Related Research Articles

ISO 8601 is an international standard covering the worldwide exchange and communication of date and time-related data. It is maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and was first published in 1988, with updates in 1991, 2000, 2004, and 2019, and an amendment in 2022. The standard provides a well-defined, unambiguous method of representing calendar dates and times in worldwide communications, especially to avoid misinterpreting numeric dates and times when such data is transferred between countries with different conventions for writing numeric dates and times.
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when communicating with another IP address. For example, an error is indicated when a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications.
NT File System (NTFS) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft in the 1990s.

Windows Notepad is a simple text editor for Windows; it creates and edits plain text documents. It was first released in 1983 to commercialize the computer mouse in MS-DOS.
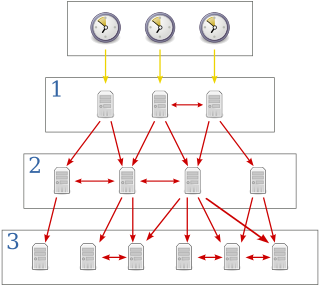
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware.
A Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit label used to uniquely identify objects in computer systems. The term Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) is also used, mostly in Microsoft systems.
Uptime is a measure of system reliability, expressed as the period of time a machine, typically a computer, has been continuously working and available. Uptime is the opposite of downtime.

The year 2038 problem is a time computing problem that leaves some computer systems unable to represent times after 03:14:07 UTC on 19 January 2038.
In computing, touch is a command used to update the access date and/or modification date of a computer file or directory. It is included in Unix and Unix-like operating systems, TSC's FLEX, Digital Research/Novell DR DOS, the AROS shell, the Microware OS-9 shell, and ReactOS. The command is also available for FreeDOS and Microsoft Windows.

A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolute notion of time, however. They can have any epoch, can be relative to any arbitrary time, such as the power-on time of a system, or to some arbitrary time in the past.

Unix time is a date and time representation widely used in computing. It measures time by the number of non-leap seconds that have elapsed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970, the Unix epoch. For example, at midnight on 1 January 2010, Unix time was 1262304000.
The Media Transfer Protocol (MTP) is an extension to the Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP) communications protocol that allows media files to be transferred automatically to and from portable devices. Whereas PTP was designed for downloading photographs from digital cameras, Media Transfer Protocol allows the transfer of music files on digital audio players and media files on portable media players, as well as personal information on personal digital assistants. MTP is a key part of WMDRM10-PD, a digital rights management (DRM) service for the Windows Media platform. In 2011, it became the standard method to transfer files to and from Android.
Microsoft Expression Web is a discontinued HTML editor and general web design software product by Microsoft. It was discontinued on December 20, 2012, and subsequently made available free of charge from Microsoft. It was a component of the also discontinued Expression Studio.
In computer science and computer programming, system time represents a computer system's notion of the passage of time. In this sense, time also includes the passing of days on the calendar.
exFAT is a file system optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards, that was introduced by Microsoft in 2006. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specification. Microsoft owns patents on several elements of its design.
Robocopy is a command-line file transfer utility for Microsoft Windows. Robocopy is functionally more comprehensive than the COPY command and XCOPY, but replaces neither. Created by Kevin Allen and first released as part of the Windows NT 4.0 Resource Kit, it has been a standard feature of Windows since Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
Trusted timestamping is the process of securely keeping track of the creation and modification time of a document. Security here means that no one—not even the owner of the document—should be able to change it once it has been recorded provided that the timestamper's integrity is never compromised.
In computer science, data type limitations and software bugs can cause errors in time and date calculation or display. These are most commonly manifestations of arithmetic overflow, but can also be the result of other issues. The best-known consequence of this type is the Y2K problem, but many other milestone dates or times exist that have caused or will cause problems depending on various programming deficiencies.
In computing, an epoch is a fixed date and time used as a reference from which a computer measures system time. Most computer systems determine time as a number representing the seconds removed from a particular arbitrary date and time. For instance, Unix and POSIX measure time as the number of seconds that have passed since Thursday 1 January 1970 00:00:00 UT, a point in time known as the Unix epoch. The C# programming language and Windows NT systems up to and including Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022 measure time as the number of 100-nanosecond intervals that have passed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January in the years AD 1 and AD 1601, respectively, making those points in time the epochs for those systems. Computing epochs are almost always specified as midnight Universal Time on some particular date.
The leap year problem is a problem for both digital (computer-related) and non-digital documentation and data storage situations which results from errors in the calculation of which years are leap years, or from manipulating dates without regard to the difference between leap years and common years.
References
- ↑ "INFO: Working with the FILETIME Structure". Microsoft . Retrieved 2011-10-25.
- ↑ "Dandelions, VCR Clocks, and Last Logon Times: These Are a Few of Our Least Favorite Things". Hey, Scripting Guy! Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2009-03-08. Retrieved 2011-10-25.