
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.
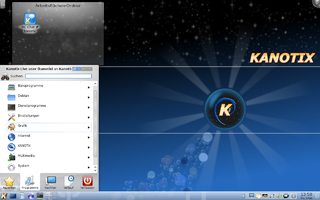
Kanotix, also referred to as KANOTIX, is an operating system based on Debian, with advanced hardware detection. It can run from an optical disc drive or other media i.e. USB-stick without using a hard disk drive.

A light-weight Linux distribution is one that uses lower memory and/or has less processor-speed requirements than a more "feature-rich" Linux distribution. The lower demands on hardware ideally result in a more responsive machine, and/or allow devices with fewer system resources to be used productively. The lower memory and/or processor-speed requirements are achieved by avoiding software bloat, i.e. by leaving out features that are perceived to have little or no practical use or advantage, or for which there is no or low demand.

Arch Linux is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required.

PCLinuxOS, often shortened to PCLOS, is a rolling release Linux distribution for x86-64 computers, with KDE Plasma, MATE, and XFCE as its default user interfaces. It is a primarily FOSS operating system for personal computers aimed at ease of use.
Puppy Linux is an operating system and family of light-weight Linux distributions that focus on ease of use and minimal memory footprint. The entire system can be run from random-access memory (RAM) with current versions generally taking up about 600 MB (64-bit), 300 MB (32-bit), allowing the boot medium to be removed after the operating system has started. Applications such as AbiWord, Gnumeric and MPlayer are included, along with a choice of lightweight web browsers and a utility for downloading other packages. The distribution was originally developed by Barry Kauler and other members of the community, until Kauler retired in 2013. The tool Woof can build a Puppy Linux distribution from the binary packages of other Linux distributions.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organizational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.

Finnix is a Debian-based Live CD operating system, developed by Ryan Finnie and intended for system administrators for tasks such as filesystem recovery, network monitoring and OS installation. Finnix is a relatively small distribution, with an ISO download size of approximately 100 MiB, and is available for the x86 and PowerPC architectures, and paravirtualized systems. Finnix can be run off a bootable CD, a USB flash drive, a hard drive, or network boot (PXE).
Squashfs is a compressed read-only file system for Linux. Squashfs compresses files, inodes and directories, and supports block sizes from 4 KiB up to 1 MiB for greater compression. Several compression algorithms are supported. Squashfs is also the name of free software, licensed under the GPL, for accessing Squashfs filesystems.

Software remastering is software development that recreates system software and applications while incorporating customizations, with the intent that it is copied and run elsewhere for "off-label" usage. The term comes from remastering in media production, where it is similarly distinguished from mere copying.
aufs implements a union mount for Linux file systems. The name originally stood for AnotherUnionFS until version 2.

The TurnKey Linux Virtual Appliance Library is a free open-source software project which develops a range of Debian-based pre-packaged server software appliances. Turnkey appliances can be deployed as a virtual machine, in cloud computing services such as Amazon Web Services or installed in physical computers.

Uzbl is a discontinued free and open-source minimalist web browser designed for simplicity and adherence to the Unix philosophy. Development began in early 2009 and is still considered in alpha software by the developers. The core component of Uzbl is written in C, but other languages are also used, most notably Python. All parts of the Uzbl project are released as free software under GNU GPL-3.0-only.

Kiwix is a free and open-source offline web browser created by Emmanuel Engelhart and Renaud Gaudin in 2007. It was first launched to allow offline access to Wikipedia, but has since expanded to include other projects from the Wikimedia Foundation, public domain texts from Project Gutenberg, many of the Stack Exchange sites, and many other resources. Available in more than 100 languages, Kiwix has been included in several high-profile projects, from smuggling operations in North Korea to Google Impact Challenge's recipient Bibliothèques Sans Frontières.

Foliate is a free e-book reading application for desktop Linux systems. The name refers to leaves, meaning "(getting) leafy" or "…-leaved".

Termux is a free and open-source terminal emulator for Android which allows for running a Linux environment on an Android device. Termux installs a minimal base system automatically; additional packages are available using its package manager, based on Debian's.












