Related Research Articles

Lupercalia was an ancient, possibly pre-Roman pastoral annual festival, observed in the city of Rome from the 13th to the 15th of February to avert evil spirits and purify the city, releasing health and fertility. Lupercalia was also called dies Februatus, after the instruments of purification called februa, which gave February (Februarius) its name.

Ptolemy IV Philopator, son of Ptolemy III and Berenice II, was the fourth Pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 221 to 204 BC.
The Battle of Cannae was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginian army, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history.

The Siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War between the Punic city of Carthage in Africa and the Roman Republic. It was a siege operation, starting sometime in 149 or 148 BC, and ending in spring 146 BC with the sack and complete destruction of the city of Carthage.

Nabis was ruler of Sparta from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First and Second Macedonian Wars and the eponymous "War against Nabis", i.e. against him. After taking the throne by executing two claimants, he began rebuilding Sparta's power. During the Second Macedonian War, he sided with King Philip V of Macedon and in return he received the city of Argos. However, when the war began to turn against the Macedonians, he defected to Rome. After the war, the Romans, urged by the Achaean League, attacked Nabis and defeated him. He then was assassinated in 192 BC by the Aetolian League and was Sparta's last independent ruler. He represented the last phase of Sparta's reformist period.

Ohrid is a city in North Macedonia and the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the eighth-largest city in the country, with over 42,000 inhabitants as of 2002. Ohrid once had 365 churches, one for each day of the year, and has been referred to as a "Jerusalem of the Balkans". The city is rich in picturesque houses and monuments, and tourism is predominant. It is located southwest of Skopje, west of Resen and Bitola. In 1979 and in 1980 respectively, Ohrid and Lake Ohrid were accepted as Cultural and Natural World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. Ohrid is one of only 28 sites that are part of UNESCO's World Heritage that are Cultural as well as Natural sites.
In ancient Roman religion, the Armilustrium was a festival in honor of Mars, the god of war, celebrated on October 19. On this day the weapons of the soldiers were ritually purified and stored for winter. The army would be assembled and reviewed in the Circus Maximus, garlanded with flowers. The trumpets (tubae) would be played as part of the purification rites. The Romans gathered with their arms and armour on the Aventine Hill, and held a procession with torches and sacrificial animals. The dancing priests of Mars known as the Salii may also have taken part in the ceremony.
The Illyrian Wars were a set of wars fought in the period 229–168 BC between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the First Illyrian War, which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the First Punic War at a time when Ardiaei power increased under queen Teuta. Attacks on trading vessels of Rome's Italic allies by Illyrian pirates and the death of a Roman envoy named Coruncanius on Teuta's orders, prompted the Roman senate to dispatch a Roman army under the command of the consuls Lucius Postumius Albinus and Gnaeus Fulvius Centumalus. Rome expelled Illyrian garrisons from a number of Greek cities including Epidamnus, Apollonia, Corcyra, Pharos and established a protectorate over these Greek towns. The Romans also set up Demetrius of Pharos as a power in Illyria to counterbalance the power of Teuta.
Demetrius of Pharos was a ruler of Pharos involved in the First Illyrian War, after which he ruled a portion of the Illyrian Adriatic coast on behalf of the Romans, as a client king.
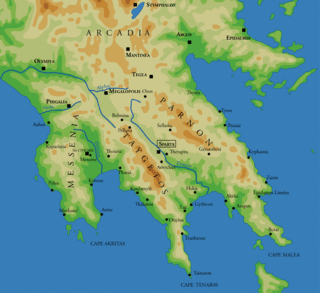
The Battle of Sellasia took place during the summer of 222 BC between Macedon and the Achaean League, led by Antigonus III Doson, and Sparta under the command of King Cleomenes III. The battle was fought at Sellasia on the northern frontier of Laconia and ended in a Macedonian-Achaean victory.

