
The Technion – Israel Institute of Technology is a public research university located in Haifa, Israel. Established in 1912 by Jews under the dominion of the Ottoman Empire, the Technion is the oldest university in the country.
Collaborative intelligence characterizes multi-agent, distributed systems where each agent, human or machine, is autonomously contributing to a problem solving network. Collaborative autonomy of organisms in their ecosystems makes evolution possible. Natural ecosystems, where each organism's unique signature is derived from its genetics, circumstances, behavior and position in its ecosystem, offer principles for design of next generation social networks to support collaborative intelligence, crowdsourcing individual expertise, preferences, and unique contributions in a problem solving process.

Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and analytic approaches like social network analysis, computational sociology develops and tests theories of complex social processes through bottom-up modeling of social interactions.
Predictive learning is a machine learning technique where an artificial intelligence model is fed new data to develop an understanding of its environment, capabilities, and limitations. The fields of neuroscience, business, robotics, computer vision, and other fields employ this technique extensively. This concept was developed and expanded by French computer scientist Yann LeCun in 1988 during his career at Bell Labs, where he trained models to detect handwriting so that financial companies could automate check processing.

Intelligence amplification (IA) refers to the effective use of information technology in augmenting human intelligence. The idea was first proposed in the 1950s and 1960s by cybernetics and early computer pioneers.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence:

Alex Paul "Sandy" Pentland is an American computer scientist, HAI Fellow at Stanford, Toshiba Professor at MIT, and serial entrepreneur.
Artificial intelligence marketing (AIM) is a form of marketing that uses artificial intelligence concepts and models such as machine learning, Natural process Languages, and Bayesian Networks to achieve marketing goals. The main difference between AIM and traditional forms of marketing resides in the reasoning, which is performed by a computer algorithm rather than a human.
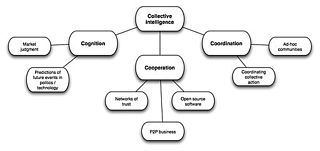
Collective intelligence (CI) is shared or group intelligence (GI) that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making. The term appears in sociobiology, political science and in context of mass peer review and crowdsourcing applications. It may involve consensus, social capital and formalisms such as voting systems, social media and other means of quantifying mass activity. Collective IQ is a measure of collective intelligence, although it is often used interchangeably with the term collective intelligence. Collective intelligence has also been attributed to bacteria and animals.
Social trading is a form of investing that allows investors to observe the trading behavior of their peers and expert traders. The primary objective is to follow their investment strategies using copy trading or mirror trading. Social trading requires little or no knowledge about financial markets.
T-Labs, formerly known as "Telekom Innovation Laboratories", is the R&D unit of Deutsche Telekom. T-Labs current research areas are: Future Networks, Spatial Computing and Decentralized Systems.
Copy trading enables individuals in the financial markets to automatically copy positions opened and managed by other selected individuals.
Humanyze, founded as Sociometric Solutions in 2010 in Boston, Massachusetts, is a people analytics software provider. Humanyze was founded by MIT doctoral students Ben Waber, Daniel Olguin, Taemie Kim, Tuomas Jaanu, and MIT Professor Alex Pentland. Humanyze's people analytics platform is based on research from the MIT Media Lab people analytics and utilizes Organizational Network Analysis to measure corporate communication data, identifying patterns in how companies operate.

Mustafa Suleyman is a British artificial intelligence (AI) entrepreneur. He is the CEO of Microsoft AI, and the co-founder and former head of applied AI at DeepMind, an AI company acquired by Google. After leaving DeepMind, he co-founded Inflection AI, a machine learning and generative AI company, in 2022.

Michael Elad is an Israeli computer scientist who is a professor of Computer Science at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology. His work includes contributions in the fields of sparse representations and generative AI, and deployment of these ideas to algorithms and applications in signal processing, image processing and machine learning.

Yuval Elovici is a computer scientist. He is a professor in the Department of Software and Information Systems Engineering at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU), where he is the incumbent of the Davide and Irene Sala Chair in Homeland Security Research. He is the director of the Cyber Security Research Center at BGU and the founder and director of the Telekom Innovation Laboratories at Ben-Gurion University. In addition to his roles at BGU, he also serves as the lab director of Singapore University of Technology and Design’s (SUTD) ST Electronics-SUTD Cyber Security Laboratory, as well as the research director of iTrust. In 2014 he co-founded Morphisec, a start-up company, that develops cyber security mechanisms related to moving target defense.

Doron Aurbach is an Israeli electrochemist, materials and surface scientist.

Louis Barry Rosenberg is an American engineer, researcher, inventor, and entrepreneur. He researches augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. He was the Cotchett Endowed Professor of Educational Technology at the California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo. He founded the Immersion Corporation and Unanimous A.I., and he wrote the screenplay for the 2009 romantic comedy film, Lab Rats.

Lex Fridman is a Russian-American computer scientist and podcaster. Since 2018 he has hosted the Lex Fridman Podcast, where he interviews notable figures from various fields such as science, technology, sports, and politics.











