Related Research Articles
Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya, commonly known as Marwan I, was the fourth Umayyad caliph, ruling for less than a year in 684–685. He founded the Marwanid ruling house of the Umayyad dynasty, which replaced the Sufyanid house after its collapse in the Second Muslim Civil War and remained in power until 750.

The Himyarite Kingdom, or Himyar, historically referred to as the Homerite Kingdom by the Greeks and the Romans, was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According to classical sources, their capital was the ancient city of Zafar, relatively near the modern-day city of Sana'a. Himyarite power eventually shifted to Sana'a as the population increased in the fifth century. After the establishment of their kingdom, it was ruled by kings from dhū-Raydān tribe. The kingdom was named Raydān.

ʿUbayd Allāh ibn Ziyād was the Umayyad governor of Basra, Kufa and Khurasan during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I and Yazid I, and the leading general of the Umayyad army under caliphs Marwan I and Abd al-Malik. Ubayd Allah is primarily remembered for his role in the killings of members of Ali ibn Abi Talib's family including Husayn ibn Ali, and he has become infamous in Muslim tradition.
The Banu Kalb was an Arab tribe which mainly dwelt in the desert between northwestern Arabia and central Syria. The Kalb was involved in the tribal politics of the eastern frontiers of the Byzantine Empire, possibly as early as the 4th century. By the 6th century, the Kalb had largely adopted Christianity and came under the authority of the Ghassanids, the chief Arab federates of the Byzantines.

The Banu Taghlib, also known as Taghlib ibn Wa'il, were an Arab tribe that originated in Najd, but later migrated and inhabited the Jazira from the late 6th century onward. Their parent tribe was the Rabi'a, and they thus traced their descent to the Adnanites. The Taghlib were among the most powerful and cohesive nomadic tribes of the pre-Islamic era and were known for their bitter wars with their kinsmen from the Banu Bakr, as well as their struggles with the Lakhmid kings of al-Hira in Iraq. The tribe embraced Miaphysite Christianity and remained largely Christian long after the advent of Islam in the mid-7th century. After early opposition to the Muslims, the Taghlib eventually secured for themselves an important place in Umayyad politics. They allied with the Umayyads and engaged in numerous battles with the rebellious Qaysi tribes during the Qays–Yaman feuding in the late 7th century.

The Judham was an Arab tribe that inhabited the southern Levant and northwestern Arabia during the Byzantine and early Islamic eras. Under the Byzantines, the tribe was nominally Christian and fought against the Muslim army between 629 and 636, until the Byzantines and their Arab allies were defeated at the Battle of Yarmouk. Afterward, the Judham converted to Islam and became the largest tribal faction of Jund Filastin.
Qays ʿAylān, often referred to simply as Qays were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe does not appear to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic era (pre-630). However, by the early Umayyad period (661-750), its constituent tribes consolidated into one of the main tribo-political factions of the caliphate.
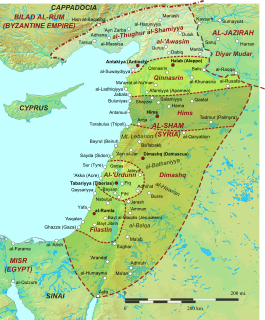
Jund Ḥimṣ was one of the military districts of the caliphal province of Syria.
The Quda'a were a confederation of Arab tribes, including the powerful Kalb and Tanukh, mainly concentrated throughout Syria and northwestern Arabia, from at least the 4th century CE, during Byzantine rule, through the 12th century, during the early Islamic era. Under the first caliphs of the Syria-based Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), the Quda'a occupied a privileged position in the administration and military. During the Second Muslim Civil War (683–692) they allied with South Arabian and other tribes in Syria as the Yaman faction in opposition to their rivals, the Qays confederation, in what became a rivalry for power and influence which continued well after the Umayyad era. In forging this alliance, the Quda'a's leaders genealogically realigned their descent to the South Arabian Himyar, discarding their north Arabian ancestor, Ma'add, a move which elicited centuries-long debate and controversy among early Islamic scholars.
The Qays–Yaman rivalry refers to the historical rivalries and feuds between the northern Arabian Qays tribes and the southern Arabian Yaman tribes. The conflict emerged among the tribes within the Umayyad Caliphate's army and administration in the 7th and 8th centuries. Membership in either faction was rooted in real or perceived genealogical origins of the tribes, which divided them into south Arabian descendants of Qahtan (Yaman) or north Arabian descendants of Adnan (Qays).
The Battle of Marj Rahit was one of the early battles of the Second Fitna. It was fought on 18 August 684 between the Kalb-dominated armies of the Yaman tribal confederation, supporting the Umayyads under Caliph Marwan I, and the Qays under al-Dahhak ibn Qays al-Fihri, who supported the Mecca-based Abdallah ibn al-Zubayr; the latter had proclaimed himself Caliph. The Kalbi victory consolidated the position of the Umayyads over Bilad al-Sham, paving the way for their eventual victory in the war against Ibn al-Zubayr. However, it also left a bitter legacy of division and rivalry between the Qays and the Yaman, which would be a constant source of strife and instability for the remainder of the Umayyad Caliphate.
Umar ibn Hubayra al-Fazari was a prominent Umayyad general and governor of Iraq, who played an important role in the Qays–Yaman conflict of this period.
Abu al-Hudhayl Zufar ibn al-Harith al-Kilabi was a Muslim commander, a chieftain of the Arab tribe of Banu Amir, and the preeminent leader of the Qays tribal–political faction in the late 7th century. During the First Muslim Civil War he commanded his tribe in A'isha's army against Caliph Ali's forces at the Battle of the Camel near Basra in 656. The following year, he relocated from Iraq to the Jazira and fought under Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan, future founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, against Ali at the Battle of Siffin. During the Second Muslim Civil War he served Mu'awiya's son, Caliph Yazid I, leading the troops of Jund Qinnasrin against anti-Umayyad rebels in the 683 Battle of al-Harra.

