
Zvi Wiener is a Professor of Finance and the former dean [1] of the Hebrew University Business School Business administration at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. [2]

Zvi Wiener is a Professor of Finance and the former dean [1] of the Hebrew University Business School Business administration at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. [2]
Wiener has Ph.D. in mathematics from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot (1994). He completed postdoc at the Wharton Business School of the University of Pennsylvania and then joined the Fixed Income division of Lehman Brothers in New York City. Since 1996 Wiener joined the Hebrew University faculty.
Wiener is the former Head of the Finance Department and the academic manager of the Executive MBA program [3] specializing in Finance and Banking at the Hebrew University.
Wiener is one of the founders [4] of the Professional Risk Managers' International Association (PRMIA) and serves as a director of PRMIA in Israel. [5] He also served as a consultant for many institutions like Pension funds, Ministry of Finance, the Bank of Israel, Israel Securities Authority [6] and the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. Wiener also served at the Bank of Israel foreign reserves investment committee.
Wiener provides lobbying services to Bank Hapoalim, and also holds a private company, named Optimize Risk Management Ltd. According to an investigation by The Marker magazine, Wiener's private activities violate the directives of the Supervisor of Wages and Labor Agreements since he serves at the same time as Dean at the Hebrew University and founded by the Israeli government. According to Wiener these activities are in line with regulations. However, the Council for Higher Education did not confirm his claim and instruct the Hebrew University to examine Wiener's employment exception. The Enforcement Branch at the Office of the Supervisor of Wages and Labor Agreements also initiated an examination of that exception. [7] It was also reported that Wiener has promoted a private entrepreneur's appointment at the Hebrew University immediately before the last contributed a large amount of money to the School of Business Administration at the Hebrew University. [8]
Wiener won the Rothschild Fellowship [9] for young scholars of outstanding academic merit and the Alon fellowship for young excellent Scientists. He also won the Teva prize named after Dan Suesskind for research on Dividend policy. [10]
His areas of expertise are Financial modeling, Risk Management, Options and other derivatives with Applications to Corporate finance, Structured product, Stochastic process, Monte Carlo Simulation and Game Theory.
In finance, bond convexity is a measure of the non-linear relationship of bond prices to changes in interest rates, and is defined as the second derivative of the price of the bond with respect to interest rates. In general, the higher the duration, the more sensitive the bond price is to the change in interest rates. Bond convexity is one of the most basic and widely used forms of convexity in finance. Convexity was based on the work of Hon-Fei Lai and popularized by Stanley Diller.

A short-rate model, in the context of interest rate derivatives, is a mathematical model that describes the future evolution of interest rates by describing the future evolution of the short rate, usually written .
Financial risk management is the practice of protecting economic value in a firm by managing exposure to financial risk - principally operational risk, credit risk and market risk, with more specific variants as listed aside. As for risk management more generally, financial risk management requires identifying the sources of risk, measuring these, and crafting plans to mitigate them. See Finance § Risk management for an overview.
Financial modeling is the task of building an abstract representation of a real world financial situation. This is a mathematical model designed to represent the performance of a financial asset or portfolio of a business, project, or any other investment.

