William Toby White is an Australian ichthyologist. He studies speciation and biodiversity of shark, ray, and skate species (subclass Elasmobranchii) through morphological and molecular systematics. [1]
William Toby White is an Australian ichthyologist. He studies speciation and biodiversity of shark, ray, and skate species (subclass Elasmobranchii) through morphological and molecular systematics. [1]
White received bachelor's (1997) and doctoral (2003) degrees in Biological Science from Murdoch University in Perth, Australia. His doctoral thesis, "Aspects of the biology of elasmobranchs in a subtropical embayment in Western Australia and of chondrichthyan fisheries in Indonesia", examined 1) spatial partitioning of food resources available to shark, ray, and skate species in Shark Bay (off the western coast of Australia), and 2) the relative frequencies of shark, ray, and skate species caught in fisheries off the coast of southeastern Indonesia. [2] From 2004 to 2006 he did post-doctoral training, also at Murdoch University.
Since 2006, White has served as ichthyologist at the Australian National Fish Collection which is part of the CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research facility in Hobart, the capital of the Australian state of Tasmania. As of 2014 [update] , he has at least 137 publications, which have been cited at least 1767 times. [3] He has described over 50 new sharks and rays, as well as 7 new bony fishes (teleosts) in publications which he authored or co-authored, [4] including the discovery and naming of the shark species Squalus formosus . [5] Another stated area of research interest is fishery management of developing countries, particularly in Papua New Guinea and the Indonesian archipelago. [4] Since 2011, he has served as editor for the journal Ichthyological Research. [6]

Elasmobranchii is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish. Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill clefts opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil.

The guitarfish are a family, Rhinobatidae, of rays. The guitarfish are known for an elongated body with a flattened head and trunk and small, ray-like wings. The combined range of the various species is tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate waters worldwide.
John Andrew Frank "Jack" Garrick was a New Zealand ichthyologist. He specialized in elasmobranchs and published many books and articles about shark and ray biology. In 1982, he published a thorough taxonomy on sharks of the genus Carcharhinus, where he identified the smoothtooth blacktip shark as a new species. He is the species authority for several types of sharks, including the New Zealand lanternshark. Garrick was a zoology professor at Victoria University of Wellington, appointed to a personal chair in 1971.
Stewart Springer was an American ichthyologist and herpetologist. He was a world-renowned expert on shark behavior, classification (taxonomy), and population distribution. More than 35 species of sharks, skates, rays, and other creatures are either classified by or named after him.
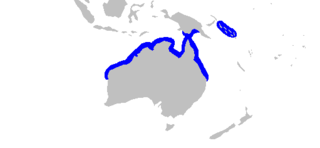
The nervous shark is a species of requiem shark, and part of the family Carcharhinidae, so named because of its timid behavior in regard to humans. It is common in shallow, coastal waters off northern Australia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands. A small brownish or grayish shark typically measuring 1.0–1.3 m (3.3–4.3 ft) long, this species has a short, blunt snout, oval eyes, and a relatively large second dorsal fin. The leading margins of most fins are finely edged with black, and the lower caudal fin lobe is black-tipped.

The milk shark is a species of requiem shark, and part of the family Carcharhinidae, whose common name comes from an Indian belief that consumption of its meat promotes lactation. The largest and most widely distributed member of its genus, the milk shark typically measures 1.1 m (3.6 ft) long, and can be found in coastal tropical waters throughout the eastern Atlantic and the Indo-Pacific regions. Occurring from the surface to a depth of 200 m (660 ft), this species is common near beaches and in estuaries, and has been recorded swimming up rivers in Cambodia. Juveniles are known to inhabit tidal pools and seagrass meadows. The milk shark has a slender body with a long, pointed snout and large eyes, and is a nondescript gray above and white below. This shark can be distinguished from similar species in its range by the long furrows at the corners of its mouth, and seven to 15 enlarged pores just above them.

