Related Research Articles

Violence is the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy. Other definitions are also used, such as the World Health Organization's definition of violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation."

Juvenile delinquency, also known as "juvenile offending", is the act of participating in unlawful behavior as a minor or individual younger than the statutory age of majority. For example, in the United States of America a juvenile delinquent is a person who is typically below 18 years of age and commits an act that otherwise would have been charged as a crime if they were an adult. Juvenile crimes can range from status offenses, to property crimes and violent crimes.
School violence encompasses physical violence, including student-on-student fighting and corporal punishment; psychological violence, including verbal abuse; sexual violence, including rape and sexual harassment; many forms of bullying, including cyberbullying; and carrying weapons in school. It is widely held to have become a serious problem in recent decades in many countries, especially where weapons such as guns or knives are involved. It includes violence between school students as well as physical attacks by students on school staff.
The Senate Judiciary Subcommittee on Criminal Justice and Counterterrorism is one of six subcommittees within the Senate Judiciary Committee. It was previously known as the Subcommittee on Crime and Terrorism

In criminal justice systems a youth detention center, known as a juvenile detention center (JDC), juvenile detention, juvenile hall, or more colloquially as juvie/juvy, also sometimes referred as observation home or remand home is a prison for people under the age of 21, often termed juvenile delinquents, to which they have been sentenced and committed for a period of time, or detained on a short-term basis while awaiting trial or placement in a long-term care program. Juveniles go through a separate court system, the juvenile court, which sentences or commits juveniles to a certain program or facility.

The Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act of 1974 (JJDPA) is a United States federal law providing formula grants to states that follow a series of federal protections on the care and treatment of youth in the juvenile justice and criminal justice systems.

The American juvenile justice system is the primary system used to handle minors who are convicted of criminal offenses. The system is composed of a federal and many separate state, territorial, and local jurisdictions, with states and the federal government sharing sovereign police power under the common authority of the United States Constitution. The juvenile justice system intervenes in delinquent behavior through police, court, and correctional involvement, with the goal of rehabilitation. Youth and their guardians can face a variety of consequences including probation, community service, youth court, youth incarceration and alternative schooling. The juvenile justice system, similar to the adult system, operates from a belief that intervening early in delinquent behavior will deter adolescents from engaging in criminal behavior as adults.

Antonio Cárdenas is an American politician who has served as the United States Representative for California's 29th congressional district since January 2013.
Crime prevention is the attempt to reduce and deter crime and criminals. It is applied specifically to efforts made by governments to reduce crime, enforce the law, and maintain criminal justice. justice law
Operation Ceasefire (also known as the Boston Gun Project and the Boston Miracle) is a problem-oriented policing initiative implemented in 1996 in Boston, Massachusetts. The program was specifically aimed at youth gun violence as a large-scale problem. The plan is based on the work of criminologist David M. Kennedy.
This page is primarily concerned with juvenile delinquency in the United States. For information on juvenile delinquency in general, see juvenile delinquency. In addition, although the term juvenile delinquency often refers to juvenile as both the victims and the aggressors, this page only refers to juveniles as the actual delinquents. The information and statistics for juveniles as victims rather than offenders is much different. For information about juveniles as the victims of violent attacks, see trafficking of children, child abuse, child sexual abuse, or prostitution of children.
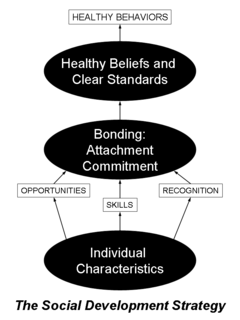
Communities That Care (CTC) is a program of the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) in the office of the United States Government's Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). CTC is a coalition-based prevention operating system that uses a public health approach to prevent youth problem behaviors such as violence, delinquency, school drop out and substance abuse. Using strategic consultation, training, and research-based tools, CTC is designed to help community stakeholders and decision makers understand and apply information about risk and protective factors, and programs that are proven to make a difference in promoting healthy youth development, in order to most effectively address the specific issues facing their community's youth.
The Interagency Working Group on Youth Programs is a group within the executive branch of the U.S. government, and is responsible for promoting healthy outcomes for all youth, including disconnected youth and youth who are at-risk. The Working Group also engages with national, state, local and tribal agencies and organizations, schools, and faith-based and community organizations that serve youth.

The United States incarcerates more of its youth than any other country in the world through the juvenile courts and the adult criminal justice system, which reflects the larger trends in incarceration practices in the United States. In 2010, approximately 70,800 juveniles were incarcerated in youth detention facilities alone. Approximately 500,000 youth are brought to detention centers in a given year. This data does not reflect juveniles tried as adults. Around 40% are incarcerated in privatized, for-profit facilities.
Trial as an adult is a situation in which a juvenile offender is tried as if they were an adult.
Violence-Free Zones, or Violence-Free Zone Initiatives, are community-based interventions for gang members and youth. Zones attempt to stem violence by providing mentorship, guidance, social development, job training and an effective environment for learning, among other tools, to help gang members and at-risk youth break free and become successful in life, crime-free and violence-free. The initiatives operate in urban schools with high levels of crime and violence.

Gender responsive approach for girls in the juvenile justice system represents an emerging trend in communities and courts throughout the United States, Australia and Latin America, as an increasing number of girls are entering the juvenile justice system. A gender responsive approach within the juvenile justice system emphasizes considering the unique circumstances and needs of females when designing juvenile justice system structures, policies, and procedures.
The National Network for Safe Communities (NNSC) is a research center at City University of New York John Jay College of Criminal Justice. The NNSC works with communities to reduce violence, minimize arrest and incarceration, and increase trust between law enforcement and the public. Working in partnership with cities around the country the NNSC provides advising on implementing evidence-based violence reduction strategies. Additionally, the NNSC provides guidance on how to build trust between law enforcement and the communities it serves, facilitates connections between practitioners within and across jurisdictions, and serves as a resource for knowledge about violence prevention and reduction strategies.

The Family and Youth Services Bureau (FYSB) is a division of the US Executive Branch under the Administration for Children and Families and the Department of Health and Human Services. The FYSB's primary purpose is to support programs for at-risk youth and their families.
Community Crime Prevention relates to interventions designed to bring reform to the social conditions that influence, and encourage, offending in residential communities. Community crime prevention has a main focus on both the social and local institutions found within communities which can influence crime rates, specifically juvenile delinquency.