The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology, such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members.

The International Organization for Standardization is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes.
An international standard is a technical standard developed by one or more international standards organizations. International standards are available for consideration and use worldwide. The most prominent such organization is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Other prominent international standards organizations including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Together, these three organizations have formed the World Standards Cooperation alliance.
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate a normalization of formerly custom processes.
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a common prerequisite that open standards use an open license that provides for extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in their development due to their inherently open nature. There is no single definition, and interpretations vary with usage. Examples of open standards include the GSM, 4G, and 5G standards that allow most modern mobile phones to work world-wide.
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpreting, or otherwise contributing to the usefulness of technical standards to those who employ them. Such an organization works to create uniformity across producers, consumers, government agencies, and other relevant parties regarding terminology, product specifications, protocols, and more. Its goals could include ensuring that Company A's external hard drive works on Company B's computer, an individual's blood pressure measures the same with Company C's sphygmomanometer as it does with Company D's, or that all shirts that should not be ironed have the same icon on the label.
Information security standards are techniques generally outlined in published materials that attempt to protect a user's or organization's cyber environment. This environment includes users themselves, networks, devices, all software, processes, information in storage or transit, applications, services, and systems that can be connected directly or indirectly to networks.
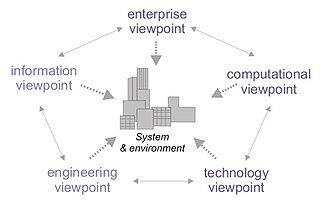
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and promote standards in the fields of information and communications technology (ICT).
Gigabit Home Networking (G.hn) is a specification for wired home networking that supports speeds up to 2 Gbit/s and operates over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers.
IEEE 2030 was a project of the standards association of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) that developed a "Guide for Smart Grid Interoperability of Energy Technology and Information Technology Operation with the Electric Power System (EPS), and End-Use Applications and Loads".
Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) is a research and standards development effort for energy management led by North American research labs and companies. The typical use is to send information and signals to cause electrical power-using devices to be turned off during periods of high demand.
IEC 62443 is a series of standards that address security for operational technology in automation and control systems. The series is divided into different sections and describes both technical and process-related aspects of automation and control systems security.
The Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) is a family of specifications published by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) used in conjunction with the ISO/IEC 14908 control networking standard for smart grid applications. OSGP is optimized to provide reliable and efficient delivery of command and control information for smart meters, direct load control modules, solar panels, gateways, and other smart grid devices. With over 5 million OSGP based smart meters and devices deployed worldwide it is one of the most widely used smart meter and smart grid device networking standards.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 Biometrics is a standardization subcommittee in the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which develops and facilitates standards within the field of biometrics. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 is the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), located in the United States.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 38 Cloud Computing and Distributed Platforms is a standardization subcommittee, which is part of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 39 Sustainability for and by Information Technology is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of sustainability and resource efficiency through Information Technology. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 39 is the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), located in the United States.
Note: This special working group has been disbanded. The work begun in ISO/IEC/JTC 1/SWG 5 on Internet of Things standardization gaps will be continued in ISO/IEC JTC 1/WG 10.

Houlin Zhao is a Chinese engineer who served as the Secretary-General of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) from 2015 to 2022. He was first elected at the 2014 Plenipotentiary Conference in Busan, and re-elected at the 2018 Plenipotentiary Conference in Dubai. ITU is the specialized United Nations Agency for Information and Communication Technology (ICT), working on promotion, collaboration, and standardization.
Harmonization is the process of minimizing redundant or conflicting standards which may have evolved independently. The name is also an analogy to the process to harmonizing discordant music.


