Related Research Articles
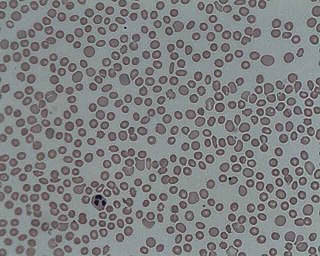
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients.

An endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They may have a large flat base (sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle (pedunculated). Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones. They range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. If pedunculated, they can protrude through the cervix into the vagina. Small blood vessels may be present, particularly in large polyps.

Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the tentorium cerebelli, and even through the foramen magnum. Herniation can be caused by a number of factors that cause a mass effect and increase intracranial pressure (ICP): these include traumatic brain injury, intracranial hemorrhage, or brain tumor.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, as well as the medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.
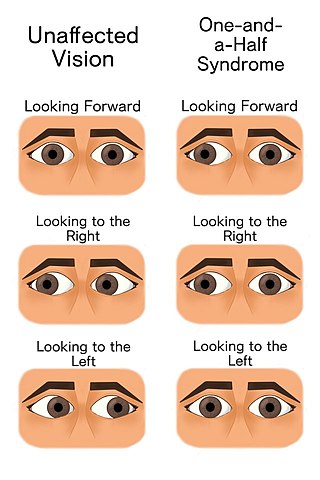
The one and a half syndrome is a rare weakness in eye movement affecting both eyes, in which one cannot move laterally at all, and the other can move only in outward direction. More formally, it is characterized by "a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other". Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is abducted. Convergence is classically spared as cranial nerve III and its nucleus is spared bilaterally.

The paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) is a subset of neurons of the oral and caudal pontine reticular nuclei. With the abducens nucleus it makes up the horizontal gaze centre. It is situated in the pons adjacent to the abducens nucleus. It projects to the ipsilateral abducens nucleus, and contralateral oculomotor nucleus to mediate conjugate horizontal gaze and saccades.

Cleidocranial dysostosis (CCD), also called cleidocranial dysplasia, is a birth defect that mostly affects the bones and teeth. The collarbones are typically either poorly developed or absent, which allows the shoulders to be brought close together. The front of the skull often does not close until later, and those affected are often shorter than average. Other symptoms may include a prominent forehead, wide set eyes, abnormal teeth, and a flat nose. Symptoms vary among people; however, cognitive function is typically unaffected.

Empty sella syndrome is the condition when the pituitary gland shrinks or becomes flattened, filling the sella turcica with cerebrospinal fluid instead of the normal pituitary. It can be discovered as part of the diagnostic workup of pituitary disorders, or as an incidental finding when imaging the brain.

The posterior thoracic nucleus, is a group of interneurons found in the medial part of Rexed lamina VII, also known as the intermediate zone, of the spinal cord. It is located from the cervical segment C8 to lumbar segment L3 of the spinal cord and is an important structure for proprioception of the lower limb.

Nezelof syndrome is an autosomal recessive congenital immunodeficiency condition due to underdevelopment of the thymus. The defect is a type of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency with inactive phosphorylase, this results in an accumulation of deoxy-GTP which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase. Ribonucleotide reductase catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides, thus, DNA replication is inhibited.
An osteochondrodysplasia, or skeletal dysplasia, is a disorder of the development of bone and cartilage. Osteochondrodysplasias are rare diseases. About 1 in 5,000 babies are born with some type of skeletal dysplasia. Nonetheless, if taken collectively, genetic skeletal dysplasias or osteochondrodysplasias comprise a recognizable group of genetically determined disorders with generalized skeletal affection. These disorders lead to disproportionate short stature and bone abnormalities, particularly in the arms, legs, and spine. Skeletal dysplasia can result in marked functional limitation and even mortality.
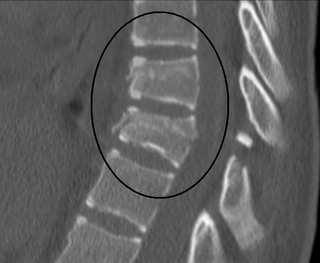
A Chance fracture is a type of vertebral fracture that results from excessive flexion of the spine. Symptoms may include abdominal bruising, or less commonly paralysis of the legs. In around half of cases there is an associated abdominal injury such as a splenic rupture, small bowel injury, pancreatic injury, or mesenteric tear. Injury to the bowel may not be apparent on the first day.

Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.

The Thomas test is a physical examination test, named after the Welsh orthopaedic surgeon, Hugh Owen Thomas (1834–1891), to rule out hip flexion contracture and psoas syndrome.
Microgenia is the medical term for an unusually small or deformed chin.

Shwachman–Diamond syndrome (SDS), or Shwachman–Bodian–Diamond syndrome, is a rare congenital disorder characterized by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, bone marrow dysfunction, skeletal and cardiac abnormalities and short stature. After cystic fibrosis (CF), it is the second most common cause of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in children. It is associated with the SBDS gene and has autosomal recessive inheritance.
An estrogen-dependent condition can be that relating to the differentiation in the steroid sex hormone that is associated with the female reproductive system and sex characteristics. These conditions can fall under the umbrella of hypoestrogenism, hyperestrogenim, or any sensitivity to the presence of estrogen in the body.
Srb's anomaly is the clinical condition describing synostosis, or fusion, between the first and second ribs. It may be either a partial or complete fusion between the two ribs to create an entirely indistinguishable new rib.
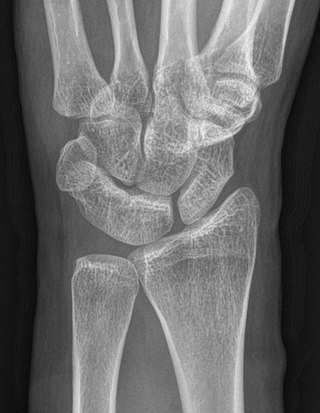
Carpal coalition is the abnormal fusion of two or more carpal bones when they fail to segment during intrauterine development. First described by Eduard Sandifort in 1779, carpal coalitions are often an isolated issue which connect two carpal bones in the same row of the wrist. These issues are congenital and occur at various rates throughout the population.

In radiology, the Terry-Thomas sign is a scapholunate ligament dissociation on an anteroposterior view of the wrist. Most commonly a result of a fall on the outstretched hand (FOOSH), the scapholunate ligament ruptures resulting in separation of the lunate and scaphoid bones. This burst causes the scaphoid bone to dorsally rotate. A gap of more than 3mm is pathognomonic for scapholunate dissociation.
References
- 1 2 Yochum, Terry R. (2004). essentials of skeletal radiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 308. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ↑ Marchiori, Dennis (2014). Clinical Imaging - E-Book: With Skeletal, Chest, & Abdominal Pattern Differentials. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 347. ISBN 9780323261944 . Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ↑ Court-Brown, Charles M.; McQueen, Margaret M.; Tornetta, Paul (2006). Trauma. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 62. ISBN 9780781750967 . Retrieved 25 January 2018.