The Five Barbarians, or Wu Hu, is a Chinese historical exonym for ancient non-Chinese peoples who immigrated to northern China in the Eastern Han dynasty, and then overthrew the Western Jin dynasty and established their own kingdoms in the 4th–5th centuries. The peoples categorized as the Five Barbarians were the Xiongnu, Jie, Xianbei, Di, and Qiang. Of these five tribal ethnic groups, the Xiongnu and Xianbei were nomadic peoples from the northern steppes. The ethnic identity of the Xiongnu is uncertain, but the Xianbei appear to have been Mongolic. The Jie, another pastoral people, may have been a branch of the Xiongnu, who may have been Yeniseian or Indo-Scythian. The Di and Qiang were from the highlands of western China. The Qiang were predominantly herdsmen and spoke Sino-Tibetan (Tibeto-Burman) languages, while the Di were farmers who may have spoken a Sino-Tibetan or Turkic language.

The Xiongnu were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Chinese sources report that Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire.
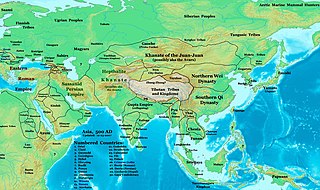
The Northern Wei or the Northern Wei Empire, also known as the Tuoba Wei (拓跋魏), Later Wei (後魏), or Yuan Wei (元魏), was a dynasty founded by the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei, which ruled northern China from 386 to 534 AD, during the period of the Southern and Northern Dynasties. Described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change", the Northern Wei Dynasty is particularly noted for unifying northern China in 439: this was also a period of introduced foreign ideas, such as Buddhism, which became firmly established.

The Xianbei were originally a nomadic tribal confederation residing in what is today's eastern Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeast China. Along with the Xiongnu, they were one of the major nomadic groups in northern China from the Han Dynasty to the Northern and Southern dynasties. They eventually established their own northern dynasties such as the Northern Wei founded in the 4th century AD by the Tuoba clan. During the Uprising of the Five Barbarians they became categorized as one of the Five Barbarians by the Han Chinese.

The Monguor, Tu people, White Mongol or Tsagaan Mongol are one of the 56 officially recognized ethnic groups in China. The "Tu" ethnic category was created in the 1950s.

The Han Zhao, or Former Zhao, or Northern Han (北漢), was a Southern Xiongnu state during Sixteen Kingdoms period coeval with the Chinese Jin Dynasty (265-420). In the Chinese historiography it was given two conditional state titles, the Han state for the state proclaimed in 304 by Liu Yuan, and the Former Zhao state for the state proclaimed in 319 by Liu Yao. The reference to them as separate states should be considered clearly erroneous, given that when Liu Yao changed the name of the state from Han to Zhao in 319, he treated the state as having been continuous from the time that Liu Yuan founded it in 304; instead, he de-established royal lineage to the Han Dynasty and claimed ancestry directly from Yu the Great of the Xia Dynasty.
The proto-Mongols emerged from an area that had been inhabited by humans and predecessor hominin species as far back as the Stone Age over 800,000 years ago. The people there went through the Bronze and Iron Ages, forming tribal alliances, peopling, and coming into conflict with early China.

Tiefu was a pre-state Xiongnu tribe during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms in China. Its chieftain Liu Bobo established the state of Xia in 407 and changed his family name into Helian.

The Wuhuan were a Proto-Mongolic nomadic people who inhabited northern China, in what is now the provinces of Hebei, Liaoning, Shanxi, the municipality of Beijing and the autonomous region of Inner Mongolia.
The Dingling were an ancient people mentioned in Chinese historiography in the context of the 1st century BCE. They are assumed to have been an early Proto-Turkic-speaking people, whose original constituents mainly assimilated into the Xiongnu and Xianbei groups. They originally lived on the bank of the Lena River in the area west of Lake Baikal, gradually moving southward to Mongolia and northern China. They were a huge independent horde for centuries, but later been defeated and temporary became subject of the Xiongnu Empire, and thus presumably related to the invaders known as Huns in the west. Around the 3rd century they were assimilated into the Tiele, also named Di (翟), DiLi (狄历), Gaoche (高車) or Chile (敕勒), who gradually expanded westward into Central Asia, expelled from Mongolia by the Rouran and establishing a state Turpan in the 5th century. The Tiele were a collection of early Turkic tribes, largely descended from the Chile.

