Related Research Articles

Southeast Alaska, often abbreviated to southeast or southeastern, and sometimes called the Alaska(n) panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The majority of southeast Alaska is situated in Tlingit Aaní, much of which is part of the Tongass National Forest, the United States' largest national forest. In many places, the international border runs along the crest of the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The region is noted for its scenery and mild, rainy climate.

Wrangell is a borough in Alaska, United States. As of the 2020 census the population was 2,127, down from 2,369 in 2010.

The Alexander Archipelago is a 300-mile (480 km) long archipelago in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the islands and cut them off from the mainland. The islands shelter the northern part of the Inside Passage as it winds its way among them.

The Dixon Entrance is a strait about 80 kilometers (50 mi) long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part of the Inside Passage shipping route. It forms part of the maritime boundary between the U.S. and Canada, although the location of that boundary here is disputed.

Clarence Strait, originally Duke of Clarence Strait, is a strait in southeastern Alaska, in the United States in the Alexander Archipelago. The strait separates Prince of Wales Island, on the west side, from Revillagigedo Island and Annette Island, on the east side. Clarence Strait is 126 miles (203 km) long, extending from Dixon Entrance to Sumner Strait. Moira Sound is on the west side of the strait.

Mitkof Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago in southeast Alaska between Kupreanof Island to the west and the Alaskan mainland to the east. It is approximately 16 km (9.9 mi) wide and 28 km (17 mi) long with a land area of 539.7 km2 (208.4 sq mi), making it the 30th largest island in the United States. Much of the island is managed as part of the Tongass National Forest.

The Wrangell Narrows is a winding, 35-km-long (22 mi) channel between Mitkof Island and Kupreanof Island in the Alexander Archipelago in Southeast Alaska. The Wrangell Narrows is one of the six Listed narrows in Southeast Alaska. There are about 60 lights and buoys to mark it because of its winding nature and navigation hazards. It was named "Proliv Vrangelya" in 1838 by G. Lindenberg after Admiral Baron Ferdinand Petrovich von Wrangell. The translation Wrangell Strait remained in use while Wrangell Narrows referred to the narrowest central portion. By 1919 Department of Commerce nautical chart 8170 was changed from Wrangell Strait to Wrangell Narrows.
Zimovia Strait is a narrow strait in the Alexander Archipelago in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is about 100 km (62 mi) long and bounded by Wrangell Island to the east and Woronkofski and Etolin Islands to the west. The strait is shown in an 1844 Russian chart, but the name was first published in 1853 on a Russian Hydrographic Department chart as "Proliv Zimov'ya".
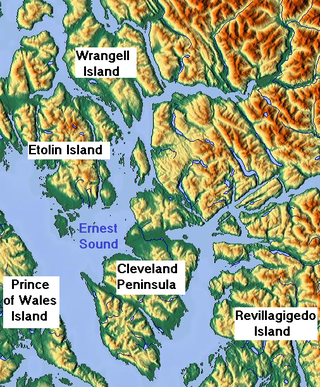
Etolin Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States at 56°05′52″N132°21′37″W. It is between Prince of Wales Island, to its west, and the Alaska mainland, to its east. It is southwest of Wrangell Island. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its southwest and east coasts, not realizing it was an island. It was originally named Duke of York Island but was renamed by the United States after the Alaska Purchase. It is named after Adolf Etolin, governor of the Russian American colonies from 1840 to 1845.

Zarembo Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies directly south of Mitkof Island and northwest of Etolin Island. To the northwest is Kupreanof Island and to the southwest is Prince of Wales Island. It has a land area of 183.14 square miles, making it the 34th largest island in the United States. It has no permanent resident population. It was first charted in 1793 by Laurenz Hartmann, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its north, west, and south coasts, not realizing it was an island. The island is named after Dionysius Zarembo, a Polish employee of the Russian American Company and explorer of Alaska. Usually known as Dionysius Zarembo, he was captain of the Russian-American Company ship Chichagof during the foundation of the Redoubt San Dionisio, named for his name-saint, a fortification at present-day Wrangell which was established to forestall encroachment on the Stikine region by the Hudson's Bay Company.