Market sentiment, also known as investor attention, is the general prevailing attitude of investors as to anticipated price development in a market. This attitude is the accumulation of a variety of fundamental and technical factors, including price history, economic reports, seasonal factors, and national and world events. If investors expect upward price movement in the stock market, the sentiment is said to be bullish. On the contrary, if the market sentiment is bearish, most investors expect downward price movement. Market participants who maintain a static sentiment, regardless of market conditions, are described as permabulls and permabears respectively. Market sentiment is usually considered as a contrarian indicator: what most people expect is a good thing to bet against. Market sentiment is used because it is believed to be a good predictor of market moves, especially when it is more extreme. Very bearish sentiment is usually followed by the market going up more than normal, and vice versa. A bull market refers to a sustained period of either realized or expected price rises, whereas a bear market is used to describe when an index or stock has fallen 20% or more from a recent high for a sustained length of time.
Momentum investing is a system of buying stocks or other securities that have had high returns over the past three to twelve months, and selling those that have had poor returns over the same period.
In financial mathematics, the Ho-Lee model is a short-rate model widely used in the pricing of bond options, swaptions and other interest rate derivatives, and in modeling future interest rates. It was developed in 1986 by Thomas Ho and Sang Bin Lee.
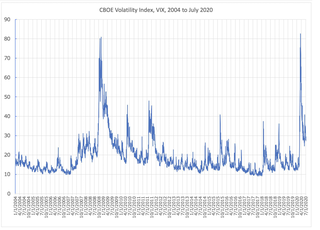
VIX is the ticker symbol and the popular name for the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index, a popular measure of the stock market's expectation of volatility based on S&P 500 index options. It is calculated and disseminated on a real-time basis by the CBOE, and is often referred to as the fear index or fear gauge.
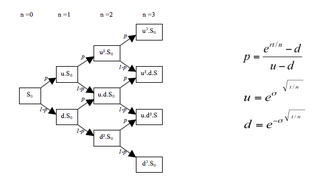
In finance, a lattice model is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where a discrete time model is required. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at "all" times before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black–Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, where because of path dependence in the payoff, Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, though methods now exist for solving this problem.

In finance, volatility is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns.
An exchange-traded note (ETN) is a senior, unsecured, unsubordinated debt security issued by an underwriting bank or by a special-purpose entity. Similar to other debt securities, ETNs may have a maturity date and are backed by the credit of the issuer, though some ETNs may have a portfolio of assets given as a collateral.
George S. Oldfield is a financial economist. He has been published extensively, and is cited for his work on the effects of a firm's unvested pension benefits on its share price published in the Journal of Money, Credit and Banking in 1977.
In finance, model risk is the risk of loss resulting from using insufficiently accurate models to make decisions, originally and frequently in the context of valuing financial securities.
Menachem Brenner is a professor of finance and a Bank and Financial Analysts Faculty Fellow at New York University Stern School of Business.
In financial mathematics, the Black–Karasinski model is a mathematical model of the term structure of interest rates; see short-rate model. It is a one-factor model as it describes interest rate movements as driven by a single source of randomness. It belongs to the class of no-arbitrage models, i.e. it can fit today's zero-coupon bond prices, and in its most general form, today's prices for a set of caps, floors or European swaptions. The model was introduced by Fischer Black and Piotr Karasinski in 1991.
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, investment management and other related finance occupations. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns.
Söhnke Matthias Bartram is a professor in the Department of Finance at Warwick Business School (WBS). He is also a research fellow in the Financial Economics programme and the International Macroeconomics and Finance programme of the Centre for Economic Policy Research (CEPR), a charter member of Risk Who's Who, and a member of an international think tank for policy advice to the German government. Prior to joining the University of Warwick, he held faculty positions at Lancaster University and Maastricht University and worked for several years in quantitative investment management at State Street Global Advisors as Head of the London Advanced Research Center.

Svetlozar (Zari) Todorov Rachev is a professor at Texas Tech University who works in the field of mathematical finance, probability theory, and statistics. He is known for his work in probability metrics, derivative pricing, financial risk modeling, and econometrics. In the practice of risk management, he is the originator of the methodology behind the flagship product of FinAnalytica.
The Hebrew University Business School, is the business school of The Hebrew University and based in Mt. Scopus. Founded in 1952 by Daniel and Raphael Recanati, The Jerusalem School of Business Administration is consistently rated as one of the top business schools in the country, for programs instructed in both Hebrew and English.

Orly Sade is a financial economist based out of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem who has been noted for her research regarding behavioral and experimental finance and crowdfunding platforms. Sade is the Israel Associate Professor of Finance at the Department of Finance, School of Business Administration at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. She is the first female professor in the field of finance at Hebrew University.