Related Research Articles

Freedom of religion in Pakistan is formally guaranteed by the Constitution of Pakistan for individuals of various religions and religious sects.

The Hudud Ordinances are laws in Pakistan enacted in 1979 as part of the Islamization of Pakistan by Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq, the sixth president of Pakistan. It replaced parts of the British-era Pakistan Penal Code, adding new criminal offences of adultery and fornication, and new punishments of whipping, amputation, and stoning to death. After much controversy and criticism parts of the law were extensively revised in 2006 by the Women's Protection Bill.

Zināʾ (زِنَاء) or zinā is an Islamic legal term referring to unlawful sexual intercourse. According to traditional jurisprudence, zina can include adultery, fornication, prostitution, sodomy, incest, and bestiality. Zina must be proved by testimony of four Muslim eyewitnesses to the actual act of penetration, confession repeated four times and not retracted later. The offenders must have acted of their own free will. Rapists could be prosecuted under different legal categories which used normal evidentiary rules. Making an accusation of zina without presenting the required eyewitnesses is called qadhf (القذف), which is itself a hudud offense.

Hudud is an Arabic word meaning "borders, boundaries, limits". In the religion of Islam, it refers to punishments that under Islamic law (sharīʿah) are believed to be mandated and fixed by God, i.e. prescribed punishments, as opposed to Ta'zeer. These punishments were applied in pre-modern Islam, and their use in some modern states has been a source of controversy.
Mohammed Younus Shaikh is a Pakistani medical doctor, human rights activist and freethinker.

Rajm in Islam refers to the Hudud punishment wherein an organized group throws stones at a convicted individual until that person dies. Under some versions of Islamic law (Sharia), it is the prescribed punishment in cases of adultery committed by a married person which requires either a confession from either the adulterer or adulteress, or producing four witnesses of sexual penetration.
Islamization or Shariazation, has a long history in Pakistan since the 1950s, but it became the primary policy, or "centerpiece" of the government of General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq, the ruler of Pakistan from 1977 until his death in 1988.

Tehmina Durrani is a Pakistani author known for her bestselling book My Feudal Lord, an artist, and a women's and children's rights activist, she is the current spouse of the Prime Minister of Pakistan Shehbaz Sharif since March 2024 having previously served in the post from 10 April 2022 to 13 August 2023.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Iran. The list of crimes punishable by death includes murder; rape; child molestation; homosexuality; drug trafficking; armed robbery; kidnapping; terrorism; burglary; incest; fornication; adultery; sodomy; sexual misconduct; prostitution; plotting to overthrow the Islamic government; political dissidence; sabotage; arson; rebellion; apostasy; blasphemy; extortion; counterfeiting; smuggling; recidivist consumption of alcohol; producing or preparing food, drink, cosmetics, or sanitary items that lead to death when consumed or used; producing and publishing pornography; using pornographic materials to solicit sex; capital perjury; recidivist theft; certain military offences ; "waging war against God"; "spreading corruption on Earth"; espionage; and treason. Iran carried out at least 977 executions in 2015, at least 567 executions in 2016, and at least 507 executions in 2017. In 2018 there were at least 249 executions, at least 273 in 2019, at least 246 in 2020, at least 290 in 2021, at least 553 in 2022, at least 834 in 2023, and at least 226 so far in 2024. In 2023, Iran was responsible for 74% of all recorded executions in the world.

The Pakistan Penal Code outlaws blasphemy against any recognized religion, with punishments ranging from a fine to the death penalty. According to various human rights organizations, Pakistan's blasphemy laws have been used to persecute religious minorities and settle personal rivalries, frequently against other Muslims, rather than to safeguard religious sensibilities.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Pakistan. Although there have been numerous amendments to the Constitution, there is yet to be a provision prohibiting the death penalty as a punitive remedy.
The Women's Protection Bill which was passed by the National Assembly of Pakistan on 15 November 2006 is an attempt to amend the heavily criticised 1979 Hudood Ordinance laws which govern the punishment for rape and adultery in Pakistan. Critics of the Hudood Ordinance alleged that it made it exceptionally difficult and dangerous to prove an allegation of rape, and thousands of women had been imprisoned as a result of the bill. The bill returned a number of offences from the Zina Ordinance to the Pakistan Penal Code, where they had been before 1979, and created an entirely new set of procedures governing the prosecution of the offences of adultery and fornication. Whipping and amputation were removed as punishments. The law meant women would not be jailed if they were unable to prove rape and their complaints of rape would not be seen as confession of adultery.

In Islamic law, Ḥirābah is a legal category that comprises highway robbery, rape, and terrorism. Ḥirābah means piracy or unlawful warfare. It comes from the triliteral root ḥrb, which means “to become angry and enraged”. The noun ḥarb means 'war' or 'wars'.

In Islam, blasphemy is impious utterance or action concerning God, but is broader than in normal English usage, including not only the mocking or vilifying of attributes of Islam but denying any of the fundamental beliefs of the religion. Examples include denying that the Quran was divinely revealed, the Prophethood of one of the Islamic prophets, insulting an angel, or maintaining God had a son.

Stoning, or lapidation, is a method of capital punishment where a group throws stones at a person until the subject dies from blunt trauma. It has been attested as a form of punishment for grave misdeeds since ancient times.
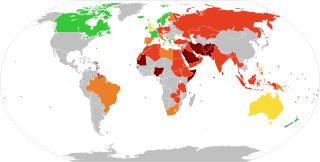
A blasphemy law is a law prohibiting blasphemy, which is the act of insulting or showing contempt or lack of reverence to a deity, or sacred objects, or toward something considered sacred or inviolable. According to Pew Research Center, about a quarter of the world's countries and territories (26%) had anti-blasphemy laws or policies as of 2014.
The use of politically and religiously-motivated violence dates back to the early history of Islam. Islam has its origins in the behavior, sayings, and rulings of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, his companions, and the first caliphs in the 7th, 8th, and 9th centuries CE. Mainstream Islamic law stipulates detailed regulations for the use of violence, including corporal and capital punishment, as well as regulations on how, when, and whom to wage war against.
Capital punishment for offenses is allowed by law in some countries. Such offenses include adultery, apostasy, blasphemy, corruption, drug trafficking, espionage, fraud, homosexuality and sodomy not involving force, perjury causing execution of an innocent person, prostitution, sorcery and witchcraft, theft, treason and espionage. In addition to civilian treason and espionage, often considered capital crimes against the state where the death penalty is retained, military laws frequently ordain execution for serious offences, including in jurisdictions where capital punishment is illegal or obsolete under civilian law.

Khadim Hussain Rizvi was a Pakistani Islamic scholar and the founder of Tehreek-e-Labbaik, a religiopolitical organization founded in 2015, known to protest against any change to Pakistan's blasphemy law.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "KARACHI: Writer of sacrilegious book gets life term". Dawn the Internet Edition. 12 August 2005. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Document - Pakistan: Fear for safety/ Prisoner of Conscience (POC), Mohammed Younus Shaikh". Amnesty International. 19 August 2005. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ↑ "Writer in Pakistan given life for "blasphemy"". National Secular Society. 27 July 2007. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ↑ "Writer gets life for defiling the Koran". 29 July 2007. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- 1 2 Kadri, Sadakat (2012). Heaven on Earth: A Journey Through Shari'a Law from the Deserts of Ancient Arabia to the Streets of the Modern Muslim World . Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 257. ISBN 978-1-4668-0218-6.