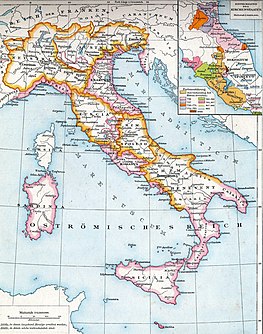
The Merovingian dynasty was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as Salian Frankish rulers of Belgica Secunda who were "kings" of the Franks in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaulish Romans under their rule. They conquered most of Gaul, defeating the Visigoths (507) and the Burgundians (534), and also extended their rule into Raetia (537). In Germania, the Alemanni, Bavarii and Saxons accepted their lordship. The Merovingian realm was the largest and most powerful of the states of western Europe following the fall of the Western Roman Empire.

Childeric I was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a King, both on his Roman-style seal ring, which was buried with him, and in fragmentary later records of his life. He was father of Clovis I, who acquired lordship over all or most Frankish kingdoms, and a significant part of Roman Gaul.

Richeza of Lotharingia was a German noblewoman by birth, a member of the Ezzonen dynasty. She married Duke Mieszko II Lambert, later King of Poland, becoming Queen of Poland. She returned to Germany following the deposition of her husband in 1031, later becoming a nun, and today is revered as Blessed Richeza of Lotharingia.

Theudebert I was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 533 to his death in 548. He was the son of Theuderic I and the father of Theudebald.

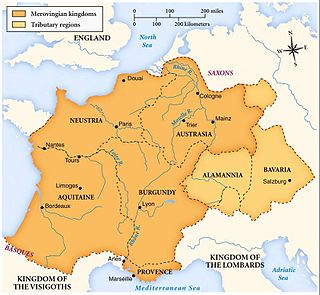
Austrasia was a territory which formed the northeastern section of the Merovingian Kingdom of the Franks during the 6th to 8th centuries. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of the Franks, including both the so-called Salians and Rhineland Franks, which Clovis I conquered after first taking control of the bordering part of Roman Gaul, now northern France, which is sometimes described in this period as Neustria.

Chlothar II, called the Great or the Young, was King of Neustria and King of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Clothar's uncle Guntram, King of Burgundy. Clothar assumed full power over Neustria upon the death of his mother, in 597; though rich this was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution in an especially brutal manner in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by moving in after the deaths of other kings.

Chilperic I was the king of Neustria from 561 to his death. He was one of the sons of the Frankish king Clotaire I and Queen Aregund.

Chlothar I, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.

Hedwige of Saxony, a member of the Ottonian dynasty, was Duchess consort of the Franks by her marriage to the Robertian duke Hugh the Great. Upon her husband's death in 956, she acted as a regent during the minority of their son Hugh Capet, the founder of the Elder House of Capet.
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks, or Frankish Empire was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. It is the predecessor of the modern states of France and Germany. After the Treaty of Verdun in 843, West Francia became the predecessor of France, and East Francia became that of Germany. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era before its partition in 843.
Fredegund or Fredegunda was the Queen consort of Chilperic I, the Merovingian Frankish king of Soissons. She served as regent during the minority of her son Chlothar II from 584 until 597.

Charibert I was the Merovingian King of Paris, the second-eldest son of Chlothar I and his first wife Ingund. His elder brother Gunthar died sometime before their father's death. He shared in the partition of the Frankish kingdom that followed his father’s death in 561, receiving the old kingdom of Childebert I, with its capital at Paris.

Brunhilda was queen regent of Austrasia, part of Francia, by marriage to the Merovingian king Sigebert I of Austrasia.

Gerberga of Saxony was a French queen who ruled as regent of France during the minority of her son Lothair in 954–959. She was a member of the Ottonian dynasty. Her first husband was Gilbert, Duke of Lorraine. Her second husband was Louis IV of France. Contemporary sources describe her as a highly educated, intelligent and forceful political player.
Hugobert was a seneschal and a count of the palace at the Merovingian court during the reigns of Theuderic III and Childebert III. He was a grandson of the dux Theotar, and it is assumed, but not proven, that his father was Chugus, who in 617 became mayor of the palace of Austrasia. The juxtaposition of names in the Vita Landiberto episcopi Traiectensis may imply a relationship between him and the family of Saint Lambert.
Emma was a member of the Austrasian royal family. She is sometimes identified with the Emma who married Eadbald of Kent.
Deuteria or Deoteria, was a Frankish Queen consort; the first spouse of king Theudebert I.
Gerberga of Burgundy was a member of the Elder House of Welf. She was married firstly to Herman I, count of Werl and secondly to Herman II, Duke of Swabia.

The Cross of Otto and Mathilde, Otto-Mathilda Cross, or First Cross of Mathilde is a medieval crux gemmata processional cross in the Essen Cathedral Treasury. It was created in the late tenth century and was used on high holidays until recently. It is named after the two persons who appear on the enamel plaque below Christ: Otto I, Duke of Swabia and Bavaria and his sister, Mathilde, the abbess of the Essen Abbey. They were grandchildren of the emperor Otto I and favourites of their uncle, Otto II. The cross is one of the items which demonstrate the very close relationship between the Liudolfing royal house and Essen Abbey. Mathilde became Abbess of Essen in 973 and her brother died in 982, so the cross is assumed to have been made between those dates, or a year or two later if it had a memorial function for Otto. Like other objects in Essen made under the patronage of Mathilde, the location of the goldsmith's workshop is uncertain, but as well as Essen itself, Cologne has often been suggested, and the enamel plaque may have been made separately in Trier.

Mathilde was Abbess of Essen Abbey from 973 to her death. As granddaughter of Holy Roman Emperor Otto the Great she was a member of the Liudolfing dynasty and became one of the most important abbesses in the history of Essen. She was responsible for the abbey, for its buildings, its precious relics, liturgical vessels and manuscripts, its political contacts, and for commissioning translations and overseeing education. In the unreliable list of Essen Abbesses from 1672, she is listed as the second Abbess Mathilde and as a result, she is sometimes called "Mathilde II" to distinguish her from the earlier abbess of the same name, who is meant to have governed Essen Abbey from 907 to 910 but whose existence is disputed.