
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvins. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15° on the Celsius scale, which equals −459.67° on the Fahrenheit scale. The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition.

An integer is colloquially defined as a number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5+1/2, and √2 are not.

The Mitsubishi A6M "Zero" was a long-range fighter aircraft formerly manufactured by Mitsubishi Aircraft Company, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1940 to 1945. The A6M was designated as the Mitsubishi Navy Type 0 carrier fighter, or the Mitsubishi A6M Rei-sen. The A6M was usually referred to by its pilots as the Reisen, "0" being the last digit of the imperial year 2600 (1940) when it entered service with the Imperial Navy. The official Allied reporting name was "Zeke", although the name "Zero" was used colloquially by the Allies as well.
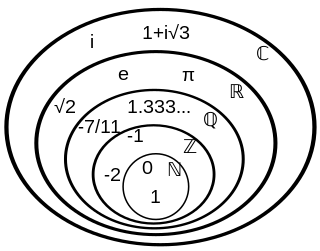
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels, for ordering, and for codes. In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents.
Observational error is the difference between a measured value of a quantity and its true value. In statistics, an error is not a "mistake". Variability is an inherent part of the results of measurements and of the measurement process.
In game theory and economic theory, a zero-sum game is a mathematical representation of a situation in which each participant's gain or loss of utility is exactly balanced by the losses or gains of the utility of the other participants. If the total gains of the participants are added up and the total losses are subtracted, they will sum to zero. Thus, cutting a cake, where taking a larger piece reduces the amount of cake available for others as much as it increases the amount available for that taker, is a zero-sum game if all participants value each unit of cake equally.
0 (zero) is a number, and the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals. It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems. Names for the number 0 in English include zero, nought (UK), naught (US), nil, or—in contexts where at least one adjacent digit distinguishes it from the letter "O"—oh or o. Informal or slang terms for zero include zilch and zip. Ought and aught, as well as cipher, have also been used historically.

In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used, with this or similar meanings, in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, rather than to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band.

A vernier scale is a visual aid to take an accurate measurement reading between two graduation markings on a linear scale by using mechanical interpolation; thereby increasing resolution and reducing measurement uncertainty by using vernier acuity to reduce human estimation error.
In relation to nuclear explosions and other large bombs, ground zero is the point on the Earth's surface closest to a detonation. In the case of an explosion above the ground, ground zero is the point on the ground directly below the nuclear detonation and is sometimes called the hypocenter.

In mathematics, division by zero is division where the divisor (denominator) is zero. Such a division can be formally expressed as a/0 where a is the dividend (numerator). In ordinary arithmetic, the expression has no meaning, as there is no number which, when multiplied by 0, gives a, and so division by zero is undefined. Since any number multiplied by zero is zero, the expression 0/0 is also undefined; when it is the form of a limit, it is an indeterminate form. Historically, one of the earliest recorded references to the mathematical impossibility of assigning a value to a/0 is contained in George Berkeley's criticism of infinitesimal calculus in 1734 in The Analyst.
A zero-tolerance policy is one which imposes a punishment for every infraction of a stated rule. Zero-tolerance policies forbid people in positions of authority from exercising discretion or changing punishments to fit the circumstances subjectively; they are required to impose a pre-determined punishment regardless of individual culpability, extenuating circumstances, or history. This pre-determined punishment, whether mild or severe, is always meted out.
The significant figures of a number written in positional notation are digits that carry meaningful contributions to its measurement resolution. This includes all digits except:
1000 or one thousand is the natural number following 999 and preceding 1001. In most English-speaking countries, it is often written with a comma separating the thousands unit: 1,000.

Zero Waste is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages the redesign of resource life cycles so that all products are reused. The goal is for no trash to be sent to landfills, incinerators or the ocean. Currently, only 9% of plastic is actually recycled. In a zero waste system, material will be reused until the optimum level of consumption. The definition adopted by the Zero Waste International Alliance (ZWIA) is:
Zero Waste: The conservation of all resources by means of responsible production, consumption, reuse and recovery of all products, packaging, and materials, without burning them, and without discharges to land, water or air that threaten the environment or human health.
The year zero does not exist in the Anno Domini (AD) system commonly used to number years in the Gregorian calendar and in its predecessor, the Julian calendar. In this system, the year 1 BC is followed by AD 1. However, there is a year zero in astronomical year numbering and in ISO 8601:2004, as well as in all Buddhist and Hindu calendars.
The zero-width space (), abbreviated ZWSP, is a non-printing character used in computerized typesetting to indicate word boundaries to text processing systems when using scripts that do not use explicit spacing, or after characters that are not followed by a visible space but after which there may nevertheless be a line break. It is also used with languages without visible space between words, for example Japanese. Normally, it is not a visible separation, but it may expand in passages that are fully justified.

Zero Dark Thirty is a 2012 American thriller film directed by Kathryn Bigelow and written by Mark Boal. The film dramatizes the nearly decade-long international manhunt for Al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden after the September 11 attacks. This search leads to the discovery of his compound in Pakistan and the military raid that resulted in bin Laden's death on May 2, 2011.

Re:Zero − Starting Life in Another World is a Japanese light novel series written by Tappei Nagatsuki and illustrated by Shin'ichirō Ōtsuka. The story centres on Subaru Natsuki, a hikikomori who suddenly finds himself transported to another world on his way home from the convenience store. The series was initially serialized on the website Shōsetsuka ni Narō from 2012 onwards. Twenty-one light novels, as well as four side story volumes and five short story collections have been published by Media Factory under their MF Bunko J imprint.









