Related Research Articles

Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as MF4.

A rotary dial is a component of a telephone or a telephone switchboard that implements a signaling technology in telecommunications known as pulse dialing. It is used when initiating a telephone call to transmit the destination telephone number to a telephone exchange.

A telephone switchboard was a device used to connect circuits of telephones to establish telephone calls between users or other switchboards throughout the 20th century. The switchboard was an essential component of a manual telephone exchange, and was operated by switchboard operators who used electrical cords or switches to establish the connections.
Direct distance dialing (DDD) is a telecommunication service feature in North America by which a caller may, without operator assistance, call any other user outside the local calling area. Direct dialing by subscribers typically requires extra digits to be dialed as prefixes to the directory telephone number of the destination. International Direct Distance Dialing (IDDD) extends the system beyond the geographic boundaries of the North American Numbering Plan (NANP).
In telephony, ringdown is a method of signaling an operator in which telephone ringing current is sent over the line to operate a lamp or cause the operation of a self-locking relay known as a drop.

A blue box is an electronic device that produces tones used to generate the in-band signaling tones formerly used within the North American long-distance telephone network to send line status and called number information over voice circuits. During that period, charges associated with long-distance calling were commonplace and could be significant, depending on the time, duration and destination of the call. A blue box device allowed for circumventing these charges by enabling an illicit user, referred to as a "phreaker" to place long-distance calls, without using the network's user facilities, that would be billed to another number or dismissed entirely by the telecom company's billing system as an incomplete call. A number of similar "color boxes" were also created to control other aspects of the phone network.

The Strowger switch is the first commercially successful electromechanical stepping switch telephone exchange system. It was developed by the Strowger Automatic Telephone Exchange Company founded in 1891 by Almon Brown Strowger. Because of its operational characteristics, it is also known as a step-by-step (SXS) switch.

A telephone call or telephone conversation, also known as a phone call or voice call, is a connection over a telephone network between the called party and the calling party. Telephone calls started in the late 19th century. As technology has improved, a majority of telephone calls are made over a cellular network through mobile phones or over the internet with Voice over IP. Telephone calls are typically used for real-time conversation between two or more parties, especially when the parties cannot meet in person.
In telephony, multi-frequency signaling (MF) is a type of signaling that was introduced by the Bell System after World War II. It uses a combination of audible tones for address transport and supervision signaling on trunk lines between central offices. The signaling is sent in-band over the same channel as the bearer channel used for voice traffic.
A sender is a type of circuit and system module in 20th-century electromechanical telephone exchanges. It registered the telephone numbers dialed by the subscriber, and transmitted that information to another part of the exchange or another exchange for the purpose of completing a telephone call. Some American exchange designs, for example, of the No. 1 Crossbar switch used originating senders and terminating senders. The corresponding device in the British director telephone system was called a "director" and, in other contexts, "register".

E and M signaling is a type of supervisory line signaling that uses DC signals on separate leads, called the "E" lead and "M" lead, traditionally used in the telecommunications industry between telephone switches. Various mnemonic names have been used to memorize these letters, such as Earth and Magneto or Ear and Mouth, the most common variation.

On analog telephone lines with special services, a flash or register-recall signal is used to control functions on the public telephone exchange, PBX or VoIP ATA.
Loop start is a telecommunications supervisory protocol between a central office or private branch exchange (PBX) and a subscriber telephone or other terminal for the purpose of starting and terminating a telephone call. It is the simplest of the telephone signaling systems, and uses the presence or absence of loop current to indicate the off-hook and on-hook loop states, respectively. It is used primarily for subscriber line signaling. An extension of the protocol that adds disconnect supervision is often called kewlstart.
In telephony, ground start is a method of signaling from a terminal of a subscriber local loop to a telephone exchange, where one side of a cable pair is temporarily grounded to request dial tone. Most middle 20th-century American payphones used coin-first ground start lines, with the starting ground connection provided by the coin itself, bridging a set of contacts as it passed through the coin chute.

The 1A2 Key Telephone System is a business telephone system developed and distributed by the Western Electric Company for the Bell System.
In telecommunication, supervision is the monitoring of a telecommunication circuit for telephony to convey to an operator, user, or a switching system, information about the operational state of the circuit. The typical operational states of trunks and lines are the idle and busy states, seizure, and disconnect. The states are indicated by various electrical signals and electrical conditions depending on the type of circuit, the type of terminating equipment, and the type of intended service.
The Number One Crossbar Switching System (1XB), was the primary technology for urban telephone exchanges served by the Bell System in the mid-20th century. Its switch fabric used the electromechanical crossbar switch to implement the topology of the panel switching system of the 1920s. The first No. 1 Crossbar was installed in the PResident-2 central office at Troy Avenue in Brooklyn, New York which became operational in February 1938.
Panel Call Indicator, or PCI, is a form of signalling used between two telephone offices. It was also originally called Relay Call Indicator (RCI).

A telephone exchange, also known as a telephone switch or central office, is a crucial component in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or large enterprise telecommunications systems. It facilitates the interconnection of telephone subscriber lines or digital system virtual circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers.
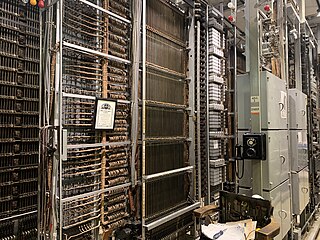
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).