
In folklore, giants are beings of human-like appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word giant is first attested in 1297 from Robert of Gloucester's chronicle. It is derived from the Gigantes of Greek mythology.

The Leshy is a tutelary deity of the forests in pagan Slavic mythology. As the spirit rules over the forest and hunting, he may be related to the Slavic god Porewit.
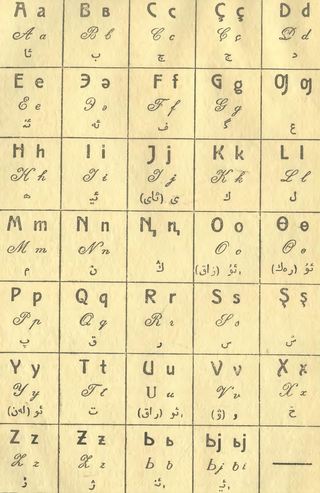
Jaꞑalif, Yangalif or Yañalif is the first Latin alphabet used during the latinisation in the Soviet Union in the 1930s for the Turkic languages. It replaced the Yaña imlâ Arabic script-based alphabet in 1928, and was replaced by the Cyrillic alphabet in 1938–1940. After their respective independence in 1991, several former Soviet states in Central Asia switched back to Latin script, with slight modifications to the original Jaꞑalif.

Şüräle is a forest spirit in Tatar and Bashkir mythology. According to legends, Şüräle lives in forests. He has long fingers, a horn on its forehead, and a woolly body. He lures victims into the thickets and can tickle them to death.

The Curupira is a mythological creature of Brazilian folklore.
Od iyesi is the Turkic and Mongolian spirit or deity of fire. In Turkic languages, Od means fire, and iye is the familiar spirit of any natural asset, literally meaning "master" or "possessor." Od iyesi protects the fire.

Turkic mythology refers to myths and legends told by the Turkic people. It features Tengrist and Shamanist strata of belief along with many other social and cultural constructs related to the nomadic and warrior way of life of Turkic and Mongol peoples in ancient times. Turkic mythology shares numerous points in common with Mongol mythology. Turkic mythology has also been influenced by other local Asiatic and Eurasian mythologies. For example, in Tatar mythology elements of Finnic and Indo-European mythologies co-exist. Beings from Tatar mythology include Äbädä, Alara, Şüräle, Şekä, Pitsen, Tulpar, and Zilant.

Pitsen is a forest creature in the Siberian Tatars' mythology.

Sheka is a dwarf-like being in the Turkic mythology, that lives in forests or derelict houses. In the legends he uses to appear in comic situation.
Ötüken was the capital of the First Turkic Khaganate and Uyghur Khaganate. It has an important place in Turkic mythology and Tengrism. Otukan (Ötüken) is also one of the names given to Mother Earth. Otuken is located in Kharkhorin district in Övörkhangai Province of present-day Mongolia.
Mythic humanoids are mythological creatures that are part human, or that resemble humans through appearance or character. Each culture has different mythical creatures that come from many different origins. A major chunk of these creatures are humanoids. They are often able to talk and in many stories they guide the hero on their journey. They are said to come before the creation of gods and goddesses.
Ev iyesi is a household deity in Turkic mythology. Also known as Uy (Oy) iyesi or Yurt iyesi.
In Turkic mythology, Su Iyesi is a water spirit. It corresponds to the nymph in Turkic cultures. It is a disembodied, incorporeal, intangible entity, but she can turn into a female creature and daughter of Yer Tanrı. Sometimes the master of water is depicted in the form of a bull.
Yel iyesi is the Turkic spirit or deity of wind. The name comes from the Turkic words "Yel," which means wind, and "iye," the familiar spirit of any natural asset.
Archura is a shapeshifting woodland spirit in Turkic mythology who protects wild animals and forests.
In Turkic mythology Ergene iyesi is an underground spirit. It is the protector spirit of mine pit, and can turn into an animal. The word "İye" means owner, master or possessor. Also known as Shakhta iyesi.
Lower mythology is a sphere of mythological representations relating to characters who have no divine status, demons and spirits, as opposed to higher gods and the official cult. This opposition is particularly pronounced in world religions.





