Related Research Articles
Vascular dementia (VaD) is dementia caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain, typically a series of minor strokes, leading to worsening cognitive decline that occurs step by step. The term refers to a syndrome consisting of a complex interaction of cerebrovascular disease and risk factors that lead to changes in the brain structures due to strokes and lesions, and resulting changes in cognition. The temporal relationship between a stroke and cognitive deficits is needed to make the diagnosis.

Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), is a form of angiopathy in which amyloid beta peptide deposits in the walls of small to medium blood vessels of the central nervous system and meninges. The term congophilic is sometimes used because the presence of the abnormal aggregations of amyloid can be demonstrated by microscopic examination of brain tissue after staining with Congo red. The amyloid material is only found in the brain and as such the disease is not related to other forms of amyloidosis.
Pittsburgh compound B (PiB) is a radioactive analog of thioflavin T, which can be used in positron emission tomography scans to image beta-amyloid plaques in neuronal tissue. Due to this property, Pittsburgh compound B may be used in investigational studies of Alzheimer's disease.
The Potamkin Prize for Research in Pick's, Alzheimer's, and Related Diseases was established in 1988 and is sponsored by the American Academy of Neurology. The prize is funded through the philanthropy of the Potamkin Foundation. The prize is awarded for achievements on emerging areas of research in Pick's disease, Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.
John Anthony Hardy FRS is a human geneticist and molecular biologist at the Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological Studies at University College London with research interests in neurological diseases.
Bart De Strooper is a Belgian molecular biologist and professor at VIB and KU Leuven and the UK Dementia Research Institute and University College London, UK. His research interests are in Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a neurocognitive disorder which involves cognitive impairments beyond those expected based on an individual's age and education but which are not significant enough to interfere with instrumental activities of daily living. MCI may occur as a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia, especially Alzheimer's disease. It includes both memory and non-memory impairments. Mild cognitive impairment has been relisted as mild neurocognitive disorder in DSM-5, and in ICD-11.
The aim of dementia prevention is to delay or prevent dementia. Dementia prevention is a global health priority and as such requires a global response. Recent initiatives include the establishment of the International Research Network on Dementia Prevention (IRNDP) which aims to link researchers in this field globally, and the establishment of the Global Dementia Observatory a web-based data knowledge and exchange platform, which will collate and disseminate key dementia data from members states. Although there is no cure for dementia currently, it is well established that modifiable risk factors influence both the likelihood of developing dementia and the age at which it is developed. Dementia can be prevented by reducing the risk factors for vascular disease and depression. Livingstone et al. (2014) and the Lancet Commission (2017) concluded that more than a third dementia cases are theoretically preventable. Among older adults both an unfavorable lifestyle and high genetic risk are independently associated with higher dementia risk. A favorable lifestyle is associated with a lower dementia risk, regardless of genetic risk. The Lancet Commission identified 9 modifiable lifestyle factors, and the early treatment of acquired hearing loss was estimated as the most significant of these factors, potentially preventing up to 9% of dementia cases.
Steven T. DeKosky is the Aerts-Cosper Professor of Alzheimer's Research at the University of Florida (UF) College of Medicine, deputy director of UF’s Evelyn F. and William L. McKnight Brain Institute (MBI) and associate director of the 1Florida Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center.
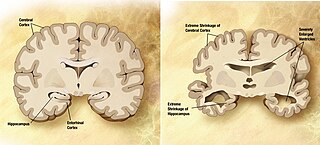
Alzheimer's disease (AD), also referred to simply as Alzheimer's, is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gradually worsens over time. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioural issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.
Samuel E. Gandy, M.D., Ph.D. is a neurologist, cell biologist, Alzheimer's Disease (AD) researcher and expert in the metabolism of the sticky substance called amyloid that clogs the brain in patients with Altzhimers. His team discovered the first drugs that could lower the formation of amyloid.
Avid Radiopharmaceuticals is an American company, founded by Dr. Daniel Skovronsky, and based at the University City Science Center research campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The company has developed a radioactive tracer called florbetapir (18F). Florbetapir can be used to detect beta amyloid plaques in patients with memory problems using positron emission tomography (PET) scans, making the company the first to bring to market an FDA-approved method that can directly detect this hallmark pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Venture investors include Alta Partners, Osage University Partners, and Safeguard Scientifics.
Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) is a multisite study that aims to improve clinical trials for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This cooperative study combines expertise and funding from the private and public sector to study subjects with AD, as well as those who may develop AD and controls with no signs of cognitive impairment. Researchers at 63 sites in the US and Canada track the progression of AD in the human brain with neuroimaging, biochemical, and genetic biological markers. This knowledge helps to find better clinical trials for the prevention and treatment of AD. ADNI has made a global impact, firstly by developing a set of standardized protocols to allow the comparison of results from multiple centers, and secondly by its data-sharing policy which makes available all at the data without embargo to qualified researchers worldwide. To date, over 1000 scientific publications have used ADNI data. A number of other initiatives related to AD and other diseases have been designed and implemented using ADNI as a model. ADNI has been running since 2004 and is currently funded until 2021.