Rhina ancylostoma, the bowmouth guitarfish, shark ray or mud skate, is a species of ray and a member of the family Rhinidae. Its evolutionary affinities are not fully resolved, though it may be related to true guitarfishes and skates. This rare species occurs widely in the tropical coastal waters of the western Indo-Pacific, at depths of up to 90 m (300 ft). Highly distinctive in appearance, Rhina ancylostoma has a wide and thick body with a rounded snout and large shark-like dorsal and tail fins. Its mouth forms a W-shaped undulating line, and there are multiple thorny ridges over its head and back. It has a dorsal color pattern of many white spots over a bluish gray to brown background, with a pair of prominent black markings over the pectoral fins. This large species can reach a length of 2.7 m (8.9 ft) and weight of 135 kg (298 lb).

The plain maskray or brown stingray, is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in shallow, soft-bottomed habitats off northern Australia. Reaching 24 cm (9.4 in) in width, this species has a diamond-shaped, grayish green pectoral fin disc. Its short, whip-like tail has alternating black and white bands and fin folds above and below. There are short rows of thorns on the back and the base of the tail, but otherwise the skin is smooth. While this species possesses the dark mask-like pattern across its eyes common to its genus, it is not ornately patterned like other maskrays.

Rhinobatos is a genus of fish in the Rhinobatidae family. Although previously used to encompass all guitarfishes, it was found to be polyphyletic, and recent authorities have transferred many species included in the genus to Acroteriobatus, Glaucostegus, and Pseudobatos.

The western shovelnose stingaree is a common species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, inhabiting shallow sandy flats and seagrass beds off southwestern Australia from Perth to Gulf St Vincent. Growing to 37 cm (15 in) long, this small ray has a rounded pectoral fin disc and a blunt, broadly triangular snout. Its nostrils have enlarged lobes along the outer rims and a skirt-shaped curtain of skin between them with a strongly fringed posterior margin. Its tail ends in a lance-like caudal fin and lacks dorsal fins and lateral skin folds. This species is colored grayish to brownish above, sometimes with lighter and darker spots, and pale below, sometimes with darker marginal bands and blotches.

Arhynchobatidae is a family of skates and is commonly known as the softnose skates. It belongs to the order Rajiformes in the superorder Batoidea of rays. At least 104 species have been described, in 13 genera. Softnose skates have at times been placed in the same family as hardnose skates, but most recent authors recognize them as a distinct family. Members of the Arhynchobatidae can be distinguished from hardnose skates in having a soft and flexible snout, as well as a more or less reduced rostrum.

The eastern shovelnose ray is a species of guitarfish in the family Rhinobatidae of order Rhinopristiformes. The species is endemic to the east coast of Australia and inhabits subtropical and temperate waters from southern Queensland to southern New South Wales.

Batoidea is a superorder of cartilaginous fishes, commonly known as rays. They and their close relatives, the sharks, comprise the subclass Elasmobranchii. Rays are the largest group of cartilaginous fishes, with well over 600 species in 26 families. Rays are distinguished by their flattened bodies, enlarged pectoral fins that are fused to the head, and gill slits that are placed on their ventral surfaces.

The brown whipray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, common in inshore, muddy habitats along the northern coast of Australia. It has often been confused in literature for the honeycomb stingray and the black-spotted whipray, which until recently was thought to be the same species. This species has an angular, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and a long, very thin tail without fin folds. It is plain brown above, sometimes with white dots or flecks near the edge of the disc, and white below; the tail is dark all over, with alternating dark and light bands near the tip. The maximum recorded disc width is 74 cm (29 in).
Peter Robert Last is an Australian ichthyologist, curator of the Australian National Fish Collection and a senior principal research scientist at CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research (CMAR) in Hobart, Tasmania. He is an elasmobranch expert and has described many new species of shark.

The western gulper shark is a species of squaliform shark discovered in 2008. The species had previously been identified as a variant of the dumb gulper shark, however was differentiated based on morphology. The western gulper is known from the waters of Western Australia, as well as Indonesia, East Timor, and islands in the Southern Indian Ocean. This shark is classified as "least concern" by the IUCN.
Rhinopristiformes is an order of rays, cartilaginous fishes related to sharks, containing shovelnose rays and allied groups.

The Sydney skate is a species of skate of the family Rajidae native to waters off the east coast of Australia.

The grey skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It was described in 2008 by Australian ichthyologist Peter R. Last.
Bigelow's ray, also called the chocolate skate or Bigelow's skate, is a species of skate in the family Rajidae. It is named in honour of the oceanographer Henry Bryant Bigelow.