
Guangdong, formerly romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.84 million across a total area of about 179,800 km2 (69,400 sq mi), Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world.

Zhuhai, also known as Chuhai, is a prefecture-level city located on the west bank of the Pearl River estuary on the central coast of southern Guangdong province, People's Republic of China, on the southeastern edge of the Pearl River Delta. Its name literally means "pearl sea", which originates from the city's location at the mouth of the Pearl River meeting the South China Sea. Zhuhai borders Jiangmen to the west, Zhongshan to the north and Macau to the southeast, and shares maritime boundaries with Shenzhen and Hong Kong to the northeast across the estuary.

The Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region is the low-lying area surrounding the Pearl River estuary, where the Pearl River flows into the South China Sea. Referred to as the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in official documents, the region is one of the most densely populated and urbanized regions in the world, and is considered a megacity by numerous scholars. It is currently the wealthiest region in Southern China and one of the wealthiest regions in China along with the Yangtze River Delta in Eastern China and Jingjinji in Northern China. Most of the region is part of the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, which is a special economic zone of China.

The Hong Kong–Zhuhai–Macau Bridge (HZMB) is a 55-kilometre (34 mi) bridge–tunnel system consisting of a series of three cable-stayed bridges, an undersea tunnel, and four artificial islands. It is both the longest sea crossing and the longest open-sea fixed link in the world. The HZMB spans the Lingding and Jiuzhou channels, connecting Hong Kong and Macau with Zhuhai— a major city on the Pearl River Delta in China.
Xiamen Special Economic Zone, established in October 1980, is one of the five special economic zones in the People's Republic of China. Originally comprising a territory of 2.5 km2 in Xiamen City, it was expanded to 131 km2 in 1984, covering the entire Xiamen Island, which comprises Huli District and Siming District excluding Gulangyu.

Nanchang is the capital of Jiangxi Province, People's Republic of China. Located in the north-central part of the province and in the hinterland of Poyang Lake Plain, it is bounded on the west by the Jiuling Mountains, and on the east by Poyang Lake. Because of its strategic location connecting the prosperous East and South China, it has become a major railway hub in Southern China in recent decades.

Xiangshan County, also spelled Hsiangshan, Siangshan, Heungsan, and Heungshan, was a former county in Southern China. Since 1912, it was a county in Kwangtung Province ("Guangdong"), in the Republic of China. It was renamed Zhongshan County in April 1925, in honor of the founder of the Republic of China, Sun Yat Sen, a Xiangshan native.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind. It stretches from the outer limit of the territorial sea out to 200 nautical miles (nmi) from the coast of the state in question. It is also referred to as a maritime continental margin and, in colloquial usage, may include the continental shelf. The term does not include either the territorial sea or the continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit. The difference between the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone is that the first confers full sovereignty over the waters, whereas the second is merely a "sovereign right" which refers to the coastal state's rights below the surface of the sea. The surface waters are international waters.

Hengqin is an island that lies mostly in Zhuhai, a prefecture-level city and special economic zone in Guangdong Province of the People's Republic of China. It has a population of about 3,000. Parts of Hengqin are leased to Macau by the State Council of the People's Republic of China, starting from 2009, mostly to house the new campus of the University of Macau. In the leased parts of the island, Macau law applies.
In justifying opening up and the series of economic reforms that ensued, Deng referred to Marx and his theories, which predicted that nations need to undergo urbanization and a stage of capitalism for a natural socialist transition. One of the most renowned reforms under Deng was establishing four "special economic zones" along the Southeastern coast of China, with Shenzhen, Shantou, and Zhuhai located in Guangdong province and Xiamen located in Fujian province. Special economic zones (SEZs) in mainland China are granted more free market-oriented economic policies and flexible governmental measures by the government of China, compared to the planned economy elsewhere.
The Shenzhen Special Economic Zone is a special economic zone (SEZ) of China. One of four special economic zones (SEZ) established in May 1980, it was the first SEZ created by Deng Xiaoping, and, like the other three zones, was modeled after Ireland's Shannon Free Zone.
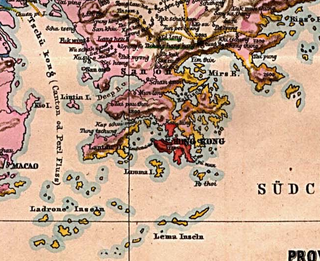
The Wanshan Archipelago, formerly known as the Ladrones Islands, is a 104-island archipelago that is a part of Xiangzhou District in Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China.
Shantou Special Economic Zone, located within Shantou, Guangdong, is one of the five special economic zones in the People's Republic of China.
The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, is a special economic zone on the southeastern coast of China. Located in the Pearl River Delta, it consists of the Chinese cities of Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, and parts of Huizhou and Zhaoqing. Adjacent Hong Kong and Macau are not part of the economic zone.
TransGlobal Airways was a cargo airline based in Clark International Airport, Philippines. The airline flies from Angeles-Clark to China and Taiwan and to key points in the Philippines, and operates regular charter flights to the Middle East in co-operation with Kang Pacific Airlines. The Airline has also expressed their intentions to fly passenger flights to South Korea with a fleet of MD-82 and MD-83 aircraft.

The economy of Guangdong is one of the most prosperous in China. Guangdong is located in southern China, bordering on Fujian Province to the east, Hunan Province to the north, Guangxi Autonomous Region to the west and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau to the south. It is also the largest economy of a sub-national entity in terms of GDP in all of Asia and 3rd largest sub-national entity in the world.
The following lists events in the year 1980 in China.
Zhuhai National High-Tech Industrial Development District (珠海高新技术产业开发区) was established in December, 1992 by the State Council of the People's Republic of China. It is also called Zhuhai National Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone. It has an initial area of 9.8 square kilometers. Following a 1999 adjustment, it now includes four industrial parks: Nanping (南屏), Sanzao (三灶), Baijiao (白蕉) and Xinqing (新青), and an innovation coast.

The Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area also referred to as the Greater Bay Area (GBA), is a megalopolis, consisting of nine cities and two special administrative regions in South China. It is envisioned as an integrated economic area aimed at taking a leading role globally by 2035.

Deng Xiaoping's southern tour, or 1992 southern tour, was the tour of Deng Xiaoping, the former Paramount leader of China, in southern China, including in Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Guangzhou and Shanghai, from January 18 to February 21, 1992. The talks and remarks made by Deng during the tour resumed and reinforced the implementation of his "Reforms and Opening-up" program in mainland China, which came to a halt after the military crackdown on 1989 Tiananmen Square protests ordered by Deng himself. The 1992 Southern Tour is widely regarded as a critical point in the modern history of China, as it saved the Chinese economic reform as well as the capital market, and preserved the stability of the society.












