Related Research Articles

The economy of Malawi is $7.522 billion by gross domestic product as of 2019,and is predominantly agricultural,with about 80% of the population living in rural areas. The landlocked country in south central Africa ranks among the world's least developed countries. In 2017,agriculture accounted for about one-third of GDP and about 80% of export revenue. The economy depends on substantial inflows of economic assistance from the IMF,the World Bank,and individual donor nations. The government faces strong challenges:to spur exports,to improve educational and health facilities,to face up to environmental problems of deforestation and erosion,and to deal with the problem of HIV/AIDS in Africa. Malawi is a least developed country according to United Nations.

Robert Merton Solow,GCIH is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology,where he has been a professor since 1949. He was awarded the John Bates Clark Medal in 1961,the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1987,and the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2014. Four of his PhD students,George Akerlof,Joseph Stiglitz,Peter Diamond and William Nordhaus later received Nobel Memorial Prizes in Economic Sciences in their own right.

HIV/AIDS originated in Africa in the early 20th century and is a major public health concern and cause of death in many African countries. AIDS rates vary dramatically although the majority of cases are concentrated in Southern Africa. Although the continent is home to about 15.2 percent of the world's population,more than two-thirds of the total infected worldwide –some 35 million people –were Africans,of whom 15 million have already died. Sub-Saharan Africa alone accounted for an estimated 69 percent of all people living with HIV and 70 percent of all AIDS deaths in 2011. In the countries of sub-Saharan Africa most affected,AIDS has raised death rates and lowered life expectancy among adults between the ages of 20 and 49 by about twenty years. Furthermore,the life expectancy in many parts of Africa is declining,largely as a result of the HIV/AIDS epidemic with life-expectancy in some countries reaching as low as thirty-nine years.

Poverty reduction,poverty relief,or poverty alleviation,is a set of measures,both economic and humanitarian,that are intended to permanently lift people out of poverty.

Malawi is one of the world's least developed countries and is ranked 170 out of 187 countries according to the 2010 Human Development Index. It has about 16 million people,53% of whom live under the national poverty line,and 90% of whom live on less than $2 per day. The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) estimated that there are 46,000 severely malnourished children.

Kwesi Botchwey is a Ghanaian former government official and Professor of Practice in Development Economics at The Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy of Tufts University.
Widow inheritance is a cultural and social practice whereby a widow is required to marry a male relative of her late husband,often his brother. The practice is more commonly referred as a levirate marriage,examples of which can be found in ancient and biblical times.
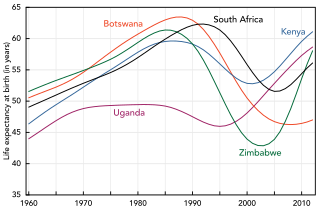
HIV/AIDS affects economic growth by reducing the availability of human capital. Without proper prevention,nutrition,health care and medicine that is available in developing countries,large numbers of people are developing AIDS.

Erik Thorbecke is a development economist. He is a co-originator of the widely used Foster-Greer-Thorbecke poverty measure and played a significant role in the development and popularization of Social Accounting Matrix. Currently,he is H. E. Babcock Professor of Economics,Emeritus,and Graduate School Professor at Cornell University.
Nigeria had one of the world's highest economic growth rates,averaging 7.4% according to the Nigeria economic report that was released in July 2019 by the World Bank. Following the oil price collapse in 2014–2016,combined with negative production shocks,the gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate dropped to 2.7% in 2015. In 2016 during its first recession in 25 years,the economy contracted by 1.6%. Nationally,43 percent of Nigerians live below the poverty line,while another 25 percent are vulnerable. For a country with massive wealth and a huge population to support commerce,a well-developed economy,and plenty of natural resources such as oil,the level of poverty remains unacceptable. However,poverty may have been overestimated due to the lack of information on the extremely huge informal sector of the economy,estimated at around 60% more,of the current GDP figures. As of 2018,the population growth rate is higher than the economic growth rate,leading to a slow rise in poverty. According to a 2018 report by the World Bank,almost half the population is living below the international poverty line,and unemployment peaked at 23.1%. Nigeria had one of the world's highest economic growth rates,averaging 7.4% according to the Nigeria economic report that was released in July 2019 by the World Bank. Following the oil price collapse in 2014–2016,combined with negative production shocks,the GDP growth rate dropped to 2.7% in 2015. In 2016 during its first recession in 25 years,the economy contracted by 1.6%. Many individuals are faced with limited financial opportunities,extreme information poverty and unemployment,a lack of access to information technology resources,and other uniquely debilitating environmental circumstances as poverty.
Energy use and development in Africa varies widely across the continent,with some African countries exporting energy to neighbors or the global market,while others lack even basic infrastructures or systems to acquire energy. The World Bank has declared 32 of the 48 nations on the continent to be in an energy crisis. Energy development has not kept pace with rising demand in developing regions,placing a large strain on the continent's existing resources over the first decade of the new century. From 2001 to 2005,GDP for over half of the countries in Sub Saharan Africa rose by over 4.5% annually,while generation capacity grew at a rate of 1.2%.

