
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the 3+1⁄2-mile (5.6-kilometer) wide, 295-foot deep Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; geologically, the two bodies are a single lake that is, by area, the largest freshwater lake in the world.

Whitehorse is the capital of the Yukon, and the largest city in Northern Canada. It was incorporated in 1950 and is located at kilometre 1426 on the Alaska Highway in southern Yukon. Whitehorse's downtown and Riverdale areas occupy both shores of the Yukon River, which rises in British Columbia and meets the Bering Sea in Alaska. The city was named after the White Horse Rapids for their resemblance to the mane of a white horse, near Miles Canyon, before the river was dammed.

Lake Huron is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French explorers who named it for the indigenous people they knew as Huron (Wyandot) inhabiting the region. Hydrologically, Lake Huron comprises the eastern portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the 5-mile-wide (8.0 km), 20-fathom-deep Straits of Mackinac. Combined, Lake Michigan–Huron is the largest freshwater lake by area in the world. The Huronian glaciation was named from evidence collected from Lake Huron region. The northern parts of the lake include the North Channel and Georgian Bay. Saginaw Bay is located in the southwest corner of the lake. The main inlet is the St. Marys River, and the main outlet is through the St. Clair River to Lake Erie. Lake Huron has a fairly large drainage basin covering parts of Michigan and Ontario. Water flows through Lake Huron faster than the other Great Lakes with a retention time of only 22 years.

Ludington is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat and the largest city in Mason County. The population was 7,655 at the 2020 census.

Montague is a city in Muskegon County, Michigan, United States. The population was 2,417 at the 2020 census. The city is politically independent from Montague Township, which borders it on three sides.

Whitehall is a city in Muskegon County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 2,909 at the 2020 census. The city is located to the west of Whitehall Township. Montague is its neighbor.

Grand Haven is a city within the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Ottawa County. Grand Haven is located on the eastern shore of Lake Michigan at the mouth of the Grand River, for which it is named. As of the 2010 census, Grand Haven had a population of 10,412. The city is home to the Grand Haven Memorial Airpark (3GM) and is located just north of Grand Haven Charter Township.

Houghton Lake is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Roscommon County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 5,294 during the 2020 census, making it the largest unincorporated community in Northern Michigan. The CDP is located within Denton, Lake, and Roscommon townships.

A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word vane comes from the Old English word fana, meaning "flag".

Father Time is a weathervane at Lord's Cricket Ground, London, in the shape of Father Time removing the bails from a wicket. The full weathervane is 6 ft 6 in (1.98 m) tall, with the figure of Father Time standing at 5 ft 4 in (1.63 m). It was given to Lord's in 1926 by the architect of the Grandstand, Sir Herbert Baker. The symbolism of the figure derives from Law 12(3) of the Laws of Cricket: "After the call of Time, the bails shall be removed from both wickets." The weathervane is frequently referred to as Old Father Time in television and radio broadcasts, but "Old" is not part of its official title.

The Great Smoky Mountains are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains and form part of the Blue Ridge Physiographic Province. The range is sometimes called the Smoky Mountains, and the name is commonly shortened to the Smokies. The Smokies are best known as the home of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, which protects most of the range. The park was established in 1934 and, with over 11 million visits per year, is the most visited national park in the United States.
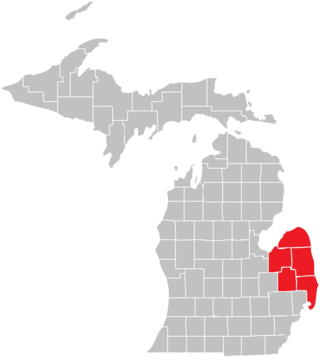
The Thumb is a region and a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan, so named because the Lower Peninsula is shaped like a mitten. The Thumb area is generally considered to be in the Central Michigan region, east of the Flint area and the Tri-Cities and north of Metro Detroit. The region is also branded as the Blue Water Area.

An iceboat is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats with a support structure, riding on the runners and steered with a rear blade, as with a conventional rudder. As iceboats evolved, the structure became a frame with a seat or cockpit for the iceboat sailor, resting on runners. Steering was shifted to the front.
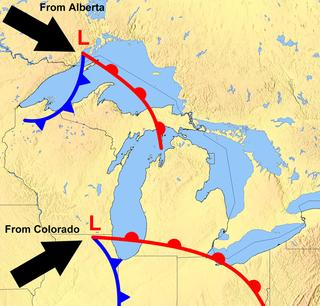
The Great Lakes Storm of 1913 was a blizzard with hurricane-force winds that devastated the Great Lakes Basin in the Midwestern United States and Southwestern Ontario, Canada, from November 7 to 10, 1913. The storm was most powerful on November 9, battering and overturning ships on four of the five Great Lakes, particularly Lake Huron.

Erik Nielsen Whitehorse International Airport is an airport of entry located in Whitehorse, Yukon, Canada. It is part of the National Airports System, and is owned and operated by the Government of Yukon. The airport was renamed in honour of longtime Yukon Member of Parliament Erik Nielsen on December 15, 2008. The terminal handled 294,000 passengers in 2012, representing a 94% increase in passenger traffic since 2002. By 2017, this number had risen to 366,000. Air North is based in Whitehorse.

Deacon Shem Drowne was a colonial coppersmith and tinplate worker in Boston, Massachusetts, and was America's first documented weathervane maker. He is most famous for the grasshopper weathervane atop of Faneuil Hall, well known as a symbol of Boston.
Global weather activity of 2007 profiles the major worldwide weather events, including blizzards, ice storms, tornadoes, tropical cyclones, and other weather events, from January 1, 2007, to December 31, 2007. Winter storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are formed during cold temperatures; they include snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice, including freezing rain, to form. Thehy may be marked by strong wind, thunder, lightning thunderstorms, heavy precipitation, including ice storm, wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere, including dust storms, snowstorms, and hail storms. Other major non winter events such as large dust storms, hurricanes, cyclones, tornados, gales, flooding, and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena.

The Barre Firehouse Weathervane is a hammered cooper weathervane that used to sit atop the Firehouse in Barre, Vermont. Created in 1904, the weathervane depicts a “flying team” of horses pulling a hook and ladder wagon. It is currently displayed in the Vermont History Center also in downtown Barre.

Travis Tuck was a Martha's Vineyard based metal sculptor known for his hand-crafted weather vanes of repoussé copper and bronze. His works turn in the wind above Steven Spielberg's East Hampton estate and 110 feet over Penn State's Beaver Stadium.

The Yukon Transportation Museum (YTM) is a non-profit organization and registered charity located in Whitehorse, Yukon, Canada, on the traditional territories of the Ta'an Kwächan Council and the Kwanlin Dün First Nation. Founded in 1990, YTM specializes in exhibiting and examining the Yukon Territory's rugged character through stories of ingenious and self-sufficient transportation modes, entrepreneurs, pioneers and inventors. The museum's mandate is to 'identify, acquire, preserve and conserve the history, cultural material and artifacts of Yukon's transportation modes, and to interpret this history in an educational manner for all Yukoners and visitors alike.'




















