
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers make contributions in doing citizen science, such as by monitoring variable stars, double stars, sunspots, or occultations of stars by the Moon or asteroids, or by discovering transient astronomical events, such as comets, galactic novae or supernovae in other galaxies.

A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a multi-purpose mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android, and thus saw a rapid decline in use after 2007.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.
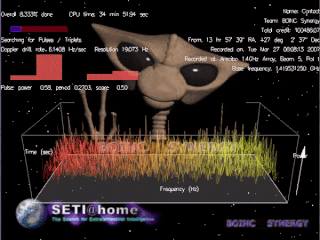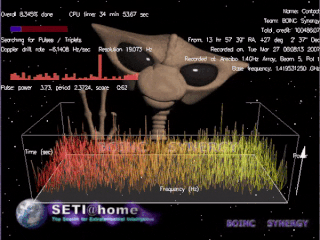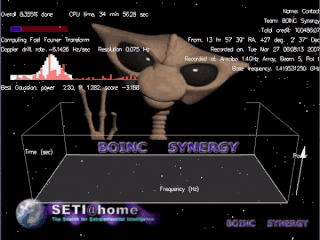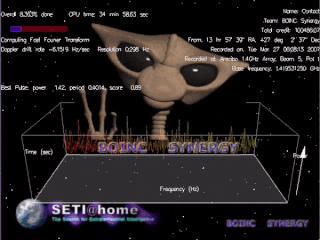
SETI@home is a project of the Berkeley SETI Research Center to analyze radio signals with the aim of searching for signs of extraterrestrial intelligence. Until March 2020, it was run as an Internet-based public volunteer computing project that employed the BOINC software platform. It is hosted by the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley, and is one of many activities undertaken as part of the worldwide SETI effort.
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes (STB) with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.
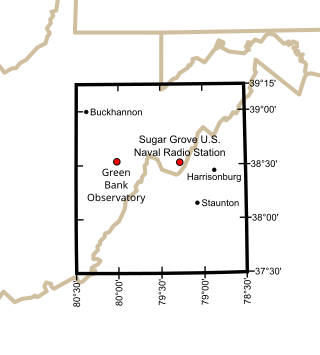
The National Radio Quiet Zone (NRQZ) is a large area of land in the United States designated as a radio quiet zone, in which radio transmissions are restricted by law to facilitate scientific research and the gathering of military intelligence. About half of the zone is located in the Blue Ridge Mountains of west-central Virginia while the other half is in the Allegheny Mountains of east-central West Virginia; a small part of the zone is in the southernmost tip of the Maryland panhandle.
A rake receiver is a radio receiver designed to counter the effects of multipath fading. It does this by using several "sub-receivers" called fingers, that is, several correlators each assigned to a different multipath component. Each finger independently decodes a single multipath component; at a later stage the contribution of all fingers are combined in order to make the most use of the different transmission characteristics of each transmission path. This could very well result in higher signal-to-noise ratio (or Eb/N0) in a multipath environment than in a "clean" environment.
Pirate decryption is the decryption, or decoding, of pay TV or pay radio signals without permission from the original broadcaster. The term "pirate" is used in the sense of copyright infringement. The MPAA and other groups which lobby in favour of intellectual property regulations have labelled such decryption as "signal theft" even though there is no direct tangible loss on the part of the original broadcaster, arguing that losing out on a potential chance to profit from a consumer's subscription fees counts as a loss of actual profit.

Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both human-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras. EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science.
Datacasting is the broadcasting of data over a wide area via radio waves. It most often refers to supplemental information sent by television stations along with digital terrestrial television (DTT), but may also be applied to digital signals on analog TV or radio. It generally does not apply to data inherent to the medium, such as PSIP data that defines virtual channels for DTT or direct broadcast satellite system, or to things like cable modems or satellite modems, which use a completely separate channel for data.

Wireless security is the prevention of unauthorized access or damage to computers or data using wireless networks, which include Wi-Fi networks. The term may also refer to the protection of the wireless network itself from adversaries seeking to damage the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network. The most common type is Wi-Fi security, which includes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). WEP is an old IEEE 802.11 standard from 1997. It is a notoriously weak security standard: the password it uses can often be cracked in a few minutes with a basic laptop computer and widely available software tools. WEP was superseded in 2003 by WPA, a quick alternative at the time to improve security over WEP. The current standard is WPA2; some hardware cannot support WPA2 without firmware upgrade or replacement. WPA2 uses an encryption device that encrypts the network with a 256-bit key; the longer key length improves security over WEP. Enterprises often enforce security using a certificate-based system to authenticate the connecting device, following the standard 802.11X.

ASCOM is an open initiative to provide a standard interface to a range of astronomy equipment including mounts, focusers and imaging devices in a Microsoft Windows environment.
D-STAR is a digital voice and data protocol specification for amateur radio. The system was developed in the late 1990s by the Japan Amateur Radio League and uses minimum-shift keying in its packet-based standard. There are other digital modes that have been adapted for use by amateurs, but D-STAR was the first that was designed specifically for amateur radio.

The Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) is a joint project between an international consortium of organisations to construct and operate a low-frequency radio array. 'Widefield' refers to its very large field of view. Operating in the frequency range 70–300 MHz, the main scientific goals of the MWA are to detect neutral atomic Hydrogen emission from the cosmological Epoch of Reionization (EoR), to study the Sun, the heliosphere, the Earth's ionosphere, and radio transient phenomena, as well as map the extragalactic radio sky. It is located at the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO).
Milan Hudecek is a Czech-born Australian inventor and entrepreneur. He pioneered the fields of assistive technology for the blind and radio communications. He is a Member of the Order of Australia, winner of the Winston Gordon Award for Technological Advancement in the Field of Blindness and Visual Impairment, and Rolls-Royce & Qantas Award of Engineering Excellence.

MeerKAT, originally the Karoo Array Telescope, is a radio telescope consisting of 64 antennas in the Meerkat National Park, in the Northern Cape of South Africa. In 2003, South Africa submitted an expression of interest to host the Square Kilometre Array (SKA) Radio Telescope in Africa, and the locally designed and built MeerKAT was incorporated into the first phase of the SKA. MeerKAT was launched in 2018.

John O'Sullivan is an Australian engineer.

A dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.













