Further reading
- Staff (March 2009) "China Needs More Innovations: Interview with Dr. Y. H. Michael Pao" iChina Magazine
Yih-Ho Michael Pao is an American entrepreneur and hydro-engineer. He was an early pioneer in developing large-scale wind turbines. In 2000, Dr. Pao was elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering for his research, development, and commercialization of ultrahigh-pressure waterjet technology. [1]
Pao graduated from Johns Hopkins University in 1962.
Between 1970 and 2000, he formed and led six commercial companies in the United States based upon new technologies. These efforts created, developed and commercialized four new technologies that produce industrial tools: [1] [2]

A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, by tradition specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but in some parts of the English-speaking world the term has also been extended to encompass windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications. The term wind engine is also sometimes used to describe such devices.

A windpump is a type of windmill which is used for pumping water.

David Da-i Ho is a Taiwanese-American AIDS researcher, physician, and virologist who has made a number of scientific contributions to the understanding and treatment of HIV infection. He championed for combination anti-retroviral therapy instead of single therapy, which turned HIV from absolute terminal disease into a chronic disease.

Savonius wind turbines are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT), used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft. The turbine consists of a number of aerofoils, usually—but not always—vertically mounted on a rotating shaft or framework, either ground stationed or tethered in airborne systems.
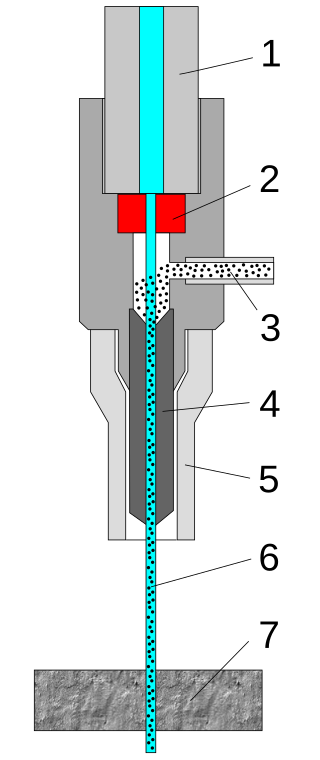
A water jet cutter, also known as a water jet or waterjet, is an industrial tool capable of cutting a wide variety of materials using an extremely high-pressure jet of water, or a mixture of water and an abrasive substance. The term abrasive jet refers specifically to the use of a mixture of water and an abrasive to cut hard materials such as metal, stone or glass, while the terms pure waterjet and water-only cutting refer to waterjet cutting without the use of added abrasives, often used for softer materials such as wood or rubber.
Pao or PAO may refer to:

Unconventional wind turbines are those that differ significantly from the most common types in use.

Wind power has been used as long as humans have put sails into the wind. King Hammurabi's Codex already mentioned windmills for generating mechanical energy. Wind-powered machines used to grind grain and pump water, the windmill and wind pump, were developed in what is now Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan by the 9th century. Wind power was widely available and not confined to the banks of fast-flowing streams, or later, requiring sources of fuel. Wind-powered pumps drained the polders of the Netherlands, and in arid regions such as the American mid-west or the Australian outback, wind pumps provided water for livestock and steam engines.
Wind power in Ohio has a long history, and as of 2016, Ohio had 545 megawatts (MW) of utility-scale wind power installations installed, responsible for 1.1% of in-state electricity generated. Over 1000 MW more were under construction or pending approval. Some installations have become tourist attractions. There has been a sudden increase in generating capacity, as total wind power capacity in the state was just 9.7 MW in 2010. By 2019, there were 738 MW of capacity, which generated 1.71% of Ohio's electricity.
Charles R. Cutler was an American engineer who specialized in the field of advanced process control. He was an elected member of the National Academy of Engineering.

A panemone windmill is a type of vertical-axis wind turbine. It has a rotating axis positioned vertically, while the wind-catching blades move parallel to the wind. By contrast, the shaft of a horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT) points into the wind while its blades move at right-angles to the wind's thrust. That is, a panemone primarily uses drag whereas the blades of a HAWT use lift.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. As of 2020, hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, as of 2009, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources.
Victor Mikhailovitch Lyatkher (1933) was born in Kerch. He holds a Ph.D. in Engineering Science from the University of Leningrad and a doctorate in science from Moscow State University. Lyatkher is a professor, engineer, and inventor. Lyatkher has developed and patented numerous processes and machines. These deal mainly with renewable energy sources such as tidal power, water turbines, and vertical axis wind turbines. He developed a new method to forecast long-term variations in the Caspian Sea level, and designed a new kind of low head turbine. Mr. Lyatkher has worked for over thirty years in the wind and hydro-power industry. He has received several prizes and awards for his accomplishments, including the Prize of the Council of Ministers of the USSR, the Award of the Indian Society of Earthquake Technology, and five medals of the All Union USSR Exhibition, gold, silver and bronze.

Starting in 1975, NASA managed a program for the United States Department of Energy and the United States Department of Interior to develop utility-scale wind turbines for electric power, in response to the increase in oil prices. A number of the world's largest wind turbines were developed and tested under this pioneering program. The program was an attempt to leap well beyond the then-current state of the art of wind turbine generators, and developed a number of technologies later adopted by the wind turbine industry. The development of the commercial industry however was delayed by a significant decrease in competing energy prices during the 1980s.

James G.P. Dehlsen is an American businessman, inventor, and entrepreneur. He is a pioneering figure in wind power and renewable energy development in the United States and holds 25 patents.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to wind energy:

John Oluseun Dabiri is a Nigerian-American aeronautics engineer and the Centennial Chair Professor at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), with appointments in the Graduate Aerospace Laboratories (GALCIT) and Mechanical Engineering. His research focuses on unsteady fluid mechanics and flow physics, with particular emphasis on topics relevant to biology, energy, and the environment. He is best known for his research of the hydrodynamics of jellyfish propulsion and the design of a vertical-axis wind farm adapted from schooling fish. He is the director of the Biological Propulsion Laboratory, which examines fluid transport with applications in aquatic locomotion, fluid dynamic energy conversion, and cardiac flows, as well as applying theoretical methods in fluid dynamics and concepts of optimal vortex formation.

Hi-VAWT is a renewable energy solutions provider headquartered in Linkou District, New Taipei City, Taiwan. Hi-VAWT has installations in many countries/territories worldwide, and on every continent including Antarctica. The company also a member of Taiwan Wind Turbine Industry Association.
The Gamma 60 wind turbine, a 1.5 MW two-bladed upwind horizontal axis wind turbine, was installed by Wind Energy Systems Taranto S.p.A. (WEST) at Alta Nurra, Sardinia, Italy in April 1992. Founded on original research and development work by NASA and Hamilton Standard, the Gamma 60 wind turbine was the world's first variable speed wind turbine with a teetering hinge.

A vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT) is a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind while the main components are located at the base of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be located close to the ground, facilitating service and repair. VAWTs do not need to be pointed into the wind, which removes the need for wind-sensing and orientation mechanisms. Major drawbacks for the early designs included the significant torque ripple during each revolution, and the large bending moments on the blades. Later designs addressed the torque ripple by sweeping the blades helically. Savonius vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT) are not widespread, but their simplicity and better performance in disturbed flow-fields, compared to small horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT) make them a good alternative for distributed generation devices in an urban environment.