| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events from the year 1507 in India.
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events from the year 1507 in India.

Amerigo Vespucci was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Florence, from whose name the term "America" is derived.

Year 1507 (MDVII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.
Year 1442 (MCDXLII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar.

Joanna, historically known as Joanna the Mad, was the nominal queen of Castile from 1504 and queen of Aragon from 1516 to her death in 1555. She was the daughter of Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. Joanna was married by arrangement to the Austrian archduke Philip the Handsome on 20 October 1496. Following the deaths of her elder brother John, elder sister Isabella, and nephew Miguel between 1497 and 1500, Joanna became the heir presumptive to the crowns of Castile and Aragon. When her mother died in 1504, she became queen of Castile. Her father proclaimed himself governor and administrator of Castile.

Martin Behaim, also known as Martin von Behaim and by various forms of Martin of Bohemia, was a German textile merchant and cartographer. He served John II of Portugal as an adviser in matters of navigation and participated in a voyage to West Africa. He is now best known for his Erdapfel, the world's oldest known globe, which he produced for the Imperial City of Nuremberg in 1492.

Matthias Ringmann (1482–1511), also known as Philesius Vogesigena was an Alsatian German humanist scholar and cosmographer. Along with cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, he is credited with the first documented usage of the word America, on the 1507 map Universalis Cosmographia in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci.

Ferdinand of Portugal, Duke of Guarda was a Portuguese infante (prince), the son of King Manuel I of Portugal and his second wife, Maria of Aragon.

St. Angelo Fort is a fort facing the Arabian Sea, situated 3 km from Canannore (Kannur), a city in Kerala state, south India.

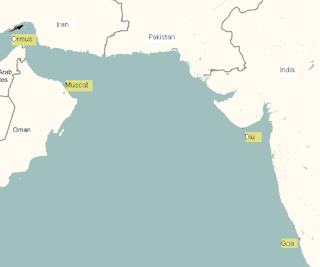
The Fort of Our Lady of the Conception, also known as the Portuguese Castle, is a red stone fortress on Hormuz Island, Iran. It is one of the last surviving monuments of Portuguese colonial rule in the Persian Gulf. Ormuz was an important maritime city and a small kingdom near the entrance to the Persian Gulf. The original site of the city was on the north shore of the Gulf, about 30 miles east of the current Bandar Abbas. Around 1300, apparently in response to attacks from the Tartars, it moved to the small island of Gerun, which can be identified as the Organa of Nearcho, about 12 miles west and 5 miles from the coast.
Johannes Ruysch, a.k.a. Johann Ruijsch or Giovanni Ruisch was an explorer, cartographer, astronomer, manuscript illustrator and painter from the Low Countries who produced a famous map of the world: the second oldest known printed representation of the New World. This Ruysch map was published and widely distributed in 1507.
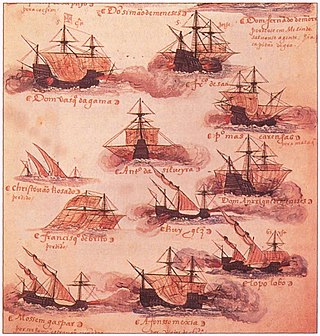
The Battle of Chaul was a naval battle between the Portuguese and an Egyptian Mamluk fleet in 1508 in the harbour of Chaul in India. The battle ended in a Mamluk victory. It followed the Siege of Cannanore in which a Portuguese garrison successfully resisted an attack by Southern Indian rulers. This was the first Portuguese defeat at sea in the Indian Ocean.
The Battle of Cannanore took place in 1506 off the harbour of Cannanore in India, between the Indian fleet of the Zamorin of Calicut and a Portuguese fleet under Lourenço de Almeida, son of the Viceroy Almeida.

The siege of Cannanore was a four-month siege, from 27 April 1507 to 27 August 1507, when troops of the local ruler, supported by the Zamorin of Calicut and Arabs, besieged the Portuguese garrison at St. Angelo Fort in Cannanore, in what is now the Indian state of Kerala. It followed the Battle of Cannanore, in which the fleet of the Zamorin was defeated by the Portuguese.

The Portuguese conquest of Hormuz in 1507 occurred when the Portuguese Afonso de Albuquerque attacked Hormuz Island to establish the Fortress of Hormuz. This conquest gave the Portuguese full control of the trade between India and Europe passing through the Persian Gulf.

The Portuguese–Safavid wars were a series of wars between the Portuguese Empire and Safavid Iran from 1507 to 1625. The Portuguese were also supported by Kingdom of Hormuz, its vassal, and Safavids had the help of the Kingdom of England on the other side.
Diogo Fernandes Pereira, sometimes called simply Diogo Fernandes, was a Portuguese 16th-century navigator, originally from Setúbal, Portugal. Diogo Fernandes was the first known European captain to visit the island of Socotra in 1503 and the discoverer of the Mascarenes archipelago in 1507. He may also have been the first European to sail east of Madagascar island.
Egyptian Mamluk–Portuguese conflicts refers to the armed engagements between the Egyptian state of the Mamluks and the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean, following the expansion of the Portuguese after sailing around the Cape of Good Hope in 1498. The conflict took place during the early part of the 16th century, from 1505 to the fall of the Mamluk Sultanate in 1517.

The capture of Muscat occurred in 1552, when an Ottoman fleet under Piri Reis attacked Old Muscat, in modern Oman, and plundered the town from the Portuguese. These events followed the important Ottoman defeat in the third siege of Diu in 1546, which put a stop to their attempts in India, but also the successful capture of Aden in 1548, which allowed the Ottomans to resist the Portuguese in the northwestern part of the Indian Ocean.

The Battle of Barawa was an armed military encounter between the Portuguese Empire and the Ajuran Sultanate, in the city of Barawa. The Portuguese staged a landing and achieved their objectives of sacking the city.