Wrangell Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle of southeastern Alaska. It is 28.5 miles long and 3.75 to 14.2 miles wide. It has a land area of 210.05 square miles, making it the 29th largest island in the United States. Wrangell is separated from the mainland by the narrow Blake Channel.

The Duncan Canal is a naturally occurring inland waterway in the Alexander Archipelago in Alaska, United States. It deeply penetrates Kupreanof Island, separating the Lindenberg Peninsula, on the southeast side of the island from the main island. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. It was named after the English missionary William Duncan.
Fort Stikine was a fur trade post and fortification in what is now the Alaska Panhandle, at the site of the present-day of Wrangell, Alaska. Originally built as the Redoubt San Dionisio or Redoubt Saint Dionysius in 1834, the site was transferred to the British-owned Hudson's Bay Company as part of a lease signed in the region in 1838, and renamed Fort Stikine when turned into a Hudson's Bay Company post in 1839. The post was closed and decommissioned by 1843 but the name remained for the large village of the Stikine people which had grown around it, becoming known as Shakesville in reference to its ruling Chief Shakes by the 1860s. With the Alaska Purchase of 1867, the fortification became occupied by the US Army and was renamed Fort Wrangel, a reference to Baron von Wrangel, who had been Governor of Russian America when the fort was founded. The site today is now part of the city of Wrangell.
The Stikine Strait is a strait in the Alexander Archipelago of Alaska, located between Zarembo Island to the west and Etolin and Woronkofski Islands just southwest of the City of Wrangell. The strait's name derives from that of the Stikine River, the outlet of which is just northeast of Wrangell. The strait is shown on an 1844 Russian chart, but the name was first published on Russian Admiralty charts in 1848 as Proliv Stakhinskiy or Stakhin Strait. Other spelling variants over time have been Frances Strait, Stachin Strait, Stachine Strait, Stackine Strait, Stahkeen Strait, Stahkin Strait, Stakeen Strait, Stakhinski Strait, Stickeen Strait, and Stikeen Strait
Cordova Bay is a bay in the Alexander Archipelago of southeast Alaska. It opens onto Dixon Entrance to the south, between Cape Muzon on Dall Island and Point Marsh. The name Puerto Cordova y Cordova was given by the Spanish explorer Lieutenant Don Jacinto Caamaño in 1792, in honor of Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova. The name was published by George Vancouver in 1798.
Woewodski Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of Southeast Alaska, United States. It is separated from Kupreanof Island to the west by Duncan Canal, and Mitkof Island to the east by the Wrangell Narrows. It is named after Captain Lieutenant Stepan Vasilivich Woewodski, who was chief director of the Russian American colonies from 1854 to 1859. The name first appears on a Russian Hydrographic Department chart of 1848 as "O(strov)va Voyevodskago". Earlier, in 1838, G. Lindenberg called part of the island "Medvezhiy". The first European to sight the island was James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition, in 1793. He circumnavigated it, proving its insular nature.

Ernest Sound is a strait in Southeast Alaska, U.S.A. It extends 48 kilometres (30 mi) southwest, from the mouth of Bradfield Canal to Clarence Strait, separating Wrangell and Etolin Islands from the mainland. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. Vancouver later named it "Prince Ernest's Sound", after Prince Ernest, Duke of Cumberland.
The Narrows is a channel in Southeast Alaska, U.S.A. It is the shortest and narrowest stretch of waterway separating Wrangell Island from the mainland, connecting Blake Channel and Eastern Passage. It was named in 1917 by the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition.
Eastern Passage is a channel in Southeast Alaska, United States. It extends southeast 29 kilometres (18 mi) from the mouth of the Stikine River to The Narrows, separating the northeastern half of Wrangell Island from the mainland. It was named in 1877 by William Healy Dall of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition.
References
- ↑ Vancouver, George, and John Vancouver (1801). A voyage of discovery to the North Pacific ocean, and round the world. London: J. Stockdale.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Woronkofski Island
- Woronkofski Island: Block 1029, Census Tract 3, Wrangell-Petersburg Census Area, Alaska United States Census Bureau
- Wrangell Community Database Online State of Alaska Commerce Department
56°23′49″N132°28′52″W / 56.39694°N 132.48111°W