The Elusive Quest For Growth:Economists’Adventures and Misadventures in the Tropics is a 2001 book by World Bank development economist William Easterly. Upon its release,the book received acclaim from such figures as Bruce Bartlett,Robert Solow,and Paul Romer,and has since become widely cited in the Economic Development literature.

Bad Samaritans:The Myth of Free Trade and the Secret History of Capitalism is a book about economics written by Ha-Joon Chang,a South Korean institutional economist specializing in development economics. It criticizes mainstream economics of globalization and neo-liberalism. Chang claims that developed countries want developing countries to change their economic policy and open their markets. Rich and powerful governments and institutions are actually "Bad Samaritans";their intentions may be worthy but their simplistic,free-market ideology and poor understanding of history leads them into policy errors.

Elizabeth Asiedu is a professor of economics at the University of Kansas. She has facilitated research that is centered around foreign aid,foreign directed investment (FDI),and gender. She is a founder of the Association for the Advancement of African Women (AAAWE),as well as the current president of the organization. Asiedu is an editor of the Journal of African Development.
Rachael Meager is an Australian economist and statistician. She currently holds an Assistant Professorship at the London School of Economics,within the STICERD research centre.
Ezekiel Kalipeni was a Malawian geographer who specialized in population and environmental studies,medical geography,and Third World development issues. His research focused on sub-saharan Africa and the spread of pandemics in developing countries. He is most well known for his work in mapping and spatial analysis of the HIV/AIDS epidemic in Africa. In 2014 he was recognized as the Kwado-Konadu-Agyemang Distinguished Scholar in African Geography by the American Association of Geographers.
Mary Tiffen was a British economic historian,scholar and development professional. She specialised in ancient irrigation systems and African drylands.
Reginald Herbold Green was an American development economist who focused on African economic issues. His research focus included studying the economies of eastern and southern Africa,South African Development Community (SADC),international organizations and aid disbursement,and the Economic Commission on Africa,specializing in poverty alleviation,development enablement,and economic liberalization.

Yingyao Hu 胡颖尧 is an econometrician,a professor of economics,and currently the Chair of the Department of Economics,Johns Hopkins University.
References
- ↑ "Our Stories | United Nations in Malawi". malawi.un.org. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ Chilundu, Steve (2022-05-20). "No quick fixes to forex scarcity". The Nation Online. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "Winford Masanjala". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "economics.cc.ac.mw/people/staff/Winford_Masanjala". economics.cc.ac.mw. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "Rough and lonely road to prosperity: a reexamination of the sources of growth in Africa using Bayesian model averaging". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "The poverty-HIV/AIDS nexus in Africa: a livelihood approach". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "Cash crop liberalization and poverty alleviation in Africa: evidence from Malawi". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "The Solow model with CES technology: Nonlinearities and parameter heterogeneity". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "Initial conditions, and post-war growth in sub-Saharan Africa". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ↑ "Tackling Malawi's medical brain drain". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.