Yves Rumpler (born 1938), is a French researcher and primatologist. He was a professor of embryology and primatology at the Louis Pasteur University of Strasbourg until he retired in 2007.
Yves Rumpler (born 1938), is a French researcher and primatologist. He was a professor of embryology and primatology at the Louis Pasteur University of Strasbourg until he retired in 2007.
In 1959 Yves Rumpler was appointed assistant chief in the Institute of Embryology at the University of Strasbourg and until 1966 his research focused on traditional subjects studied at Strasbourg e.g. thyroid hormones, teratology. From 1966 to 1976, Yves Rumpler was an associate lecturer in histology and embryology at the National School of Medicine, Tananarive, Madagascar (now part of the University of Antananarivo). He undertook studies on the systematic and chromosomal evolution of the lemurs in Madagascar and is consequently recognized for his work in primatology. He then served as department head of the Laboratory of Reproductive Biology and Cytogenetics Laboratory, studying quantitative cytology and histology at the teaching hospital of Strasbourg. From 1980 to 2007 Yves Rumpler taught at the Institute of Embryology in the University of Strasbourg.
He has received an honorary doctorate from the Ruhr University of Bochum, Germany.
Yves Rumpler took part in the description of new species of primates:
With Elwyn L. Simons, he also created the genus name for the true lemurs: Eulemur (Simons & Rumpler 1988). [1] This new genus joined together the species Eulemur fulvus , E. mongoz , E. macaco , E. rubriventer and E. coronatus which were previously in the genus Lemur .
Selected work from scientific magazines and the field of the primatology:

The Cheirogaleidae are the family of strepsirrhine primates containing the various dwarf and mouse lemurs. Like all other lemurs, cheirogaleids live exclusively on the island of Madagascar.

The sportive lemurs are the medium-sized primates that make up the family Lepilemuridae. The family consists of only one extant genus, Lepilemur. They are closely related to the other lemurs and exclusively live on the island of Madagascar. For a time, this family was named Megaladapidae, but the current name was given precedence since the extinct genus Megaladapis was removed from the family.

The woolly lemurs, also known as avahis or woolly indris, are nine species of strepsirrhine primates in the genus Avahi. Like all other lemurs, they live only on the island of Madagascar.

The red-tailed sportive lemur, or red-tailed weasel lemur, is native to Madagascar like all lemurs. It is a nocturnal species feeding largely on leaves, though they also eat some fruit. Individuals weigh around 800 g (1.8 lb), and there is little sexual dimorphism. In general they live in mated pairs, with a home range of about 10,000 square metres. Both members of the pair use the same home range, and there is little overlap between the home ranges of neighbouring pairs. Travel distances each night are between 100 m (330 ft) and 1 km (0.6 mi), making this a relatively inactive species. This species can be found in the Madagascar dry deciduous forests.

The small-toothed sportive lemur, or small-toothed weasel lemur, is a primate species in the family Lepilemuridae that—like all extant lemurs—is endemic to Madagascar. The species lives in dense rainforest in southeastern Madagascar, and can be found in Ranomafana and Andringitra National Parks. Described in 1894, it was considered either a subspecies or taxonomic synonym of the weasel sportive lemur throughout most of the 20th century. Phylogenetic studies not only support its species status, but also suggest that it is the only eastern Malagasy sportive lemur that is more closely related to western than to other eastern species.

The northern sportive lemur, also known as the Sahafary sportive lemur or northern weasel lemur, is a species of lemur in the family Lepilemuridae. It is endemic to Madagascar. As a result of severe ecological and human pressures, the lemur is classified as Critically Endangered (CR) by the IUCN Red List.

The mouse lemurs are nocturnal lemurs of the genus Microcebus. Like all lemurs, mouse lemurs are native to Madagascar.

The Sahamalaza sportive lemur is a species of sportive lemur endemic to northern Madagascar.

The Antafia sportive lemur, or red-shouldered sportive lemur is a sportive lemur endemic to Madagascar. It has a total length of about 52 to 59 cm, of which 24–26 cm (9.4–10.2 in) are tail. The AEECL's sportive lemur is found in western Madagascar, living in dry deciduous forests.

Randrianasolo's sportive lemur, or the Bemaraha sportive lemur, is a sportive lemur endemic to Madagascar. It has a total length of about 49 to 56 cm, of which 21–26 cm (8.3–10.2 in) are tail. Randrianasolo's sportive lemur is found in western Madagascar.

The southern woolly lemur, or southern avahi, has been recently recognized as a separate species of woolly lemur in 2006 by Zaramody et al. It is a nocturnal and pair-living species. Groups can range from 2 to 5 individuals. A study in Sainte Luce forest revealed home range varied from 2.2 to 3.5 ha and that males can have larger home range and cover longer daily distances than females, in agreement with the territory defence and mate guarding hypotheses.

The Betsileo woolly lemur or Betsileo avahi is a species of woolly lemur native to southeastern Madagascar, in the District of Fandriana. The pelage differs significantly from other southeastern woolly lemurs in that it is primarily light reddish brown on most of the body and grey under the jaw and on the extremities. The pelage is thicker on the head than other eastern woolly lemurs.

Peyrieras's woolly lemur or Peyrieras's avahi is a species of woolly lemur native to southeastern Madagascar. It weighs about 1 kg.

Ramanantsoavana's woolly lemur, also known as Ramanantsoavana's avahi or the Manombo woolly lemur, is a species of woolly lemur native to southeastern Madagascar. It weighs about 1 kg. It was originally considered a subspecies of the southern woolly lemur, A. m. ramanantsoavana, but was elevated to a separate species in 2006 based on molecular, phenotypic and morphological data.
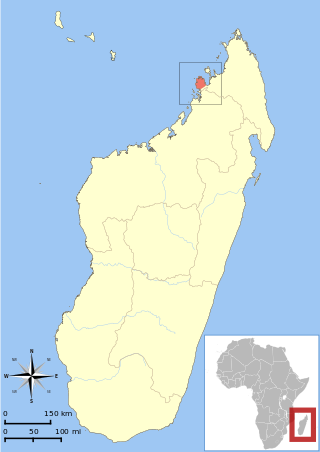
Mittermeier's sportive lemur is a sportive lemur endemic to the Ampasindava Peninsula in Madagascar.

Lemurs were first classified in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus, and the taxonomy remains controversial today, with approximately 70 to 100 species and subspecies recognized, depending on how the term "species" is defined. Having undergone their own independent evolution on Madagascar, lemurs have diversified to fill many ecological niches normally filled by other types of mammals. They include the smallest primates in the world, and once included some of the largest. Since the arrival of humans approximately 2,000 years ago, lemurs have become restricted to 10% of the island, or approximately 60,000 square kilometers (23,000 sq mi), and many face extinction. Concerns over lemur conservation have affected lemur taxonomy, since distinct species receive increased conservation attention compared to subspecies.