auto-Start Wireless System, Festool Autostart (2018‒) and Bosch Wireless Auto-Start (2024‒) are Bluetooth-based systems for remotely starting industrial vacuum cleaners from power tools. Several power tools, cordless battery packs, and industrial vacuum cleaners ship with wireless connectivity, mostly using Bluetooth Low Energy to communicate, but as of 2024 the systems remained incompatible between different brands.
Samsara Inc. is an American IoT company headquartered in San Francisco, California that provides software and insights for physical operations. The company has customers across North America and Europe. Samsara developed a connected operations cloud platform that provides insights to physical operations organizations in the transportation, construction, energy, utilities, public sector and retail industries, and supports the safety and efficiency of those operations.
Ambient IoT, from ambient and Internet of things, is a concept originally coined by 3GPP that is used in the technology industry referring to an ecosystem of a large number of objects in which every item is connected into a wireless sensor network using low-cost self-powered sensor nodes. Bluetooth SIG has assessed the total addressable market of Ambient IoT to be more than 10 trillion devices across different verticals.








