
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) coordinates standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. ITU-T is one of the three Sectors of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
3G is the third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology. It is the upgrade for 2.5G GPRS and 2.75G EDGE networks, for faster data transfer. This is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications use services and networks that comply with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G finds application in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV.
4G is the fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology, succeeding 3G, and preceding 5G. A 4G system must provide capabilities defined by ITU in IMT Advanced. Potential and current applications include amended mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and 3D television.
Automatically Switched Optical Network (ASON) is a concept for the evolution of transport networks which allows for dynamic policy-driven control of an optical or SDH network based on signaling between a user and components of the network. Its aim is to automate the resource and connection management within the network. The IETF defines ASON as an alternative/supplement to NMS based connection management.
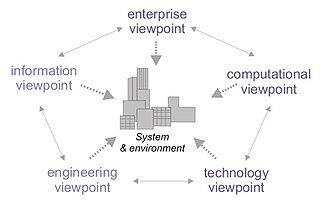
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.

LTE Advanced is a mobile communication standard and a major enhancement of the Long Term Evolution (LTE) standard. It was formally submitted as a candidate 4G to ITU-T in late 2009 as meeting the requirements of the IMT-Advanced standard, and was standardized by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in March 2011 as 3GPP Release 10.
International Mobile Telecommunications-Advanced are the requirements issued by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 2008 for what is marketed as 4G mobile phone and Internet access service.

ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2020 or BT.2020, defines various aspects of ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) with standard dynamic range (SDR) and wide color gamut (WCG), including picture resolutions, frame rates with progressive scan, bit depths, color primaries, RGB and luma-chroma color representations, chroma subsamplings, and an opto-electronic transfer function. The first version of Rec. 2020 was posted on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) website on August 23, 2012, and two further editions have been published since then. It is expanded in several ways by Rec. 2100.
Long Term Evolution (LTE) telecommunications networks use several frequency bands with associated bandwidths.
International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 are the requirements issued by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 2015 for 5G networks, devices and services.
PyTorch is an open source machine learning library based on the Torch library, used for applications such as computer vision and natural language processing, primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab (FAIR). It is free and open-source software released under the Modified BSD license. Although the Python interface is more polished and the primary focus of development, PyTorch also has a C++ interface.

Automated machine learning (AutoML) is the process of automating the tasks of applying machine learning to real-world problems. AutoML covers the complete pipeline from the raw dataset to the deployable machine learning model. AutoML was proposed as an artificial intelligence-based solution to the ever-growing challenge of applying machine learning. The high degree of automation in AutoML allows non-experts to make use of machine learning models and techniques without requiring them to become experts in machine learning. Automating the process of applying machine learning end-to-end additionally offers the advantages of producing simpler solutions, faster creation of those solutions, and models that often outperform hand-designed models. AutoML has been used to compare the relative importance of each factor in a prediction model.

ML.NET is a free software machine learning library for the C# and F# programming languages. It also supports Python models when used together with NimbusML. The preview release of ML.NET included transforms for feature engineering like n-gram creation, and learners to handle binary classification, multi-class classification, and regression tasks. Additional ML tasks like anomaly detection and recommendation systems have since been added, and other approaches like deep learning will be included in future versions.

Chaesub Lee PhD is the Director of ITU Telecommunication Standardization Bureau, the permanent secretariat of the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and as such, an Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations.
MLOps is the process of taking an experimental Machine Learning model into a production system. The word is a compound of “Machine Learning” and the continuous development practice of DevOps in the software field. Machine Learning models are tested and developed in isolated experimental systems. When an algorithm is ready to be launched, MLOps is practiced between Data Scientists, DevOps, and Machine Learning engineers to transition the algorithm to production systems. Similar to DevOps or DataOps approaches, MLOps seeks to increase automation and improve the quality of production models, while also focusing on business and regulatory requirements. While MLOps started as a set of best practices, it is slowly evolving into an independent approach to ML lifecycle management. MLOps applies to the entire lifecycle - from integrating with model generation, orchestration, and deployment, to health, diagnostics, governance, and business metrics.
Amazon SageMaker is a cloud machine-learning platform that was launched in November 2017. SageMaker enables developers to create, train, and deploy machine-learning (ML) models in the cloud. SageMaker also enables developers to deploy ML models on embedded systems and edge-devices.

Y.3172 is an ITU-T Recommendation specifying an architecture for machine learning in future networks including 5G (IMT-2020). The architecture describes a machine learning pipeline in the context of telecommunication networks that involves the training of machine learning models, and also the deployment using methods such as containers and orchestration.

The ITU-WHO Focus Group on Artificial Intelligence for Health is an inter-agency collaboration between the World Health Organization and the ITU, which created a benchmarking framework to assess the accuracy of AI in health.

Y.3173 is an ITU-T Recommendation building upon Y.3172 specifying a framework for evaluation intelligence levels of future networks such as 5G (IMT-2020). This includes:

Y.3174 is an ITU-T Recommendation, building upon Y.3172 and Y.3173, specifying a framework for data handling for machine learning in future networks such as 5G (IMT-2020).









