Related Research Articles
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion, the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials.
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics.
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state.
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century.
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit, or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons.

A potential energy surface (PES) describes the energy of a system, especially a collection of atoms, in terms of certain parameters, normally the positions of the atoms. The surface might define the energy as a function of one or more coordinates; if there is only one coordinate, the surface is called a potential energy curve or energy profile. An example is the Morse/Long-range potential.
MNDO, or Modified Neglect of Diatomic Overlap is a semi-empirical method for the quantum calculation of molecular electronic structure in computational chemistry. It is based on the Neglect of Diatomic Differential Overlap integral approximation. Similarly, this method replaced the earlier MINDO method. It is part of the MOPAC program and was developed in the group of Michael Dewar. It is also part of the AMPAC, GAMESS (US), PC GAMESS, GAMESS (UK), Gaussian, ORCA and CP2K programs.
CNDO is the abbreviation for Complete Neglect of Differential Overlap, one of the first semi empirical methods in quantum chemistry. It uses two approximations:

In the context of chemistry and molecular modelling, a force field is a computational method that is used to estimate the forces between atoms within molecules and also between molecules. More precisely, the force field refers to the functional form and parameter sets used to calculate the potential energy of a system of atoms or coarse-grained particles in molecular mechanics, molecular dynamics, or Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters for a chosen energy function may be derived from experiments in physics and chemistry, calculations in quantum mechanics, or both. Force fields are interatomic potentials and utilize the same concept as force fields in classical physics, with the difference that the force field parameters in chemistry describe the energy landscape, from which the acting forces on every particle are derived as a gradient of the potential energy with respect to the particle coordinates.
MINDO, or Modified Intermediate Neglect of Differential Overlap is a semi-empirical method for the quantum calculation of molecular electronic structure in computational chemistry. It is based on the Intermediate Neglect of Differential Overlap (INDO) method of John Pople. It was developed by the group of Michael Dewar and was the original method in the MOPAC program. The method should actually be referred to as MINDO/3. It was later replaced by the MNDO method, which in turn was replaced by the PM3 and AM1 methods.
Zero differential overlap is an approximation in computational molecular orbital theory that is the central technique of semi-empirical methods in quantum chemistry. When computers were first used to calculate bonding in molecules, it was only possible to calculate diatomic molecules. As computers advanced, it became possible to study larger molecules, but the use of this approximation has always allowed the study of even larger molecules. Currently semi-empirical methods can be applied to molecules as large as whole proteins. The approximation involves ignoring certain integrals, usually two-electron repulsion integrals. If the number of orbitals used in the calculation is N, the number of two-electron repulsion integrals scales as N4. After the approximation is applied the number of such integrals scales as N2, a much smaller number, simplifying the calculation.

Spartan is a molecular modelling and computational chemistry application from Wavefunction. It contains code for molecular mechanics, semi-empirical methods, ab initio models, density functional models, post-Hartree–Fock models, and thermochemical recipes including G3(MP2) and T1. Quantum chemistry calculations in Spartan are powered by Q-Chem.
Semi-empirical quantum chemistry methods are based on the Hartree–Fock formalism, but make many approximations and obtain some parameters from empirical data. They are very important in computational chemistry for treating large molecules where the full Hartree–Fock method without the approximations is too expensive. The use of empirical parameters appears to allow some inclusion of electron correlation effects into the methods.
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initio was first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene. The background is described by Parr. Ab initio means "from first principles" or "from the beginning", implying that the only inputs into an ab initio calculation are physical constants. Ab initio quantum chemistry methods attempt to solve the electronic Schrödinger equation given the positions of the nuclei and the number of electrons in order to yield useful information such as electron densities, energies and other properties of the system. The ability to run these calculations has enabled theoretical chemists to solve a range of problems and their importance is highlighted by the awarding of the Nobel prize to John Pople and Walter Kohn.
Quantum chemistry composite methods are computational chemistry methods that aim for high accuracy by combining the results of several calculations. They combine methods with a high level of theory and a small basis set with methods that employ lower levels of theory with larger basis sets. They are commonly used to calculate thermodynamic quantities such as enthalpies of formation, atomization energies, ionization energies and electron affinities. They aim for chemical accuracy which is usually defined as within 1 kcal/mol of the experimental value. The first systematic model chemistry of this type with broad applicability was called Gaussian-1 (G1) introduced by John Pople. This was quickly replaced by the Gaussian-2 (G2) which has been used extensively. The Gaussian-3 (G3) was introduced later.

A sextuple bond is a type of covalent bond involving 12 bonding electrons and in which the bond order is 6. The only known molecules with true sextuple bonds are the diatomic dimolybdenum (Mo2) and ditungsten (W2), which exist in the gaseous phase and have boiling points of 4,639 °C (8,382 °F) and 5,930 °C (10,710 °F).

Walter Thiel was a German theoretical chemist. He was the president of the World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists (WATOC) from 2011.
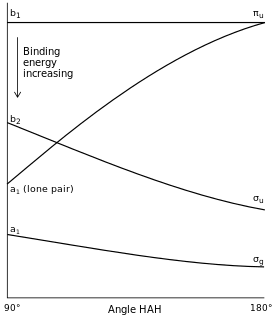
Walsh diagrams, often called angular coordinate diagrams or correlation diagrams, are representations of calculated orbital binding energies of a molecule versus a distortion coordinate, used for making quick predictions about the geometries of small molecules. By plotting the change in molecular orbital levels of a molecule as a function of geometrical change, Walsh diagrams explain why molecules are more stable in certain spatial configurations.
Michael Charles Zerner was an American theoretical chemist, professor at the University of Guelph from 1970 to 1981 and University of Florida from 1981 to 2000. Zerner earned his Ph.D. under Martin Gouterman at Harvard, working with the spectroscopy of porphyrins. He conceived and wrote a quantum chemistry program, known as BIGSPEC or ZINDO, for calculating electronic spectra of big molecules. In 1996 Zerner was diagnosed with liver cancer, and died on February 2, 2000, survived by his wife and two children.
References
- ↑ J. Ridley, M. Zerner, Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 32, 111–134.
- ↑ M. Zerner, Reviews in Computational Chemistry, Volume 2, Eds. K. B. Lipkowitz and D. B. Boyd, VCH, New York, 313, (1991)ю
- ↑ J. D. Da Motta Neto, M. Zerner, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2001, 81, 187–201.