Brain positron emission tomography is a form of positron emission tomography (PET) that is used to measure brain metabolism and the distribution of exogenous radiolabeled chemical agents throughout the brain. PET measures emissions from radioactively labeled metabolically active chemicals that have been injected into the bloodstream. The emission data from brain PET are computer-processed to produce multi-dimensional images of the distribution of the chemicals throughout the brain.
Florbetapir (18F) is a PET scanning radiopharmaceutical compound containing the radionuclide fluorine-18, FDA approved in 2012 as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease. Florbetapir, like Pittsburgh compound B (PiB), binds to beta-amyloid, however fluorine-18 has a half-life of 109.75 minutes, in contrast to PiB's radioactive half life of 20 minutes. Wong et al. found that the longer life allowed the tracer to accumulate significantly more in the brains of people with AD, particularly in the regions known to be associated with beta-amyloid deposits.
Florbetaben, a fluorine-18 (18F)-labeled stilbene derivative, trade name NeuraCeq , is a diagnostic radiotracer developed for routine clinical application to visualize β-amyloid plaques in the brain. It is indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of β-amyloid neuritic plaque density in the brains of adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other causes of cognitive impairment. β-amyloid is a key neuropathological hallmark of AD, so markers of β-amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain are useful in distinguishing AD from other causes of dementia. The tracer successfully completed a global multicenter phase 0–III development program and obtained approval in Europe, US and South Korea in 2014.

Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) are abnormal differences seen in neuroimaging of Alzheimer's Disease patients, associated with amyloid-modifying therapies, particularly human monoclonal antibodies such as aducanumab. There are two types of ARIA - ARIA-E and ARIA-H. The phenomenon was first seen in trials of bapineuzumab.
Mathias Jucker, born 7 July 1961 in Zürich, Switzerland, is a Swiss neuroscientist, Professor, and a Director at the Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research of the University of Tübingen, Germany. He is also a Group Leader at the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Tübingen. Jucker is known for his research on the basic biologic mechanisms underlying brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease.
Julie C. Price is an American physicist and professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School as well as the director of PET Pharmacokinetic Modeling at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center at Massachusetts General Hospital. Price is a leader in the study and applications of quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) and led the first fully quantitative pharmacokinetic evaluations of Pittsburgh compound-B (PIB), one of the most widely used PET ligands for imaging amyloid beta plaques. As a principal investigator at Harvard and continuing collaborator with the University of Pittsburgh, Price innovates novel PET methods for imaging biological markers of health and disease such as glucose metabolism, protein expression, neurotransmitter system function, and tau and amyloid beta plaque burden.
Lary Walker is an American neuroscientist and researcher at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia. He is Associate Director of the Goizueta Alzheimer's Disease Research Center at Emory, and he is known for his research on the role of abnormal proteins in the causation of Alzheimer’s disease.
References
- ↑ "MetLife Foundation Awards for Medical Research in Alzheimer's Disease" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 October 2018.
- ↑ "William E. Klunk". pitt.edu. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ↑ "William E. Klunk". upmc.com. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ↑ "William E. Klunk, MD, PhD". UPMC | Life Changing Medicine. Retrieved 2019-05-28.
- ↑ Rabinovici, G. D.; Jagust, W. J. (2009). "Amyloid imaging in aging and dementia: testing the amyloid hypothesis in vivo". Behavioural Neurology. 21 (1): 117–128. doi:10.1155/2009/609839. ISSN 1875-8584. PMC 2804478 . PMID 19847050.
| This article about a United States psychiatrist is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |