The Occupational Safety and Health Administration is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established the agency under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, which President Richard M. Nixon signed into law on December 29, 1970. OSHA's mission is to "assure safe and healthy working conditions for working men and women by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education, and assistance." The agency is also charged with enforcing a variety of whistleblower statutes and regulations. OSHA's workplace safety inspections have been shown to reduce injury rates and injury costs without adverse effects on employment, sales, credit ratings, or firm survival.

Agriculture is a major industry in the United States, which is a net exporter of food. As of the 2017 census of agriculture, there were 2.04 million farms, covering an area of 900 million acres (1,400,000 sq mi), an average of 441 acres per farm.

Child labor laws in the United States address issues related to the employment and welfare of working children in the United States. The most sweeping federal law that restricts the employment and abuse of child workers is the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (FLSA), which came into force during the Franklin D. Roosevelt administration. Child labor provisions under FLSA are designed to protect the educational opportunities of youth and prohibit their employment in jobs that are detrimental to their health and safety. FLSA restricts the hours that youth under 16 years of age can work and lists hazardous occupations too dangerous for young workers to perform.

The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 is a US labor law governing the federal law of occupational health and safety in the private sector and federal government in the United States. It was enacted by Congress in 1970 and was signed by President Richard Nixon on December 29, 1970. Its main goal is to ensure that employers provide employees with an environment free from recognized hazards, such as exposure to toxic chemicals, excessive noise levels, mechanical dangers, heat or cold stress, or unsanitary conditions. The Act created the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).

An occupational injury is bodily damage resulting from working. The most common organs involved are the spine, hands, the head, lungs, eyes, skeleton, and skin. Occupational injuries can result from exposure to occupational hazards, such as temperature, noise, insect or animal bites, blood-borne pathogens, aerosols, hazardous chemicals, radiation, and occupational burnout.

The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Despite its name, it is not part of either the National Institutes of Health nor OSHA. Its current director is John Howard.
Contingent work, casual work, or contract work, is an employment relationship with limited job security, payment on a piece work basis, typically part-time that is considered non-permanent. Although there is less job security, freelancers often report incomes higher than their former traditional jobs.
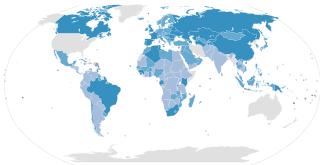
The legal working age is the minimum age required by law for a person to work, in each country or jurisdiction, if they have not reached the age of majority. Activities that are dangerous, harmful to the health or that may affect the morals of minors fall into this category.

The Health Hazard Evaluation (HHE) program is a workplace health program administered by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). NIOSH developed the HHE program to comply with a mandate in the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 to investigate workplace health hazards reported by employers and employees. According to Section 20(a)(6) of the Act, the Secretary of Health and Human Services is authorized "following a written request by any employer or authorized representative of employees, to determine whether any substance normally found in the place of employment has potentially toxic effects in such concentrations as used or found."
North American Occupational Safety and Health (NAOSH) Week is an annual celebration that happens during the first full week of May. The aim of the event is to raise awareness about occupational safety, health, and the environment (OSH&E) in order to avoid workplace injuries and illnesses.
An occupational fatality is a death that occurs while a person is at work or performing work related tasks. Occupational fatalities are also commonly called "occupational deaths" or "work-related deaths/fatalities" and can occur in any industry or occupation.

A physical hazard is an agent, factor or circumstance that can cause harm with contact. They can be classified as type of occupational hazard or environmental hazard. Physical hazards include ergonomic hazards, radiation, heat and cold stress, vibration hazards, and noise hazards. Engineering controls are often used to mitigate physical hazards.
Children's Act for Responsible Employment (CARE Act) is a United States bill that would address the labor conditions of child field workers by imposing the same age, work hour, and pesticide exposure limits as other occupations and increasing the penalties for child labor violations. Representative Lucille Roybal-Allard's introduced the Children's Act for Responsible Employment (CARE Act, HR 3564) bill in September 2009 and has subsequently reintroduced it.

Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS), also known simply as occupational health or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of occupational safety and health program/department etc. OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene.

People who are driving as part of their work duties are an important road user category. First, workers themselves are at risk of road traffic injury. Contributing factors include fatigue and long work hours, delivery pressures, distractions from mobile phones and other devices, lack of training to operate the assigned vehicle, vehicle defects, use of prescription and non-prescription medications, medical conditions, and poor journey planning. Death, disability, or injury of a family wage earner due to road traffic injury, in addition to causing emotional pain and suffering, creates economic hardship for the injured worker and family members that may persist well beyond the event itself.

Agricultural safety and health is an aspect of occupational safety and health in the agricultural workplace. It specifically addresses the health and safety of farmers, farm workers, and their families.

Workplace robotics safety is an aspect of occupational safety and health when robots are used in the workplace. This includes traditional industrial robots as well as emerging technologies such as drone aircraft and wearable robotic exoskeletons. Types of accidents include collisions, crushing, and injuries from mechanical parts. Hazard controls include physical barriers, good work practices, and proper maintenance.
The Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries, or the CFOI Program is a Federal/State cooperative program that publishes data on fatal cases of work-related injuries for all States, Territories, and New York City. The CFOI has detailed information on those who died at work due to a traumatic injury. CFOI data include all fatalities that occurred in the reference year that were the result of a workplace injury, regardless of when the injury occurred.
The Survey of Occupational Injuries and Illnesses or the SOII program is a Federal/State cooperative program that publishes annual estimates on nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses. Each year, approximately 200,000 employers report for establishments in private industry and the public sector. In-scope cases include work-related injuries or illnesses to workers who require medical care beyond first aid. See the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) for the entire record-keeping guidelines. The SOII excludes all work-related fatalities as well as nonfatal work injuries and illnesses to the self–employed; to workers on farms with 11 or fewer employees; to private household workers; to volunteers; and to federal government workers.

Farmworkers in the United States have unique demographics, wages, working conditions, organizing, and environmental aspects. According to The National Institute for Occupational Safety & Health in Agricultural Safety, approximately 2,112,626 full-time workers were employed in production agriculture in the US in 2019 and approximately 1.4 to 2.1 million hired crop workers are employed annually on crop farms in the US. A study by the USDA found the average age of a farmworker to be 33. In 2017, the Department of Labor and Statistics found the median wage to be $23,730 a year, or $11.42 per hour.