The Western Wei followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei, and ruled northern China from 535 to 557. As with the Northern Wei state that preceded it, the ruling family of Western Wei were members of the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei.
Donghu was a tribal confederation of nomadic people that was first recorded from the 7th century BCE and was destroyed by the Xiongnu in 150 BCE. They lived in northern Hebei, southeastern Inner Mongolia and the western part of Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang along the Yan Mountains and Greater Khingan Range.
Murong Hui (慕容廆), (269–333) Xianbei chief and Duke Xiang of Liaodong, posthumously honored as Prince Wuxuan of Yan.
Gao Huan (496–547), courtesy name Heliuhun (賀六渾), formally Prince Xianwu of Qi (齊獻武王), later further formally honored by Northern Qi initially as Emperor Xianwu (獻武皇帝), then as Emperor Shenwu (神武皇帝,) with the temple name Gaozu (高祖), was the Han Chinese paramount general of the Chinese/Xianbei dynasty Northern Wei and Northern Wei's branch successor state Eastern Wei. Though being ethnically Han, Gao was deeply affected by Xianbei culture and was often considered more Xianbei than Han by his contemporaries. During his career, he and his family became firmly in control of the government of Eastern Wei, and eventually, in 550, his son Gao Yang forced Emperor Xiaojing of Eastern Wei to yield the throne to him, establishing the Gao clan as the imperial clan of a new Northern Qi state.
The Kumo Xi (traditional Chinese: 庫莫奚; simplified Chinese: 库莫奚; pinyin: Kùmò Xī;, also known as the Qay or Tatabi, were a Mongolic steppe people located in current northeast China from 207 AD to 907 AD. After the death of their ancestor Tadun in 207 they were no longer called Wuhuan but joined the Khitan Xianbei in submitting to the Yuwen Xianbei. Their history is widely linked to the more famous Khitan. During their history the Kumo Xi engaged in conflict with numerous Chinese dynasties and with the Khitans, eventually suffering a series of disastrous defeats to Chinese armies and coming under the domination of the Khitans. In 1007, the Kumo Xi were completely assimilated into the Khitan Liao Dynasty.

The Xianbei state or Xianbei confederation was a nomadic empire which existed in modern-day Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, northern Xinjiang, Northeast China, Gansu, Buryatia, Zabaykalsky Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, Tuva, Altai Republic and eastern Kazakhstan from 156-234. Like most ancient peoples known through Chinese historiography, the ethnic makeup of the Xianbei is unclear.

The Sixteen Kingdoms, less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439, when the political order of northern China fractured into a series of short-lived sovereign states, most of which were founded by the "Five Barbarians," ethnic minority peoples who had settled in northern China during the preceding centuries and participated in the overthrow of the Western Jin dynasty in the early 4th century. The kingdoms founded by ethnic Xiongnu, Xianbei, Di, Jie, Qiang, as well as Han Chinese and other ethnicities, fought against each other and the Eastern Jin dynasty, which succeeded the Western Jin and ruled southern China. The period ended with the unification of northern China in the early 5th century by the Northern Wei, a dynasty that evolved from a kingdom founded by ethnic Xianbei.
Dugu (獨孤) is a Chinese compound surname of Xianbei/Xiongnu origin. There is still very few, in single digits, Chinese people with the surname today, mainly reside in Shanghai. There is a small Korean population with this surname in North Korea, mainly in Ryongchon County and Uiju County near the Chinese border.
Yuwen Zhiji was a Chinese military officer of the Sui dynasty. He was the son of Yuwen Shu, the Duke of Xu. He was the younger brother of Yuwen Huaji and older brother of Yuwen Huiji (宇文惠及). He had another younger half-brother Yuwen Shiji. His ancestors were from Xiongnu descent with the surname Pòyětóu (破野头). The Poyetous later were naturalized to Xianbei ethnicity and changed their surname to Yuwen (宇文).












