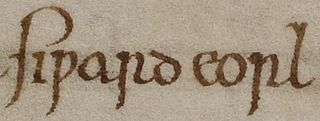Domesday Book is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of King William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name Liber de Wintonia, meaning "Book of Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him.

Le Morte d'Arthur is a 15th-century Middle English prose reworking by Sir Thomas Malory of tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table, along with their respective folklore. In order to tell a "complete" story of Arthur from his conception to his death, Malory compiled, rearranged, interpreted and modified material from various French and English sources. Today, this is one of the best-known works of Arthurian literature. Many authors since the 19th-century revival of the legend have used Malory as their principal source.

Crondall is a village and large civil parish in the north east of Hampshire in England, in the Crondall Hundred surveyed in the Domesday Book of 1086. The village is on the gentle slopes of the low western end of the North Downs range, and has the remains of a Roman villa. Despite the English Reformation, Winchester Cathedral held the chief manors representing much of its land from 975 until 1861. A large collection of Anglo-Saxon and Merovingian coins found in the parish has become known as the Crondall Hoard.
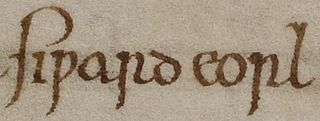
Siward or Sigurd was an important earl of 11th-century northern England. The Old Norse nickname Digri and its Latin translation Grossus are given to him by near-contemporary texts. It is possible Siward may have been of Scandinavian or Anglo-Scandinavian origin, perhaps a relative of Earl Ulf, although this is speculative. He emerged as a regional strongman in England during the reign of Cnut. Cnut was a Scandinavian ruler who conquered most of England in the 1010s, and Siward was one of many Scandinavians who came to England in the aftermath, rising to become sub-ruler of most of northern England. From 1033 at the latest, he was in control of southern Northumbria, present-day Yorkshire, governing as earl on Cnut's behalf.
The hide was an English unit of land measurement originally intended to represent the amount of land sufficient to support a household. It was traditionally taken to be 120 acres, but was in fact a measure of value and tax assessment, including obligations for food-rent, maintenance and repair of bridges and fortifications, manpower for the army, and (eventually) the geld land tax.
Roger Vacarius (1120–1200?) was an Italian authority in civil and canon law who was known to author the Liber pauperum which between the years 1190-1220 influenced the development of legal studies in the University of Oxford. According to Gervase of Canterbury, Vacarius became the first known teacher of Roman law in England.

Seacourt is a deserted medieval village near the City of Oxford. The site is now mostly beneath the Oxford Western By-pass, about 0.3 miles (0.48 km) south of the Seacourt / Hinksey Stream crossing.
Henry Royston Loyn, FBA, was a British historian specialising in the history of Anglo-Saxon England. His eminence in his field made him a natural candidate to run the Sylloge of the Coins of the British Isles, which he chaired from 1979 to 1993. He was Professor of Medieval History in the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire and afterwards Professor of Medieval History at Westfield College in the University of London.
The text of Domesday Book, the record of the great survey of England completed in 1086 executed for William I of England, was first edited by Abraham Farley in the 1770s. The first facsimile edition of the manuscripts was made in a project led by the cartographer Henry James in the 1860s. An English translation of the Latin text for most counties was published by the Victoria County History (VCH) during much of the 20th century.
St. Mary's Abbey, also known as the Nunnaminster, was a Benedictine nunnery in Winchester, Hampshire, England. It was founded between 899 and 902 by Alfred the Great's widow Ealhswith, who was described as the 'builder' of the Nunnaminster in the New Minster Liber Vitae. The first buildings were completed by their son, Edward the Elder. Among the house's early members was Edward's daughter Edburga.

The Liber Eliensis is a 12th-century English chronicle and history, written in Latin. Composed in three books, it was written at Ely Abbey on the island of Ely in the fenlands of eastern Cambridgeshire. Ely Abbey became the cathedral of a newly formed bishopric in 1109. Traditionally the author of the anonymous work has been given as Richard or Thomas, two monks at Ely, one of whom, Richard, has been identified with an official of the monastery, but some historians hold that neither Richard nor Thomas was the author.
John White was a Headmaster and Warden of Winchester College during the English Reformation who, remaining staunchly Roman Catholic in duty to his mentor Stephen Gardiner, became Bishop of Lincoln and finally Bishop of Winchester during the reign of Queen Mary. For several years he led the college successfully through very difficult circumstances. A capable if somewhat scholastic composer of Latin verse, he embraced the rule of Philip and Mary enthusiastically and vigorously opposed the Reformation theology.

The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
Ralph Basset was a medieval English royal justice during the reign of King Henry I of England. He was a native of Normandy, and may have come to Henry's notice while Henry held land in Normandy prior to becoming king. Basset is first mentioned in documents about 1102, and from then until his death around 1127, he was frequently employed as a royal justice. His son Richard Basset also became a royal judge.

The Book of Fees is the colloquial title of a modern edition, transcript, rearrangement and enhancement of the medieval Liber Feodorum which is a listing of feudal landholdings or fief, compiled in about 1302, but from earlier records, for the use of the English Exchequer. Originally in two volumes of parchment, the Liber Feodorum is a collection of about 500 written brief notes made between 1198 and 1292 concerning fiefs held in capite or in-chief, that is to say directly from the Crown.
The Liber Exoniensis or Exon Domesday is the oldest of the three manuscripts originating with the Domesday Survey of 1086, covering south-west England. It contains a variety of administrative materials concerning the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset and Wiltshire. It is MS 3500 in Exeter Cathedral Library.

St Swithun upon Kingsgate is a Church of England church in Winchester, Hampshire, England, built in the Middle Ages in the Early English style. Located above the medieval Kingsgate, one of the principal entrances to the city, the church is unusual in forming a part of the fabric of the old city walls. St Swithun's first appears in 13th century records, and under the fictional name of St Cuthbert's, is mentioned in Anthony Trollope's novel The Warden.
The Record Commissions were a series of six Royal Commissions of Great Britain and the United Kingdom which sat between 1800 and 1837 to inquire into the custody and public accessibility of the state archives. The Commissioners' work paved the way for the establishment of the Public Record Office in 1838. The Commissioners were also responsible for publishing various historical records, including the Statutes of the Realm to 1714 and the Acts of Parliament of Scotland to 1707, as well as a number of important medieval records.
Derek John Keene, FRHistS, was an English urban historian. He was founding director of the Centre for Metropolitan History from 1987 to 2002 at the Institute of Historical Research (IHR) and then Leverhulme Professor of Comparative Metropolitan History until retirement in 2008; since which he was Emeritus Professor of Metropolitan History and an honorary fellow of the IHR.

In a charter of c. 957 AD, King Eadwig granted twenty hides of land to Abingdon Abbey.
aet Hengestesige , and aet Seofecanwyrthe , and aet Wihtham