
The Claymore mine is a directional anti-personnel mine developed for the United States Armed Forces. Its inventor, Norman MacLeod, named the mine after a large medieval Scottish sword. Unlike a conventional land mine, the Claymore may be command-detonated, and is directional, shooting a wide pattern of metal balls into a kill zone. The Claymore can also be activated by a booby-trap tripwire firing system for use in area denial operations.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz. It lies between the medium frequency band (MF) and the bottom of the VHF band.

Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth, or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

A walkie-talkie, more formally known as a handheld transceiver, HT, or handheld radio, is a hand-held, portable, two-way radio transceiver. Its development during the Second World War has been variously credited to Donald Hings, radio engineer Alfred J. Gross, Henryk Magnuski and engineering teams at Motorola. First used for infantry, similar designs were created for field artillery and tank units, and after the war, walkie-talkies spread to public safety and eventually commercial and jobsite work.

The Tank, Infantry, Mk III, Valentine was an infantry tank produced in the United Kingdom during World War II. More than 8,000 Valentines were produced in eleven marks, plus specialised variants, accounting for about a quarter of wartime British tank production. The variants included riveted and welded construction, petrol and diesel engines and increases in armament. It was supplied in large numbers to the USSR and built under licence in Canada. It was used by the British in the North African campaign. Developed by Vickers, it proved to be strong and reliable.
Extremely high frequency is the International Telecommunication Union designation specifically included in the electromagnetic spectrum classification group with 8 other principal dedicated channel allocation. Extremely high frequency or commonly known as "EHF", is a large broadband that span a radius of about (30 GHz to 300 GHz) for the molecular spectra of radio frequencies. It lies between the super high frequency (3 GHz to 30 GHz) band and the far infrared band (300 GHz to 1015), for which the lower part is the terahertz band. Radio waves in this band have wavelengths from ten to one millimeter, so it is also called the millimeter band and radiation in this band is called millimeter waves, sometimes abbreviated MMW or mmWave. Millimeter-length electromagnetic waves were first investigated by Jagadish Chandra Bose, who generated waves of frequency up to 60 GHz during experiments in 1894–1896.

The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere.

A two-way radio is a radio transceiver, which is used for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication with other users with similar radios, in contrast to a broadcast receiver, which only receives transmissions.

The 2-pounder gun, officially the QF 2-pounder and universally known as the pom-pom, was a 40 mm (1.6 in) British autocannon, used as an anti-aircraft gun by the Royal Navy. The name came from the sound that the original models make when firing. This QF 2-pounder was not the same gun as the Ordnance QF 2-pounder, used by the British Army as an anti-tank gun and a tank gun, although they both fired 2 lb (0.91 kg), 40 mm (1.6 in) projectiles.
Shortwave bands are frequency allocations for use within the shortwave radio spectrum. Radio waves in these frequency ranges can be used for very long distance (transcontinental) communication because they can reflect off layers of charged particles in the ionosphere and return to Earth beyond the horizon, a mechanism called skywave or “skip” propagation. They are allocated by the ITU for radio services such as maritime communications, international shortwave broadcasting and worldwide amateur radio. The bands are conventionally named by their wavelength in metres, for example the ‘20 meter band’. Radio propagation and possible communication distances vary depending on the time of day, the season and the level of solar activity.

The RP-3 was a British air-to-ground rocket projectile introduced during the Second World War. The "3 inch" designation referred to the nominal diameter of the rocket motor tube. The use of a 60 lb (27 kg) warhead gave rise to the alternative name of the "60-pound rocket". Though an air-to-ground weapon, it saw limited use in other roles. They were generally used by British fighter-bomber aircraft against targets such as tanks, trains, motor transport and buildings, as well as by Coastal Command and Royal Navy aircraft against U-boats and ships.

The Ordnance QF 20 pounder was a British 84 mm (3.307 inch) tank gun. It was introduced in 1948 and used in the Centurion main battle tank, Charioteer medium tank, and Caernarvon Mark II heavy tank. After the 20 pounder gun was found to have inadequate performance against the Soviet T-54 the gun was mostly replaced in service by the larger calibre 105 mm L7 gun.

Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates oscillating electrical energy, often characterized as a wave. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.

The Wireless Set No. 19 was a Second World War mobile radio transceiver designed for use by armoured troops of the British Army. First introduced in 1940, the No. 19 began to replace the pre-war Wireless Set No. 11. Two modified versions were introduced, Mk. II in 1941 and Mk. III in 1942. An improved version from Canada was introduced in 1942 for use primarily with other forces. In British service, the No. 19 was replaced in the post-war era by the Larkspur radio system. Canadian-built No. 19s saw continued service for many years with a variety of users.
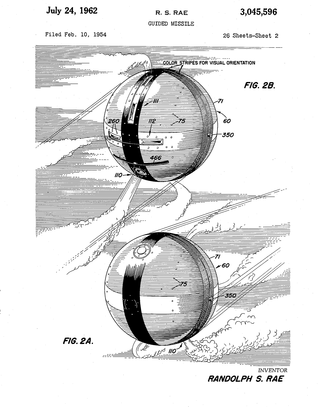
The Cannonball Missile also known as the D-40 was designed by the Applied Physics Laboratory of the Johns Hopkins University under a United States Navy contract in the early 1950s. The missile originally started out as an anti-ship missile to be launched from submarines. In 1952 the US Army Chief of Ordnance funded the project for development as an anti-tank missile. Between 1953 and 1956, around 50 D-40 missiles were test fired.

The SCR-300, designated AN/VRC-3 under the Joint Electronics Type Designation System, was a portable radio transceiver used by US Signal Corps in World War II. This backpack-mounted unit was the first radio to be nicknamed a "walkie talkie".

Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorized person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest" ; and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety, or professional two-way radio services.

















