
Xerox Phaser is the brand name for a line of color and monochrome printers produced and sold by Xerox. Some Phaser printers use Xerox Solid Ink. Phaser printers were originally manufactured and marketed by Tektronix, of Wilsonville, Oregon.

Xerox Phaser is the brand name for a line of color and monochrome printers produced and sold by Xerox. Some Phaser printers use Xerox Solid Ink. Phaser printers were originally manufactured and marketed by Tektronix, of Wilsonville, Oregon.
Xerox acquired the Tektronix Color Printing and Imaging Division, including the Phaser brand, in 2000. [1] The Phaser brand has become a key component of Xerox's office product portfolio, and the company continues to expand the product line.
One important aspect of the acquisition of the Tektronix divisions is that Xerox kept Tektronix staff and support services, as Tektronix was known for high-performance and high-quality printers. [2]
The Xerox Phaser 7700 Series of color laser printers use the VxWorks Operating System on its 20GB PATA IDE Hard Drive.
The 7700 Series is a wide format duplex-capable laser printer capable of printing up to 12x18 page sizes. The average 8.5x11 Letter size speed is 23 pages per minute. ()
The Xerox Phaser 6100 is a low-price office color printer. The New York Times reported in 2004 that "revenue from color machines .. represents about 25 percent" of the company's revenue. [3]
The Xerox Phaser 2135 was a 21 page-per-minute color printer that printed at 1200 dots-per-inch. [4] Other models were the 7500N, the 6700 and the 3600.

In computing, a printer is a peripheral machine which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Different types of printers include 3D printers, inkjet printers, laser printers, and thermal printers.

Xerox Holdings Corporation is an American corporation that sells print and digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut, though it is incorporated in New York with its largest population of employees based around Rochester, New York, the area in which the company was founded. The company purchased Affiliated Computer Services for $6.4 billion in early 2010. As a large developed company, it is consistently placed in the list of Fortune 500 companies.

Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylinder called a "drum" to define a differentially charged image. The drum then selectively collects electrically charged powdered ink (toner), and transfers the image to paper, which is then heated to permanently fuse the text, imagery, or both, to the paper. As with digital photocopiers, laser printers employ a xerographic printing process. Laser printing differs from traditional xerography as implemented in analog photocopiers in that in the latter, the image is formed by reflecting light off an existing document onto the exposed drum.

Daisy wheel printing is an impact printing technology invented in 1970 by Andrew Gabor at Diablo Data Systems. It uses interchangeable pre-formed type elements, each with typically 96 glyphs, to generate high-quality output comparable to premium typewriters such as the IBM Selectric, but two to three times faster. Daisy wheel printing was used in electronic typewriters, word processors and computers from 1972. The daisy wheel is so named because of its resemblance to the daisy flower.

An MFP, multi-functional, all-in-one (AIO), or multi-function device (MFD), is an office machine which incorporates the functionality of multiple devices in one, so as to have a smaller footprint in a home or small business setting, or to provide centralized document management/distribution/production in a large-office setting. A typical MFP may act as a combination of some or all of the following devices: email, fax, photocopier, printer, scanner.
Centronics Data Computer Corporation was an American manufacturer of computer printers, now remembered primarily for the parallel interface that bears its name, the Centronics connector.

Konica Minolta, Inc. is a Japanese multinational technology company headquartered in Marunouchi, Chiyoda, Tokyo, with offices in 49 countries worldwide. The company manufactures business and industrial imaging products, including copiers, laser printers, multi-functional peripherals (MFPs) and digital print systems for the production printing market. Konica Minolta's Managed Print Service (MPS) is called Optimised Print Services. The company also makes optical devices, including lenses and LCD film; medical and graphic imaging products, such as X-ray image processing systems, colour proofing systems, and X-ray film; photometers, 3-D digitizers, and other sensing products; and textile printers. It once had camera and photo operations inherited from Konica and Minolta but they were sold in 2006 to Sony, with Sony's Alpha series being the successor SLR division brand.
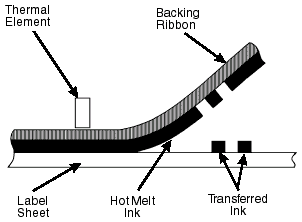
Thermal-transfer printing is a digital printing method in which material is applied to paper by melting a coating of ribbon so that it stays glued to the material on which the print is applied. It contrasts with direct thermal printing, where no ribbon is present in the process.

