Related Research Articles

Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan Siddiqi also known as Chin Qilich Qamaruddin Khan, Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah and Nizam I, was the first Nizam of Hyderabad.

Mirza Mu'izz-ud-Din Beg Muhammad Khan, better known by his title Jahandar Shah, was briefly the ninth Mughal emperor from 1712 to 1713. He was the son of emperor Bahadur Shah I, and the grandson of emperor Aurangzeb.

Mirza Muhammad Mu'azzam, commonly known as Bahadur Shah I and Shah Alam I, was the eighth Mughal Emperor from 1707 to 1712. He was the second son of the sixth Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, who he conspired to overthrow in his youth. He was also governor of the imperial provinces of Agra, Kabul and Lahore and had to face revolts of Rajputs and Sikhs.

Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State. Nizam is a shortened form of Niẓām ul-Mulk, and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I when he was appointed Viceroy of the Deccan by the Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar. In addition to being the Mughal Viceroy (Naib) of the Deccan, Asaf Jah I was also the premier courtier of the Mughal Empire until 1724, when he established an independent realm based in Hyderabad, but in practice, continued to recognise the nominal authority of emperor.

Mirza Aziz-ud-Din Muhammad, better known by his regnal name Alamgir II, was the fifteenth Mughal emperor from 1754 to 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah.

Ahmad Shah Bahadur, also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi, was the fourteenth Mughal emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age of 22. When Ahmed Shah Bahadur came to power, the Mughal Empire started to decline. Furthermore, his administrative weakness eventually led to the rise of the usurping Imad-ul-Mulk.

Mir Ahmad Ali Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi, Nasir Jung, was the second Nizam of Hyderabad State. He was the son of Asaf Jah I and his wife Saeed-un-nisa Begum. He was born 26 February 1712. He had taken up a title of Humayun Jah, Nizam ud-Daula, Nawab Mir Ahmad Ali Khan Siddiqi Bahadur, Nasir Jung, Nawab Subadar of the Deccan. However, he is most famously known as Nasir Jung.

Salabat Jung, born as Mir Sa'id Muhammad Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi on 24 November 1718, was the fourth Nizam of Hyderabad State. He was the third son of Asaf Jah I.

The Malwa Sultanate was a late medieval kingdom in the Malwa region, covering the present day Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and south-eastern Rajasthan from 1401 to 1562. It was founded by Dilawar Khan, who following Timur's invasion and the disintegration of the Delhi Sultanate, in 1401, made Malwa an independent realm.

The Asaf Jahi was a Muslim dynasty that ruled the Hyderabad State. The family came to India in the late 17th century and became employees of the Mughal Empire. They were great patrons of Indo-Persian culture, language, and literature, and the family found ready patronage.

Hafiz Rahmat Khan was the Regent of Rohilkhand in North India, from 1749 to 1774. He was a Pashtun by background, ruling over Rohillas. Hafiz Rahmat Khan had served honorably throughout the reign of three Mughal Emperors: Ahmad Shah Bahadur, Alamgir II and Shah Alam II. He was also a mentor of Prince Mirza Jawan Bakht.

Khawaja Abid Khan Siddiqi, or Nawab Khawaja Abid Siddiqi, better known as Kilich Khan, was a Nawab and military general under Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. He was a loyal general of the Mughal Empire. He was the father of the Mughal general Ghazi ud-Din Khan Feroze Jung I and the grandfather of Mir Qamar-ud-din Siddiqi, Asaf Jah I. Kilich Khan was a descendant of Abu Bakr, first Rashidun caliph.

Feroze Jung III or Nizam Shahabuddin Muhammad Feroz Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi also known by his sobriquet Imad-ul-Mulk, was the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire when it was under Maratha suzerainty, making them the de facto rulers.

Mir Shihab-ud-Din Siddiqi, known by his title Ghaziuddin Khan, was a leading military general and noble of Central Asian origin in the Mughal Empire. He was a favoured member of emperor Aurangzeb's court, and the father of Chin Qilich Khan, founder of Hyderabad State. Under Aurangzeb, he distinguished himself in key battles over the Deccan, and held the governorship of Berar Subah. He briefly served as the governor of Gujarat Subah during the reign of Aurangzeb's successor Bahadur Shah, and died in office. He is buried in a madrasa complex he founded during his lifetime, known as Madrasa Ghaziuddin Khan, which is located in Old Delhi.

The siege of Golconda was a siege of Golconda Fort between the Qutb Shahi dynasty and the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, occurring in January 1687, lasting 8 months. The fort was home of the Kollur Mine. The Golconda Fort was considered to be an impregnable fort on the Indian subcontinent. At the end of the siege, Aurangzeb and the Mughals entered Golconda victorious.

The siege of Bijapur began in March 1685 and ended in September 1686 with a Mughal victory. The siege began when Aurangzeb dispatched his son, Muhammad Azam Shah, with a force of nearly 50,000 men to capture Bijapur Fort and defeat Sikandar Adil Shah, the then Sultan of Bijapur, who refused to be a vassal of the Mughal Empire. The siege of Bijapur was among the longest military engagements of the Mughals, lasting more than 15 months until Aurangzeb personally arrived to organise a victory.

The siege of Jinji,, began when the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb appointed Zulfiqar Ali Khan as the Nawab of the Carnatic and dispatched him to besiege and capture Jinji Fort, which had been sacked and captured by Maratha Empire troops led by Rajaram, they had also ambushed and killed about 300 Mughal Sowars in the Carnatic. The Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb then ordered Ghazi ud-Din Khan Feroze Jung I to protect the supply routes leading to Jinji Fort and to support and provide reinforcements to Zulfiqar Ali Khan when needed.
Intizam-ud-Daula, Ghazi ud-Din Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi Feroze Jung II was the eldest son of Asaf Jah I Mir Qamaruddin Khan Siddiqi. He was born on 13 March 1709, his mother is Sa'id un-Nisa Begum, the daughter of a Sayyid nobleman at Gulbarga. He died in Aurangabad on 16 October 1752.
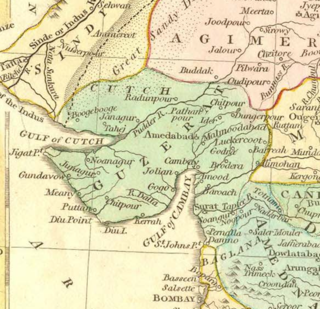
The Gujarat Subah was a province (subah) of the Mughal Empire, encompassing the Gujarat region. The region first fell under Mughal control in 1573, when the Mughal emperor Akbar defeated the Gujarat Sultanate under Muzaffar Shah III.
Turkic peoples have historically been associated as one of the non-native peoples to have ruled areas of the Indian subcontinent. Various dynasties of the later medieval era and early modern era in India were of Turkic and mixed Indian or Afghan descent. Two of the dynasties of the Delhi Sultanate, viz. the Tughlaqs and Khaljis, for instance, were of mixed Turkic origin, with Indian and Afghan ancestry respectively. The terms Indo-Turkic or Turco-Indian is used to refer to people and dynasties of mixed Turkic and Indian descent, as well as the fusion culture formed as a result.
References
- ↑ "Bahādur Shah I | Mughal emperor". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2020-05-03.
- ↑ "Bahadur Shah I: Some interesting facts about the seventh Mughal Emperor of India". India Today. October 14, 2016. Retrieved 2020-05-03.
- ↑ "Ghazi ud-Din Khan Feroze Jung Iの意味・使い方・読み方 | Weblio英和辞書". ejje.weblio.jp (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2020-08-20. Retrieved 2020-05-03.