The prisoner's dilemma is a game theory thought experiment that involves two rational agents, each of whom can cooperate for mutual benefit or betray their partner ("defect") for individual reward. This dilemma was originally framed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher in 1950 while they worked at the RAND Corporation. Albert W. Tucker later formalized the game by structuring the rewards in terms of prison sentences and named it the "prisoner's dilemma".

The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People, first published in 1989, is a business and self-help book written by Stephen R. Covey. The book goes over his ideas on how to spur and nurture personal change, such as his thinking about effectiveness as a relationship between desired results and caring for that which produces results, his argument for the character ethic rather than the personality ethic, or his articulation of principles versus values. As named, his book is laid out through seven habits he has identified as conducive to personal growth.

Tit for tat is an English saying meaning "equivalent retaliation". It is an alteration of tip for tap "blow for blow", first recorded in 1558.

A zero tolerance policy is one which imposes a punishment for every infraction of a stated rule. Zero tolerance policies forbid people in positions of authority from exercising discretion or changing punishments to fit the circumstances subjectively; they are required to impose a predetermined punishment regardless of individual culpability, extenuating circumstances, or history. This predetermined punishment, whether mild or severe, is always meted out.
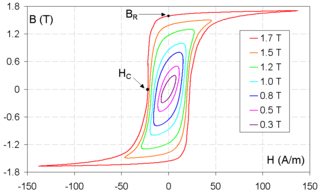
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized. Coercivity is usually measured in oersted or ampere/meter units and is denoted HC.

In politics, a defector is a person who gives up allegiance to one state in exchange for allegiance to another, changing sides in a way which is considered illegitimate by the first state. More broadly, defection involves abandoning a person, cause, or doctrine to which one is bound by some tie, as of allegiance or duty.
In aviation air safety, a tombstone mentality informally is a pervasive attitude of ignoring design defects until people have died because of them.
In game theory, a win–win game or win–win scenario is a situation that produces a mutually beneficial outcome for two or more parties. It is also called a positive-sum game as it is the opposite of a zero-sum game. If a win–win scenario is not achieved, the scenario becomes a lose–lose situation by default, since it had caused failure for at least one of the parties. While she did not coin the term, Mary Parker Follett's process of integration described in her book Creative Experience forms the basis of what we now refer to as the idea of "win-win" conflict resolution.

An induction cut, also referred to as a mighty fine, is the shortest possible hairstyle without shaving the head with a razor. The style is so named as it is traditionally the first haircut given to new male recruits during initial entry into many of the world's armed forces, but most particularly in the United States.
In the semiconductor industry, the term high-κ dielectric refers to a material with a high dielectric constant, as compared to silicon dioxide. High-κ dielectrics are used in semiconductor manufacturing processes where they are usually used to replace a silicon dioxide gate dielectric or another dielectric layer of a device. The implementation of high-κ gate dielectrics is one of several strategies developed to allow further miniaturization of microelectronic components, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's Law.
Philip Bayard "Phil" Crosby, was an American businessman and author who contributed to management theory and quality management practices.
The cleanroom software engineering process is a software development process intended to produce software with a certifiable level of reliability. The central principles are software development based on formal methods, incremental implementation under statistical quality control, and statistically sound testing.

A relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD), also known as a Marcus Gunn pupil, is a medical sign observed during the swinging-flashlight test whereupon the patient's pupils dilate when a bright light is swung from the unaffected eye to the affected eye. The affected eye still senses the light and produces pupillary sphincter constriction to some degree, albeit reduced.
Zero Defects was a management-led program to eliminate defects in industrial production that enjoyed brief popularity in American industry from 1964 to the early 1970s. Quality expert Philip Crosby later incorporated it into his "Absolutes of Quality Management" and it enjoyed a renaissance in the American automobile industry—as a performance goal more than as a program—in the 1990s. Although applicable to any type of enterprise, it has been primarily adopted within supply chains wherever large volumes of components are being purchased.

A dihedron is a type of polyhedron, made of two polygon faces which share the same set of n edges. In three-dimensional Euclidean space, it is degenerate if its faces are flat, while in three-dimensional spherical space, a dihedron with flat faces can be thought of as a lens, an example of which is the fundamental domain of a lens space L(p,q). Dihedra have also been called bihedra, flat polyhedra, or doubly covered polygons.
Zero tolerance is a type of punishment policy. The term can also refer to:

Crab mentality, also known as crab theory, crabs in a bucket mentality, or the crab-bucket effect, is a way of thinking usually described by the phrase "if I can't have it, neither can you".

The early insurgency phase of the Syrian civil war lasted from late July 2011 to April 2012, and was associated with the rise of armed oppositional militias across Syria and the beginning of armed rebellion against the authorities of the Syrian Arab Republic. Though armed insurrection incidents began as early as June 2011 when rebels killed 120–140 Syrian security personnel, the beginning of organized insurgency is typically marked by the formation of the Free Syrian Army (FSA) on 29 July 2011, when a group of defected officers declared the establishment of the first organized oppositional military force. Composed of defected Syrian Armed Forces personnel, the rebel army aimed to remove Bashar al-Assad and his government from power.

Bioculture is the second studio album by Electro Assassin, released in November 1993 by Hyperium Records. The album was reissued on 16 May 1995 by Metropolis Records for distribution in the United States.










