Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship.
Contents
- Arts and entertainment
- Businesses and organisations
- People
- Places
- Transportation
- Other uses
- See also
Zeppelin may also refer to:
Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship.
Zeppelin may also refer to:

Svalbard, previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it lies about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed in size by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen on the west coast of Spitsbergen.

A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874 and developed in detail in 1893. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word zeppelin came to be commonly used to refer to all forms of rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and as scouts. Numerous bombing raids on Britain resulted in over 500 deaths.
Hansa may refer to:

A non-rigid airship, commonly called a blimp (/blɪmp/), is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships, blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas inside the envelope and the strength of the envelope itself to maintain their shape. Blimps are known for their use in advertising, surveillance, and as observation platforms due to their maneuverability and steady flight capabilities.

An airship, dirigible balloon or dirigible is a type of aerostat (lighter-than-air) aircraft that can navigate through the air flying under its own power. Aerostats use buoyancy from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air to achieve the lift needed to stay airborne.

Spitsbergen is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway in the Arctic Ocean.

A zeppelin bend is an end-to-end joining knot formed by two symmetrically interlinked overhand knots. It is stable, secure, and highly resistant to jamming. It is also resistant to the effects of slack shaking and cyclic loading.
The polar archipelago of Svalbard was first discovered by Willem Barentsz in 1596, although there is disputed evidence of use by Pomors or Norsemen. Whaling for bowhead whales started in 1611, dominated by English and Dutch companies, though other countries participated. At that time there was no agreement about sovereignty. Whaling stations, the largest being Smeerenburg, were built during the 17th century, but gradually whaling decreased. Hunting was carried out from the 17th century by Pomors, but from the 19th century it became more dominated by Norwegians.
A hunter is a person who hunts.

Umberto Nobile was an Italian aviator, aeronautical engineer and Arctic explorer.

The Svalbard Treaty recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty restricts military uses of the archipelago, but it is not demilitarized. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities on the islands. As of 2024, Norway and Russia make use of this right.

Pyramiden is an abandoned Soviet coal mining settlement on the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard which has become a tourist destination. Founded by Sweden in 1910 and sold to the Soviet Union in 1927, Pyramiden was closed in 1998 and has since remained largely abandoned with most of its infrastructure and buildings still in place, the cold climate preserving much of the infrastructure left behind.
A pyramid is a structure with triangular lateral surfaces converging to an apex.
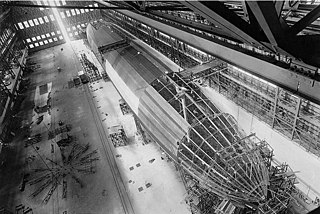
A rigid airship is a type of airship in which the envelope is supported by an internal framework rather than by being kept in shape by the pressure of the lifting gas within the envelope, as in blimps and semi-rigid airships. Rigid airships are often commonly called Zeppelins, though this technically refers only to airships built by the Luftschiffbau Zeppelin company.
Lanz may refer to:

A semi-rigid airship is an airship which has a stiff keel or truss supporting the main envelope along its length. The keel may be partially flexible or articulated and may be located inside or outside the main envelope. The outer shape of the airship is maintained by gas pressure, as with the non-rigid "blimp". Semi-rigid dirigibles were built in significant quantity from the late 19th century but in the late 1930s they fell out of favour along with rigid airships. No more were constructed until the semi-rigid design was revived by the Zeppelin NT in 1997.
Virgohamna is a small bay on the northern coast of Danes Island, an island off the northwestern coast of Spitsbergen. Spitsbergen and Danes Island are islands of the Svalbard archipelago. The bay is named after SS Virgo, the vessel of Swedish engineer and explorer Salomon August Andrée's 1896 expedition. Virgohamna is located across a small strait from Smeerenburg, a historical whaling station on Amsterdam Island about 2 km to the north.
Zeppelinhamna is a cove at the northern side of the peninsula Brøggerhalvøya in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It extends between the points Mainzodden and Gluudneset, and the island Prins Heinrichøya is located in the bay. The cove is named after German airships designer Ferdinand von Zeppelin.

Zeppelinfjellet is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It reaches a height of 556 m.a.s.l. and is located on the peninsula of Brøggerhalvøya, south of the former mining society of Ny-Ålesund and near Zeppelinhamna. The mountain is named after German military officer and airship designer Ferdinand von Zeppelin.

The Imperial German Navy Zeppelin LZ 24 was a M-class World War I zeppelin.