
An electrical insulator is a material in which the electron does not flow freely or the atom of the insulator have tightly bound electrons whose internal electric charges do not flow freely; very little electric current will flow through it under the influence of an electric field. This contrasts with other materials, semiconductors and conductors, which conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals.

A transmission medium is something that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication.
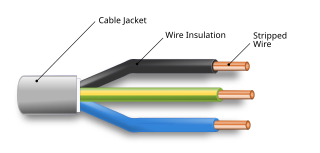
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current.

Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell.

An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to join electrical conductors and create an electrical circuit. Most electrical connectors have a gender – i.e. the male component, called a plug, connects to the female component, or socket. The connection may be removable, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two points. An adapter can be used to join dissimilar connectors.

A ferrule is any of a number of types of objects, generally used for fastening, joining, sealing, or reinforcement. They are often narrow circular rings made from metal, or less commonly, plastic. Ferrules are also often referred to as eyelets or grommets within the manufacturing industry.

The 25-pair color code, originally known as even-count color code, is a color code used to identify individual conductors in twisted-pair wiring for telecommunications.
Electrical wiring in North America follows regulations and standards for installation of building wiring which ultimately provides mains electricity.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.

An extension cord, power extender, drop cord, or extension lead is a length of flexible electrical power cable (flex) with a plug on one end and one or more sockets on the other end. The term usually refers to mains extensions but is also used to refer to extensions for other types of cabling. If the plug and power outlet are of different types, the term "adapter cord" may be used. Most extension cords range from around two to thirty feet in length although they are made up to 300 feet in length.
A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed.

A submarine power cable is a transmission cable for carrying electric power below the surface of the water. These are called "submarine" because they usually carry electric power beneath salt water but it is also possible to use submarine power cables beneath fresh water. Examples of the latter exist that connect the mainland with large islands in the St. Lawrence River.

A patch cable, patch cord or patch lead is an electrical or optical cable used to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types are connected with patch cords.

Speaker wire is used to make the electrical connection between loudspeakers and audio amplifiers. Modern speaker wire consists of two or more electrical conductors individually insulated by plastic or, less commonly, rubber. The two wires are electrically identical, but are marked to identify the correct audio signal polarity. Most commonly, speaker wire comes in the form of zip cord.
An optical ground wire is a type of cable that is used in overhead power lines. Such cable combines the functions of grounding and communications. An OPGW cable contains a tubular structure with one or more optical fibers in it, surrounded by layers of steel and aluminum wire. The OPGW cable is run between the tops of high-voltage electricity pylons. The conductive part of the cable serves to bond adjacent towers to earth ground, and shields the high-voltage conductors from lightning strikes. The optical fibers within the cable can be used for high-speed transmission of data, either for the electrical utility's own purposes of protection and control of the transmission line, for the utility's own voice and data communication, or may be leased or sold to third parties to serve as a high-speed fiber interconnection between cities.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example, long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
Networking cables are networking hardware used to connect one network device to other network devices or to connect two or more computers to share printers, scanners etc. Different types of network cables, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber cable, and twisted pair cables, are used depending on the network's physical layer, topology, and size. The devices can be separated by a few meters or nearly unlimited distances.

Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.
Physical media refers to the physical materials that are used to store or transmit information in data communications. These physical media are generally physical objects made of materials such as copper or glass. They can be touched and felt, and have physical properties such as weight and color. For a number of years, copper and glass were the only media used in computer networking.
In telecommunications, a line splice is a method of connecting electrical cables or optical fibers.














