Related Research Articles

The thylacine, also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The thylacine neared extinction throughout most of its range in mainland Australia by about 2,000 years ago, most likely because of the introduction of dingoes. Prior to European settlement around 5,000 remained in the wild on Tasmania. Beginning in the nineteenth century they were perceived as a threat to the livestock of farmers and bounty hunting was introduced. The last known of its species died in 1936 at Hobart Zoo in Tasmania. The thylacine is widespread in popular culture and is a cultural icon in Australia.

Thylacinidae is an extinct family of carnivorous, superficially dog-like marsupials from the order Dasyuromorphia. The only species to survive into modern times was the thylacine, which became extinct in 1936.

Othniel Charles Marsh was an American professor of paleontology at Yale College and president of the National Academy of Sciences. He was one of the preeminent scientists in the field of paleontology. Among his legacies are the discovery or description of dozens of new species and theories on the origins of birds.

Kollikodon is an extinct species of mammal, it is usually considered to be a member of Australosphenida and closely allied with monotremes, but is alternatively suggested to be a haramiyidan. It is known only from an opalised dentary fragment, with one premolar and two molars in situ, as well as a referred maxillary fragment containing the last premolar and all four molars. The fossils were found in the Griman Creek Formation at Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, Australia, as was Steropodon. Kollikodon lived in the Late Cretaceous period, during the Cenomanian age.

The New Guinean long-nosed bandicoots are members of the order Peramelemorphia. They are small to medium-sized marsupial omnivores native to New Guinea.

Nimbacinus dicksoni is an extinct thylacinid marsupial, a close relative of the recent but extinct thylacinid known as the Tasmanian tiger. It lived approximately 23-16 million years ago in the Miocene period. Nimbacinus dicksoni was about 1.6 ft (50 cm) long. Being a predator, it likely ate birds, small mammals, and reptiles. Like the recently-extinct thylacine, it may have been an awkward runner and used stamina to catch prey rather than speed. Fossils have been found in Australia at Riversleigh in north-western Queensland and Bullock Creek in the Northern Territory.

Archaeoceti, or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene. Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia 53 to 45 mya, resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation 36 to 35 mya.
Badjcinus turnbulli is an extinct thylacinid marsupial.

Bryanictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, from the early to late Paleocene.

Didymictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.
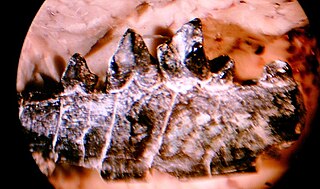
Ictidopappus is an extinct genus of mammals from extinct subfamily Ictidopappinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during the early Paleocene.
Intyrictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during early Paleocene.
Pristinictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during middle Paleocene.

Raphictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during late Paleocene.
Mutpuracinus archibaldi is an extinct carnivorous, quadrupedal marsupial that lived during the middle Miocene and is the smallest known thylacinid at approximately 1.1 kilograms, the size of a quoll, though, more closely related to the recently extinct thylacine.
Bryan Patterson was an American paleontologist at the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago.
The Washakie Formation is a geologic formation in northern Colorado and southern Wyoming. It preserves many mammal, bird, reptile and other fossils dating back to the Lutetian stage of the Eocene within the Paleogene period. The sediments fall in the Bridgerian and Uintan stages of the NALMA classification.
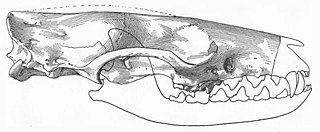
Viverravus is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Viverravinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, Europe and Asia from the middle Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Protictis is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America from early Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Viverravinae is an extinct subfamily of mammals from extinct family Viverravidae, that lived from the early Palaeocene to the middle Eocene in North America, Asia and Europe.
References
- ↑ Megan, Graydon (16 October 2011). "William D. Turnbull, 1922-2011". chicagotribune.com.
- ↑ Muirhead, Jeanette; Wroe, Stephen (September 1998). "A New Genus and Species, Badjcinus turnbulli (Thylacinidae: Marsupialia), from the LateOligocene of Riversleigh, Northern Australia, and an Investigation of Thylacinid Phylogeny". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 18 (3): 612–626. doi:10.1080/02724634.1998.10011088.