LaserJet as a brand name identifies the line of laser printers marketed by the American computer company Hewlett-Packard (HP). The HP LaserJet was the world's first desktop laser printer. Canon supplies both mechanisms and cartridges for most HP laser printers; some larger A3 models use Samsung print engines.
Variable Data Intelligent Postscript Printware is an open language from Xerox that enables highest-performance output of variable-data PostScript documents. It is used by the FreeFlow VI Suite (VIPP) front end.

Solid ink is a type of ink used in printing. Solid ink is a waxy resin-based polymer that must be melted prior to usage unlike conventional liquid inks. The technology is used most in graphics and large format printing environments where color vividness and cost efficiency are important.
DocuTech is the name given to a line of electronic production-publishing systems produced by Xerox Corporation. It allowed paper documents to be scanned, electronically edited, and then printed on demand. DocuTech systems were the last known to use the XNS protocol for networking.
The Tektronix Phaser 740 was a series of color laser printers sold by Tektronix's printer division, now a part of Xerox. The Phaser 740 is notable for being the industry's first true 1200×1200 dpi color laser printer. The printer was available in several different configurations, from the 740L to the fully tricked out 740 Extended. The "plus" feature set was required for 1200×1200 color printing. Standard features included 10BASE-T Ethernet, LPT connectivity, SCSI connectivity, an expansion port for other networking options, 133 MHz PowerPC CPU, and PostScript. Network protocols included Telnet, FTP, AppSocket, IPP, HTTP, and AppleTalk. One upgraded the lowest model to the Extended functionality by adding components. A notable feature of this printer is its ability to accept PDF files directly, through FTP or Telnet. The onboard computer would then process the PDF to PS and print it. Phaser 740 series printers required little maintenance compared to other printers of the time. The only consumables were toner, fuser, imaging drum, and transfer roller.

A photocopier is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called xerography, a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying.
Dataproducts Corporation was an early manufacturer of computer peripheral equipment.

The IBM 3800 is a discontinued continuous forms laser printer designed and manufactured by IBM. It is significant as a product because it was both the first laser printer manufactured by IBM, and the first commercially available laser printer.

HP Inc. is an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California, that develops personal computers (PCs), printers and related supplies, as well as 3D printing solutions.
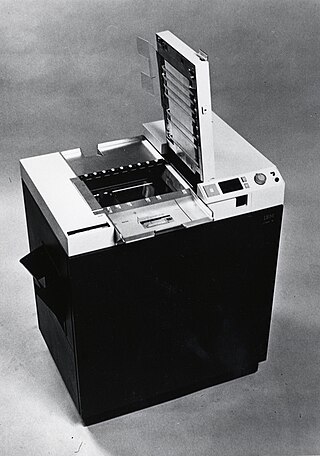
IBM Office Products Division (OPD) manufactured and sold copier equipment and supplies from 1970 till IBM withdrew from the copier market in 1988. IBM's decision to compete in this market resulted in the first commercial use of an organic photoconductor now widely used in most photocopiers. It is often held up as an example of a corporate u-turn, where a company rejects a technology and then adopts it. It showed that despite the size of IBM's sales and engineering organisations, this did not guarantee success in every market it chose to compete in. The development effort that resulted in the IBM Copier helped in the development of IBMs first laser printer, the IBM 3800.`

The Honeywell Page Printing System (PPS) announced in 1974, is notable because it was the first commercially successful high speed non-impact printer. It could produce output at up to 18,000 lines per minute, where the earlier Xerox 1200 ran at 4000 lines per minute and the contemporary IBM 3211, ran at 2000 lines per minute. Most printer history has focused on the later IBM 3800 and the Xerox 9700.
The Xerox 2700 is a discontinued monochrome laser printer from Xerox Corporation. The 2700 was announced in March, 1982, and can print up to 12 pages per minute (PPM), one-sided, on standard A4 or Letter cut-sheet paper. It occupies 5 square feet (0.46 m2) of floor space, and cost $18,995. The 2700 is rated for a print volume of 15,000 pages per month, although some users got up to 100,000 pages.