Related Research Articles

Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. Prostatitis is classified into acute, chronic, asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, and chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the human body. It is composed of around 270 bones at birth – this total decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. The bone mass in the skeleton makes up about 14% of the total body weight and reaches maximum density around age 21. The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton is formed by the vertebral column, the rib cage, the skull and other associated bones. The appendicular skeleton, which is attached to the axial skeleton, is formed by the shoulder girdle, the pelvic girdle and the bones of the upper and lower limbs.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of a bone. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

Mary Lillian Ellison was an American professional wrestler better known by her ring name The Fabulous Moolah.
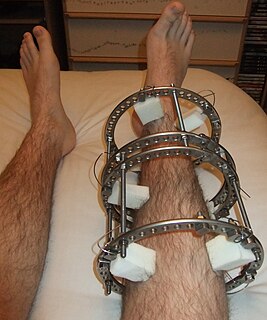
External fixation is a surgical treatment wherein rods are screwed into bone and exit the body to be attached to a stabilizing structure on the outside of the body. It is an alternative to internal fixation, where the components used to provide stability are positioned entirely within the patient's body. It is used to stabilize bone and soft tissues at a distance from the operative or injury focus. They provide unobstructed access to the relevant skeletal and soft tissue structures for their initial assessment and also for secondary interventions needed to restore bony continuity and a functional soft tissue cover.
A traction splint most commonly refers to a splinting device that uses straps attaching over the pelvis or hip as an anchor, a metal rod(s) to mimic normal bone stability and limb length, and a mechanical device to apply traction to the limb.

The ischium forms the lower and back part of the hip bone.

Crime Classification Manual: A Standard System for Investigating and Classifying Violent Crimes (1992) is a text on the classification of violent crimes by John E. Douglas, Ann W. Burgess, Allen G. Burgess and Robert K. Ressler. The publication is a result of a project by the Federal Bureau of Investigation's National Center for the Analysis of Violent Crime.
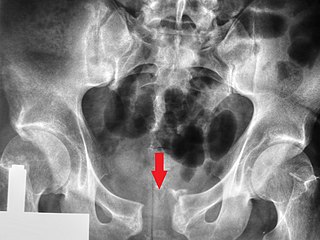
A pelvic fracture is a break of the bony structure of the pelvis. This includes any break of the sacrum, hip bones, or tailbone. Symptoms include pain, particularly with movement. Complications may include internal bleeding, injury to the bladder, or vaginal trauma.

A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate or growth plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures. This type of fracture and its classification system is named for Robert B. Salter and William H. Harris who created and published this classification system in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery in 1963.
LCIII or variation, may refer to:
Duverney fractures are isolated pelvic fractures involving only the iliac wing. They are caused by direct trauma to the iliac wing, and are generally stable fractures as they do not disrupt the weight bearing pelvic ring.

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.
Orthopedic surgery is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal injuries, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, bone tumours, and congenital limb deformities. Trauma surgery and traumatology is a sub-specialty dealing with the operative management of fractures, major trauma and the multiply-injured patient.
The Tile classification is a system of categorizing pelvic fractures based on fracture pattern, allowing judgment on the stability of the pelvic ring.
A Malgaigne fracture is vertical pelvic fracture with bilateral sacroiliac dislocation and fracture of the pubic rami.

A proximal humerus fracture is a break of the upper part of the bone of the arm (humerus). Symptoms include pain, swelling, and a decreased ability to move the shoulder. Complications may include axillary nerve or axillary artery injury.

A pelvic binder is a device used to compress the pelvis in people with a pelvic fracture in an effort to stop bleeding.
LCII or variation, may refer to:
References
- ↑ Burgess AR, Eastridge BJ, Young JW, Ellison TS, Ellison PS Jr, Poka A, Bathon GH, Brumback RJ (1990). "Pelvic ring disruptions: effective classification system and treatment protocols". J Trauma. 30 (7): 848–56. doi:10.1097/00005373-199007000-00015. PMID 2381002.