The Macedonians were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Axios in the northeastern part of mainland Greece. Essentially an ancient Greek people, they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracian and Illyrian. They spoke Ancient Macedonian, a language closely related to Ancient Greek or a Doric Greek dialect, although the prestige language of the region was at first Attic and then Koine Greek. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of other Greeks, following the main deities of the Greek pantheon, although the Macedonians continued Archaic burial practices that had ceased in other parts of Greece after the 6th century BC. Aside from the monarchy, the core of Macedonian society was its nobility. Similar to the aristocracy of neighboring Thessaly, their wealth was largely built on herding horses and cattle.

Scerdilaidas or Skerdilaid was an Illyrian king of the Ardiaean Kingdom. Before taking the throne Scerdilaidas was commander of the Illyrian armies and played a major role in the Illyrian Wars against the Romans.
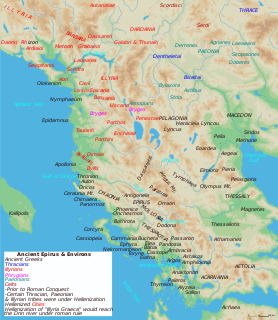
Antigonea, also transliterated as Antigonia and Antigoneia, was an ancient Greek city in Chaonia, Epirus, and the chief inland city of the ancient Chaonians. It was founded in the 3rd century BC by Pyrrhus of Epirus, who named it after one of his wives, Antigone, daughter of Berenice I and step-daughter of Ptolemy I of Egypt.
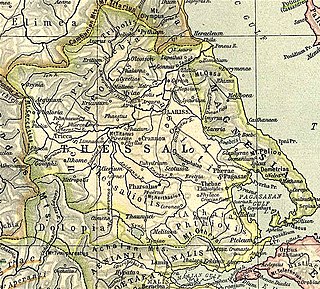
Pythion or Pythium, also Pythoion (Πύθοιον) was a city and polis (city-state) of Perrhaebia in ancient Thessaly, situated at the foot of Mount Olympus, and forming a Tripolis with the two neighbouring towns of Azorus and Doliche. Pythion derived its name from a temple of Apollo Pythius situated on one of the summits of Olympus, as we learn from an epigram of Xeinagoras, a Greek mathematician, who measured the height of Olympus from these parts. Games were also celebrated here in honour of Apollo.

Attalus I, surnamed Soter ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis, first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the first cousin once removed and the adoptive son of Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king in 238 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis.
The Macedonian–Carthaginian Treaty was an anti-Roman treaty between Philip V of Macedon and Hannibal, leader of the Carthaginians, which was drawn up after the Battle of Cannae when Hannibal seemed poised to conquer Rome. Philip V, who feared Roman expansion, wanted to ride on the coat tails of the victor in the Second Punic War. The discovery of this treaty inevitably led to the outbreak of the First Macedonian War between Rome and its Greek allies against Macedonia.

The Cleomenean War was fought by Sparta and its ally, Elis, against the Achaean League and Macedon. The war ended in a Macedonian and Achaean victory.
Pamboeotia was a major festive panegyris of all the Boeotians, celebrated probably annually. The grammarians compare the Pamboeotia with the Panathenaea of the Atticans, and the Panionia of the Ionians. Though probably quite older than this, even primitive, the festival is celebrated with the name "Pamboeotia" only starting in the 3rd century BC. The festival was celebrated in the tenth month of the Boeotian calendar, Pamboiotos, at a temple of Athena Itonia in the neighborhood of Coronea.

The Antigonid Macedonian army was the army that evolved from the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia in the period when it was ruled by the Antigonid dynasty from 276 BC to 168 BC. It was seen as one of the principal Hellenistic fighting forces until its ultimate defeat at Roman hands at the Battle of Pydna in 168 BC. However, there was a brief resurgence in 150-148 during the revolt of Andriscus, a supposed heir to Perseus.
Pellene was a city and polis (city-state) of ancient Achaea, the most easterly of the twelve Achaean cities. Its territory bordered upon that of Sicyon on the east and upon that of Aegeira on the west. Pellene was situated 60 stadia from the sea, upon a strongly fortified hill, the summit of which rose into an inaccessible peak, dividing the city into two parts. Its port was at Aristonautae.
References
- ↑
- Homo Necans: The Anthropology of Ancient Greek Sacrificial Ritual and Myth Page 54 ISBN 0-520-05875-5 -Pausanias 3.14.8 3.20.8