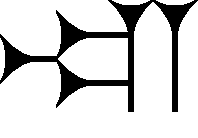The cuneiform lu sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for lu, and an alphabetic sign used for l, or u; it has many other sub-uses, as seen in the Epic of Gilgamesh over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. Its other uses show other syllabic and alphabetic forms that it can be used for: other vowels, or consonants;. There are also four sumerogrammic sub-forms for "lu" in the Epic of Gilgamesh, LU, and UDU, and DAB and DIB; LU transposes to Akkadian language, "lullû", for English language, (primitive) man; DAB transposes to ṣabātu, English for to seize, capture.

The cuneiform ma sign, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Epic it is also used as the Sumerogram MA, . The ma sign is often used at the end of words, besides its alphabetic usage inside words as syllabic ma, elsewhere for m, or a.

The cuneiform Ne sign, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Amarna letters, it is especially used in the opening, and introductory paragraph of the clay tablet letter, when addressing the Pharaoh (King), or when sent to another individual who is part of the Pharaoh's correspondence, for the alternate syllabic usage of "bil",. In the Amarna letters, it is used as Bil (cuneiform), for the spelling of speaks, or "says", in the opening statement; the Akkadian language word is "qabû", for to say, tell.

The cuneiform sign 𒀀 for a, and in the Epic of Gilgamesh the sumerogram A, Akkadian for mû, "water", which is used in the Gilgamesh flood myth, Chapter XI of the Epic, or other passages. The sign is also used extensively in the Amarna letters.

The cuneiform Ri sign, or Re, is found in both the 14th-century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh; it is in the top 25 most used cuneiform signs for ri, or re, but has other syllabic or alphabetic uses, as well as the Sumerogram usage for RI.

The cuneiform pa sign,, has many uses in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is routinely and commonly used to spell the Akkadian language word "pānu", face, presence, and with a preposition, before. In the photo of the obverse of EA 364, it is used to spell Akkadian "eperu", 'dust', (EA 364, lines 7,8: "...andand \ dust"-.

The cuneiform DAGAL sign, which is a capital letter (majuscule) Sumerogram with the Akkadian language meaning of to be wide, or extensive; also "many", Akkadian "rapāšu", is a minor usage cuneiform sign used in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. An equivalent usage sign for DAGAL is used in the Amarna letters, gáb, for Akkadian language "gabbu", and is found in such letters as EA 362, EA 367, and others. Gáb has other syllabic values, which are used for separate Akkadian word components.

The cuneiform sign for the syllable ab also represents that for ap, or the vowel and consonant usages of a, b, or p: in the Akkadian language "b" is unaspirated, formed with the lips, and "p" is aspirated, with the breath). In the Akkadian language "b" and "p" are interchangeable; also, in cuneiform texts, any vowel can be interchanged with any other. The ab/ap sign also has a corresponding capital letter (majuscule) usage as a sumerogram, as found in the Epic of Gilgamesh for AB, the Akkadian language for šību, meaning "elder".

The cuneiform šu sign is a common, multi-use syllabic and alphabetic sign for šu, š, and u; it has a subsidiary usage for syllabic qat; it also has a majuscule-(capital letter) Sumerogram usage for ŠU, for Akkadian language "qātu", the word for "hand". The human hand is the shape of cuneiform character šu, and thus the origin of its creation.

The cuneiform i sign is a common use vowel sign. It can be found in many languages, examples being the Akkadian language of the Epic of Gilgamesh and the mid 14th-century BC Amarna letters; also the Hittite language-(see table of Hittite cuneiform signs below).

The cuneiform sign LÚ is the sign used for "man"; its complement is the symbol for woman: šal. Cuneiform LÚ, is found as a Sumerogram in the Epic of Gilgamesh. It also has a common usage in the 1350 BC Amarna letters as the Sumerogram for "man".
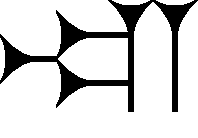
The cuneiform sign URU is a relatively distinctive sign in the cuneiform sign lists; with its two verticals at the sign's right, and the central long horizontal stroke, it is not easily confused with other signs. It is commonly found in the intrigues of the 14th century BC Amarna letters since the letters often concern city-state locations, or surrounding regions or cities/towns. URU is also used in the Epic of Gilgamesh. The cuneiform sign is almost exclusively used as a Sumerogram, and in the Akkadian language, it is the Akkadian for "ālu", city, or town. The usage of URU in the Epic of Gilgamesh is only for Sumerogram "URU",. All uses in the Epic for URU are for various spellings of ālu, and usually an added sign complement; there is one usage in the Epic of URU for the city Shuruppak: URU.Šu-ri-ip-pak,.

The cuneiform mi, sign is a distinctive sign in the wedge-stroke group, and is used as a syllabic for mi, me, and an alphabetic for m, i, or e; it is also a Sumerogram for MI, used for Akkadian language, "mūšu", night. MI, in the Epic of Gilgamesh, is used in (Chapters) Tablets I, II, III, and XII as either MI, or MI.MEŠ, a total of six times; other spellings of mūšu in other sections are alphabetic/syllabic, four times.
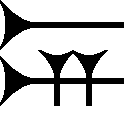
The cuneiform sign ni is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the Epic of Gilgamesh, and other cuneiform texts. It has a secondary sub-use in the Amarna letters for addressing the Pharaoh, from the vassal states of Canaan. The address to the Pharaoh is often 'King-Lord-Mine': LUGAL, EN-ia which has many varieties of expression. "LUGAL" is Akkadian language for "Šarru", English "king", and EN in Akkadian is bēlu, for "Lord",. In some Amarna letters the sub-use of ni is lí, for spelling "bēlu", be-lí often .

The cuneiform sign ši, lim, and Sumerogram IGI is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the Epic of Gilgamesh, and other cuneiform texts. As the syllabic form it is commonly used for ši, lim/lem, and for Sumerograms, it is most commonly used for IGI, and "before". Also, for ši and lim/lem it can be used syllabically for š, i, l, i/e, and m, in the spelling of words.

The cuneiform giš sign,, is a common, multi-use sign, in the Epic of Gilgamesh, the Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It also has a major usage as a sumerogram, GIŠ, for English language "wood", and is used as a determinative at the beginning of words, for items made of wood. The 12 Chapters (Tablets) of the Epic of Gilgamesh lists 16 named items beginning with "GIŠ".

The cuneiform di sign, also de, ṭe, ṭi, and sumerograms DI and SÁ is a common-use sign of the Epic of Gilgamesh, the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. In the Akkadian language for forming words, it can be used syllabically for: de, di, ṭe, and ṭi; also alphabetically for letters d, ṭ, e, or i. Some consonant-pairs (d/t), are also interchangeable.
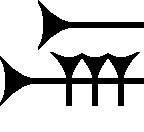
The cuneiform sa sign is a less common-use sign of the Epic of Gilgamesh, the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It also has a sumerogrammic usage for SA in the Epic of Gilgamesh. The structure of the cuneiform sign is similar to, Ir (cuneiform), .

The cuneiform sign mu, is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the Epic of Gilgamesh, and other cuneiform texts. It is also used as MU.

The cuneiform gi sign is a common multi-use sign of the Epic of Gilgamesh, the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It also has a sumerogrammic usage for GI in the Epic of Gilgamesh. The structure of the cuneiform sign is like its twin, Zi (cuneiform), .



![]() .
.