Bāhila was an Arab tribe based in Najd. Part of the tribe was settled and part of it was semi-nomadic. The Bahila was first mentioned during the early years of Islam, in the mid-7th century. During that time, many Bahila tribesmen migrated to Syria and Basra. Many of those who went to Syria later moved to Khurasan as part of the Umayyad garrison there. As a sub-tribe of Qays, they fought alongside the Qaysi coalition against the Yamani tribes during the Umayyad era. The scholar al-Asma'i and the general Qutayba ibn Muslim both belonged to the tribe. The Bahila were last mentioned in the 10th century.
The Battle of Khazir took place in August 686 near the Khazir River in Mosul's eastern environs, in modern-day Iraq. The battle occurred during the Second Muslim Civil War and was part of the larger struggle for control of Iraq between the Syria-based Umayyad Caliphate, the Kufa-based pro-Alid forces of Mukhtar al-Thaqafi, and the Mecca-based caliphate of Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. It ended in a rout for the Umayyads and the expansion of Mukhtar's rule into the region of Mosul.

The Banu Ghani was an Arab tribe that inhabited the area between Bisha and Diriyah in pre-Islamic Arabia and parts of which migrated to Syria during the Muslim conquest of that region.
Natil ibn Qays ibn Zayd al-Judhami was the chieftain of the Banu Judham tribe and a prominent tribal leader in Palestine during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I and Yazid I. In 684, he revolted against the Umayyads, took control of Palestine and gave his allegiance to Caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. He joined the latter in Mecca after pro-Zubayrid forces were routed at the Battle of Marj Rahit. He may have renewed his rebellion in Palestine in 685/86 and was slain during the hostilities.
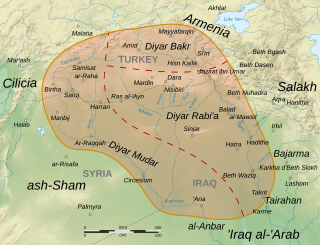
Al-Jazira, also known as Jazirat Aqur or Iqlim Aqur, was a province of the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates, spanning at minimum most of Upper Mesopotamia, divided between the districts of Diyar Bakr, Diyar Rabi'a and Diyar Mudar, and at times including Mosul, Arminiya and Adharbayjan as sub-provinces. Following its conquest by the Muslim Arabs in 639/40, it became an administrative unit attached to the larger district of Jund Hims. It was separated from Hims during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I or Yazid I and came under the jurisdiction of Jund Qinnasrin. It was made its own province in 692 by Caliph Abd al-Malik. After 702, it frequently came to span the key districts of Arminiya and Adharbayjan along the Caliphate's northern frontier, making it a super-province. The predominance of Arabs from the Qays/Mudar and Rabi'a groups made it a major recruitment pool of tribesmen for the Umayyad armies and the troops of the Jazira played a key military role under the Umayyad caliphs in the 8th century, peaking under the last Umayyad caliph, Marwan II, until the toppling of the Umayyads by the Abbasids in 750.
Muhammad ibn Salih ibn Bayhas al-Kilabi, better known as Ibn Bayhas, was the Abbasid governor of Damascus in September 813–824/825 and a prominent chief of the Qays tribes in the environs of Damascus against their Yamani rivals. Under his leadership, a succession of Umayyad claimants to the caliphate, Abu al-Umaytir al-Sufyani, Maslama ibn Ya'qub al-Marwani and Sa'id ibn Khalid al-Uthmani, were defeated, marking an end to serious challenges of Abbasid authority in Syria by remnants of the Umayyad dynasty, which had been toppled by the Abbasids in 750. Although a loyalist of Caliph al-Ma'mun, he was viewed as a rival by al-Ma'mun's viceroy of Syria, Abd Allah ibn Tahir ibn al-Husayn, who deposed him around 824/825. Two years later, he was brought to Iraq, where he eventually died.
Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Khālid ibn Yazīd ibn Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān, better known as Abū al-ʿUmayṭir al-Sufyānī, was an Umayyad rebel against Abbasid rule in Syria during the Fourth Muslim Civil War and a self-proclaimed messiah who, in 811, attempted to restore the Umayyad Caliphate, which had been toppled by the Abbasids in 750. He expelled the Abbasid governor of Syria, Sulayman ibn Abi Ja'far, from Damascus and set up a quasi-administration in the city. His claim to the caliphate soon after gained recognition in different parts of the Damascus, Homs and Qinnasrin districts, including the port of Sidon and city of Homs.
References
- ↑ Kennedy 2004 , p. 86: As yet the feud between the Qays and Yaman which was to plague Syria for so many centuries was not a major problem.; Nicholson 2018 , p. 1600
- 1 2 Kennedy 2004, p. 92.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Nicholson 2018, p. 1600.
- ↑ Kennedy 2004 , p. 92: It was also a division arising from the Islamic conquests. Some Yamani tribes like the Kalb, Tanukh, Judham Taghlib had been in Syria before the coming of Islam, while the majority of Qaysis like the Sulaym, Kilab and ‘Uqayl were newly arrived from the Arabian peninsula, many of them brought to the Jazira by Mu‘awiya in ‘Uthman’s reign.
- ↑ Rihan 2014, p. 104.