
The Miami are a Native American nation originally speaking one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as north-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory. The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of self-identified descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition.

Brownstown Charter Township is a charter township in Wayne County in the U.S. state of Michigan. Its population was 33,194 at the 2020 census. Brownstown was established in 1827, a decade prior to Michigan's admission to the Union.

Trenton is a city in Wayne County, Michigan, United States. At the 2010 census, the city population was 18,853.

The Wyandot people are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of the present-day United States and Canada. Their Wyandot language belongs to the Iroquoian language family.
Essex County is a primarily rural county in Southwestern Ontario, Canada comprising seven municipalities: Amherstburg, Kingsville, Lakeshore, LaSalle, Leamington, Tecumseh and the administrative seat, Essex.

The Potawatomi, also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie, are a Native American people of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquian family. The Potawatomi call themselves Neshnabé, a cognate of the word Anishinaabe. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibwe and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother". Their people are referred to in this context as Bodéwadmi, a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples.

The Treaty of Greenville, also known to Americans as the Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., but formally titled A treaty of peace between the United States of America, and the tribes of Indians called the Wyandots, Delawares, Shawanees, Ottawas, Chippewas, Pattawatimas, Miamis, Eel Rivers, Weas, Kickapoos, Piankeshaws, and Kaskaskias was a 1795 treaty between the United States and indigenous nations of the Northwest Territory, including the Wyandot and Delaware peoples, that redefined the boundary between indigenous peoples' lands and territory for European American community settlement.

William Hull was an American military officer and politician. He fought in the American Revolutionary War and served as governor of the Michigan Territory from 1805 to 1813, gaining large land cessions from several surrounding Native Americans / Indian tribes under the Treaty of Detroit of 1807. Hull is most widely remembered, however, as the general in the first months of the War of 1812 (1812-1815), who surrendered Fort Detroit / Shelby to the British Army on August 16, 1812 following the Siege of Detroit. After the siege, he was paroled by the enemy and returned east, but court-martialed, convicted, and sentenced to death in a military court trial by the United States Army and the U.S. War Department, but later received a pardon from fourth President and military commander-in-chief James Madison, so his military and personal reputation somewhat recovered. He was assigned to several other commands in the next two years of the war, before the 1815 peace Treaty of Ghent and return to the pre-war status quo with the British,
The Odawa are an Indigenous American people who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, now in jurisdictions of the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Their territory long preceded the creation of the current border between the two countries in the 18th and 19th centuries.
The Council of Three Fires is a long-standing Anishinaabe alliance of the Ojibwe, Odawa, and Potawatomi North American Native tribes.

The Treaty of Saginaw, also known as the Treaty with the Chippewa, was made between Gen. Lewis Cass and Chief Mash Kee Yosh, Chief John Okemos, Chief Wasso and other Native American tribes of the Great Lakes region in what is now the United States, on September 24, 1819, proclaimed by the President of the United States on March 25, 1820, and placed in law as 7 Stat. 203.

The Wyandotte Nation is a federally recognized Native American tribe headquartered in northeastern Oklahoma. They are descendants of the Wendat Confederacy and Native Americans with territory near Georgian Bay and Lake Huron. Under pressure from Haudenosaunee and other tribes, then from European settlers and the United States government, the tribe gradually moved south and west to Michigan, Ohio, Kansas, and finally Oklahoma in the United States.

The Treaty of Fort Meigs, also called the Treaty of the Maumee Rapids, formally titled, "Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., 1817", was the most significant Indian treaty by the United States in Ohio since the Treaty of Greenville in 1795. It resulted in cession by bands of several tribes of nearly all their remaining Indian lands in northwestern Ohio. It was the largest wholesale purchase by the United States of Indian land in the Ohio area. It was also the penultimate one; a small area below the St. Mary's River and north of the Greenville Treaty Line was ceded in the Treaty of St. Mary's in 1818.

Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a French and later British fortification established in 1701 on the north side of the Detroit River by Antoine Laumet de Lamothe Cadillac. A settlement based on the fur trade, farming and missionary work slowly developed in the area. The fort was located in what is now downtown Detroit, northeast of the intersection of Washington Boulevard and West Jefferson Avenue.
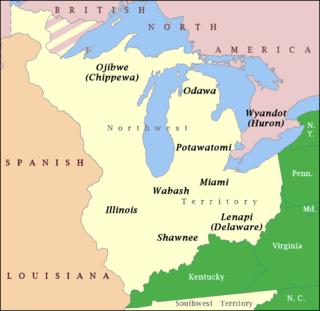
The Northwestern Confederacy, or Northwestern Indian Confederacy, was a loose confederacy of Native Americans in the Great Lakes region of the United States created after the American Revolutionary War. Formally, the confederacy referred to itself as the United Indian Nations, at their Confederate Council. It was known infrequently as the Miami Confederacy since many contemporaneous federal officials overestimated the influence and numerical strength of the Miami tribes based on the size of their principal city, Kekionga.
Roundhead, also known as Bark Carrier, Round Head, Stayeghtha, and Stiahta, was an American Indian chief of the Wyandot tribe. He was a strong member of Tecumseh's confederacy against the United States during the War of 1812. He died of unknown natural causes about a month or two before Tecumseh was killed at the Battle of the Thames.
The Indian barrier state was a British proposal to establish a Native American buffer state in the portion of the Great Lakes region of North America. It was never created. The idea was to create it west of the Appalachian Mountains, bounded by the Ohio and Mississippi rivers and the Great Lakes. The concept of establishing such a state, first conceived in the late 1750s, was part of a long-term plan to reconcile the Indian tribes to British presence and diminish hostilities between the tribes and the British Army following its victory in the French and Indian War in 1763.
Jacob Smith, was a fur trader in the Michigan Territory, the founder of Flint, Michigan, and an American spy best known for developing close relations with many Native American tribes in the Michigan Territory and brokering significant land treaties on behalf of the United States government.














