
A city is a large human settlement. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organizations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process.

Shanghai is one of the four municipalities under the direct administration of the central government of the People's Republic of China, the largest city in China by population, and the second most populous city proper in the world, with a population of 24.18 million as of 2017. It is a global financial centre and transport hub, with the world's busiest container port. Located in the Yangtze River Delta, it sits on the south edge of the estuary of the Yangtze in the middle portion of the East China coast. The municipality borders the provinces of Jiangsu and Zhejiang to the north, south and west, and is bounded to the east by the East China Sea.

Sustainable development is the organizing principle for meeting human development goals while at the same time sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services upon which the economy and society depend. The desired result is a state of society where living conditions and resource use continue to meet human needs without undermining the integrity and stability of the natural system. Sustainable development can be classified as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations.

Urbanization refers to the population shift from rural areas to urban areas, the gradual increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas, and the ways in which each society adapts to this change. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas. Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth: urbanization is "the proportion of the total national population living in areas classed as urban", while urban growth refers to "the absolute number of people living in areas classed as urban". The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008. It is predicted that by 2050 about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. That is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all global population growth from 2017 to 2030 will be absorbed by cities, about 1.1 billion new urbanites over the next 13 years.

A metropolitan area, sometimes referred to as a metro area or commuter belt, is a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure, and housing.
A metro area usually comprises multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighborhoods, townships, boroughs, cities, towns, exurbs, suburbs, counties, districts, states, and even nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions. Metropolitan areas include one or more urban areas, as well as satellite cities, towns and intervening rural areas that are socioeconomically tied to the urban core, typically measured by commuting patterns. In the United States, the concept of the metropolitan statistical area has gained prominence.

A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita compared with other nations can also be a reference point.

The World Economic Forum (WEF), based in Cologny-Geneva, Switzerland, was founded in 1971 as a not-for-profit organization. It gained formal status in January 2015 under the Swiss Host-State Act, confirming the role of the Forum as an International Institution for Public-Private Cooperation. The Forum's mission is cited as "committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas".

The Mid-Atlantic, also called Middle Atlantic states or the Mid-Atlantic states, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South Atlantic States. Its exact definition differs upon source, but the region usually includes New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Washington, D.C., Virginia, and West Virginia. When discussing climate, Connecticut is sometimes included in the region, since its climate is closer to the Middle Atlantic than the New England states. The Mid-Atlantic has played an important role in the development of American culture, commerce, trade, and industry. New York is, of course, the largest city in the Mid-Atlantic.

The Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region is the low-lying area surrounding the Pearl River estuary, where the Pearl River flows into the South China Sea. It is one of the most densely urbanized regions in the world, and is often considered an emerging megacity. The region's economy is referred to as Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, while the Chinese government's development plans consider it part of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area.

Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which companies are taxed very lightly or not at all to encourage economic activity. The taxation rules are determined by each country. The World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) has content on the conditions and benefits of free zones.

The City of New York, usually called either New York City (NYC) or simply New York (NY), is the most populous city in the United States and thus also in the state of New York. With an estimated 2017 population of 8,622,698 distributed over a land area of about 302.6 square miles (784 km2), New York is also the most densely populated major city in the United States. Located at the southern tip of the state of New York, the city is the center of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass and one of the world's most populous megacities, with an estimated 20,320,876 people in its 2017 Metropolitan Statistical Area and 23,876,155 residents in its Combined Statistical Area. A global power city, New York City has been described as the cultural, financial, and media capital of the world, and exerts a significant impact upon commerce, entertainment, research, technology, education, politics, tourism, art, fashion, and sports. The city's fast pace has inspired the term New York minute. Home to the headquarters of the United Nations, New York is an important center for international diplomacy.

The Economic Times is an English-language, Indian daily newspaper published by the Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd.. The Economic Times began publication in 1961. As of 2012, it is the world's second-most widely read English-language business newspaper, after the Wall Street Journal, with a readership of over 800,000. It is published simultaneously from 12 cities: Mumbai, Bangalore, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Chandigarh, and Pune. The Economic Times is headquartered in Mumbai at The Times of India building. Its main content is based on the Indian economy, international finance, share prices, prices of commodities as well as other matters related to finance. The founding editor of the paper when it was launched in 1961 was P.S. Hariharan. The current editor of The Economic Times is Bodhisattva Ganguli.
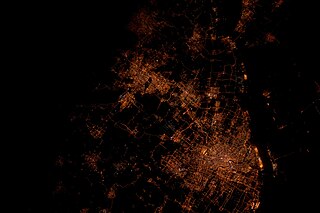
The Yangtze River Delta or YRD is a triangle-shaped metropolitan region generally comprising the Wu Chinese-speaking areas of Shanghai, southern Jiangsu province and northern Zhejiang province. The area lies in the heart of the Jiangnan region, where Yangtze River drains into the East China Sea. The urban build-up in the area has given rise to what may be the largest concentration of adjacent metropolitan areas in the world. It covers an area of 99,600 square kilometres (38,500 sq mi) and is home to over 115 million people as of 2013, of which an estimated 83 million is urban. If based on the greater Yangtze River Delta zone, it has over 140 million people in this region. Having a fertile soil, the Yangtze River Delta abundantly produces grain, cotton, hemp and tea. In 2018, the Yangtze River Delta had a GDP of approximately US$2.2 trillion, about the same size as Italy.

The economy of India is a developing mixed economy. It is the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). The country ranks 139th in per capita GDP (nominal) with $2,134 and 122nd in per capita GDP (PPP) with $7,783 as of 2018. After the 1991 economic liberalisation, India achieved 6-7% average GDP growth annually. Since 2014 with the exception of 2017, India's economy has been the world's fastest growing major economy, surpassing China.

Special economic zones of China (SEZs) are special economic zones located in mainland China. The government of China gives SEZs special economic policies and flexible governmental measures, compared to the more planned economy of most of China. This allows SEZs to utilize an economic management system that is more attractive for foreign and domestic firms to do business in than the rest of mainland China. In SEZs, "...foreign and domestic trade and investment are conducted without the authorization of the Chinese central government in Beijing." SEZs offer "tax and business incentives to attract foreign investment and technology".
The following are the international rankings of Jordan.

The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s, beginning in the United States. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations; in most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until the late-1930s. It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. In the 21st century, the Great Depression is commonly used as an example of how intensely the world's economy can decline.

Bruges is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country.
















