Related Research Articles

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
Liver tumors are abnormal growth of liver cells on or in the liver. Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. Liver tumors can be classified as benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths. They may be discovered on medical imaging, and the diagnosis is often confirmed with liver biopsy. Signs and symptoms of liver masses vary from being asymptomatic to patients presenting with an abdominal mass, hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, jaundice, or some other liver dysfunction. Treatment varies and is highly specific to the type of liver tumor.
This is a list of terms related to oncology. The original source for this list was the US National Cancer Institute's public domain Dictionary of Cancer Terms.
Fluorouracil, sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. As a cream it is used for actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and skin warts.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a minimally invasive procedure performed in interventional radiology to restrict a tumor's blood supply. Small embolic particles coated with chemotherapeutic drugs are injected selectively through a catheter into an artery directly supplying the tumor. These particles both block the blood supply and induce cytotoxicity, attacking the tumor in several ways.

Floxuridine is an oncology drug that belongs to the class known as antimetabolites. Specifically, floxuridine is a pyrimidine analog, classified as a deoxyuridine. The drug is usually administered via an artery, and most often used in the treatment of colorectal cancer. The quality of life and survival rates of individuals that receive continuous hepatic artery infusion of floxuridine for colorectal cancer metastases is significantly higher than control groups. Floxuridine can also be prescribed for the treatment of kidney and stomach cancers. In vitro uses of floxuridine include 5-minute treatments of fluorouracil, floxuridine, and mitomycin to increase cell proliferation in Tenon's capsule fibroblasts.
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant donor, this article will focus on partial resections of hepatic tissue and hepatoportoenterostomy.

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body.

Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondary, in which the cancer spreads from elsewhere in the body to the liver. Liver metastasis is the more common of the two liver cancers. Instances of liver cancer are increasing globally.
Tegafur/uracil is a chemotherapy drug combination used in the treatment of cancer, primarily bowel cancer.
Hepatic arterial infusion (HAI) is a medical procedure that delivers chemotherapy directly to the liver. The procedure, mostly used in combination with systemic chemotherapy, plays a role in the treatment of liver metastases in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Although surgical resection remains the standard of care for these liver metastases, majority of patients have lesions that are unresectable.
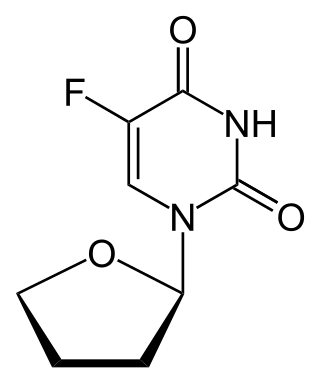
Tegafur is a chemotherapeutic prodrug of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) used in the treatment of cancers. It is a component of the combination drug tegafur/uracil. When metabolised, it becomes 5-FU.

Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), also known as transarterial radioembolization (TARE), radioembolization or intra-arterial microbrachytherapy is a form of radionuclide therapy used in interventional radiology to treat cancer. It is generally for selected patients with surgically unresectable cancers, especially hepatocellular carcinoma or metastasis to the liver. The treatment involves injecting tiny microspheres of radioactive material into the arteries that supply the tumor, where the spheres lodge in the small vessels of the tumor. Because this treatment combines radiotherapy with embolization, it is also called radioembolization. The chemotherapeutic analogue is called chemoembolization, of which transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the usual form.
Interferon alfa (INN) or HuIFN-alpha-Le, trade name Multiferon, is a pharmaceutical drug composed of natural interferon alpha (IFN-α), obtained from the leukocyte fraction of human blood following induction with Sendai virus. Interferon alfa contains several naturally occurring IFN-α subtypes and is purified by affinity chromatography. Although the pharmaceutical product is often simply called "interferon alpha" or "IFN-α" like its endogenous counterpart, the product's International nonproprietary name (INN) is interferon alfa.
Ramucirumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.
JX-594 is an oncolytic virus is designed to target and destroy cancer cells. It is also known as Pexa-Vec, INN pexastimogene devacirepvec) and was constructed in Dr. Edmund Lattime's lab at Thomas Jefferson University, tested in clinical trials on melanoma patients, and licensed and further developed by SillaJen.
Resminostat is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs), of which inhibitors are antineoplastic agents.
Radiation lobectomy is a form of radiation therapy used in interventional radiology to treat liver cancer. It is performed in patients that would be surgical candidates for resection, but cannot undergo surgery due to insufficient remaining liver tissue. It consists of injecting small radioactive beads loaded with yttrium-90 into the hepatic artery feeding the hepatic lobe in which the tumor is located. This is done with the intent of inducing growth in the contralateral hepatic lobe, not dissimilarly from portal vein embolization (PVE).
Transarterial bland embolization is a catheter-based tumor treatment of the liver. In this procedure, embolizing agents can be delivered through the tumor's feeding artery in order to completely occlude the tumor's blood supply. The anti-tumor effects are solely based on tumor ischemia and infarction of tumor tissue, as no chemotherapeutic agents are administered. The rationale for the use of bland embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and/or other hyper-vascular tumors is based on the fact that a normal liver receives a dual blood supply from the hepatic artery (25%) and the portal vein (75%). As the tumor grows, it becomes increasingly dependent on the hepatic artery for blood supply. Once a tumor nodule reaches a diameter of 2 cm or more, most of the blood supply is derived from the hepatic artery. Therefore, bland embolization and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) consist of the selective angiographic occlusion of the tumor arterial blood supply with a variety of embolizing agents, with or without the precedence of local chemotherapy infusion. The occlusion by embolic particles results in tumor hypoxia and necrosis, without affecting the normal hepatic parenchyma.

Liver angiosarcoma also known as angiosarcoma of the liver or hepatic angiosarcoma is a rare and rapidly fatal cancer arising from endothelial that line the blood vessels of the liver. It is a type of angiosarcoma. Although very rare with around 200 cases diagnosed each year, it is still considered the third most common primary liver cancer, making up around 2% of all primary liver cancers. Liver angiosarcoma can be primary, meaning it arose in the liver, or secondary, meaning the angiosarcoma arose elsewhere and metastasized to the liver. This article covers PHA, however much is also applicable to secondary tumors.
References
- ↑ "Yehuda Patt Bio Sketch" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ Yehuda Z. Patt (2003). "Phase II Trial of Systemic Continuous Fluorouracil and Subcutaneous Recombinant Interferon Alfa-2b for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinom" (PDF). Journal of Clinical Oncology. 21 (3): 421–427. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.10.103 . Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Colorectal Cancer Update 3 | 2003". Colorectalcancerupdate.com. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Dr. Patt Introduced". Umm.edu. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Selected works by Y.Z. Patt". American Society of Clinical Oncology. Retrieved 2012-09-26.