| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1662 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1662 in China .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1662 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1662 in China .

Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping, better known internationally as Koxinga, was a Southern Ming general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern coast.

Wu Sangui, courtesy name Changbai (長白) or Changbo (長伯), was a notorious Ming dynasty military officer who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty in China. In Chinese folklore, Wu Sangui is regarded as a disreputable Han Chinese traitor who played a pivotal role in several historical events, including the Battle of Shanhai Pass, Qing conquest of Ming China, the suppression of Southern Ming resistances and the execution of the Yongli Emperor, and eventually double-crossed both of his masters, the Ming and the Qing dynasties.

The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was led by the three lords of the fiefdoms in Yunnan, Guangdong and Fujian provinces against the Qing central government. These hereditary titles had been given to prominent Han Chinese defectors who had helped the Manchu conquer China during the transition from Ming to Qing. The feudatories were supported by Zheng Jing's Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan, which sent forces to invade Mainland China. Additionally, minor Han military figures, such as Wang Fuchen and the Chahar Mongols, also revolted against Qing rule. After the last remaining Han resistance had been put down, the former princely titles were abolished.

Shi Lang (1621–1696), Marquis Jinghai, also known as Secoe or Sego, was a Chinese admiral who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties in the 17th century. He was the commander-in-chief of the Qing fleets which destroyed the power of Zheng Chenggong's descendants in the 1660s, and led the conquest of the Zheng family's Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan in 1683. Shi later governed part of Taiwan as a marquis.

The Yongli Emperor, personal name Zhu Youlang, was the fourth and last emperor of the Southern Ming dynasty, reigning in turbulent times when the former Ming dynasty was overthrown and the Manchu-led Qing dynasty progressively conquered the entire China proper. He led the remnants of the Ming loyalists with the assistance of peasant armies to resist the Qing forces in southwestern China, but he was then forced to exile to Toungoo Burma and eventually captured and executed by Wu Sangui in 1662. His era title "Yongli" means "perpetual calendar".

Zheng Jing, Prince of Yanping, courtesy names Xianzhi and Yuanzhi, pseudonym Shitian, was a Chinese military general, monarch, pirate, and politician of the Ming dynasty and a loyalist and ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan.

The Kingdom of Tungning, also known as Tywan by the British at the time, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly ethnic Han state in Taiwanese history. At its zenith, the kingdom's maritime power dominated varying extents of coastal regions of southeastern China and controlled the major sea lanes across both China Seas, and its vast trade network stretched from Japan to Southeast Asia.
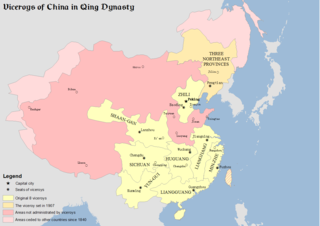
Zongdu, usually translated as Viceroy, Head of State or Governor-General, governed one territory or more provinces of China during the Ming and Qing dynasties.

Zheng Keshuang, Prince of Yanping, courtesy name Shihong, art name Huitang, was the third and last ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan in the 17th century. He was the second son of Zheng Jing and a grandson of Koxinga. After surrendering to the Qing dynasty in 1683, he was ennobled as Duke of Hanjun (漢軍公), and lived the rest of his life in Beijing.

Zheng Zhilong, Marquis of Tong'an, baptismal name Nicholas Iquan Gaspard, was a Chinese admiral, merchant, military general, pirate, and politician of the late Ming dynasty who later defected to the Qing dynasty. He was from Nan'an County in Fujian province of China. He was the father of Koxinga, Prince of Yanping, the founder of the pro-Ming Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan, and as such an ancestor of the House of Koxinga. After his defection, he was given noble titles by the Qing government, but was eventually executed because of his son's continued resistance against the Qing regime.

Yongli was the era name of the Yongli Emperor of the Southern Ming. It was used for a total of 15 years.

Zhu Yujian, nickname Changshou (長壽), originally the Prince of Tang, later reigned as the Longwu Emperor of the Southern Ming dynasty from 18 August 1645, when he was enthroned in Fuzhou, to 6 October 1646, when he was captured and executed by a contingent of the Qing army. He was an eighth generation descendant of Zhu Jing, Prince Ding of Tang, who was the 23rd son of Ming founder Zhu Yuanzhang.
The Southern Ming, also known in historiography as the Later Ming, officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun forces led by Li Zicheng captured Beijing and the Chongzhen Emperor committed suicide. The Ming general Wu Sangui then opened the gates of the Shanhai Pass in the eastern section of the Great Wall to the Qing banners, in hope of using them to annihilate the Shun forces. Ming loyalists fled to Nanjing, where they enthroned Zhu Yousong as the Hongguang Emperor, marking the start of the Southern Ming. The Nanjing regime lasted until 1645, when Qing forces captured Nanjing. Zhu fled before the city fell, but was captured and executed shortly thereafter. Later figures continued to hold court in various southern Chinese cities, although the Qing considered them to be pretenders.

Li Dingguo, formally Prince of Jin, was a Chinese military general of the Southern Ming dynasty who fought against the Qing dynasty.

The Sino-Dutch War 1661, also known as Hero Zheng Chenggong, is a 2000 Chinese historical drama film directed by Wu Ziniu, starring Vincent Zhao, Jiang Qinqin, Du Zhiguo, Yoko Shimada, Xu Min and Zhang Shan. The film is loosely based on the life of Koxinga and focuses on his battle with the Dutch East India Company for control of Taiwan at the Siege of Fort Zeelandia. The film was released in 2002 in Japan under the title Kokusenya Kassen.

The transition from Ming to Qing or the Manchu conquest of China from 1618 to 1683 saw the transition between two major dynasties in Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging Qing dynasty, the incumbent Ming dynasty, and several smaller factions. It ended with the consolidation of Qing rule, and the fall of the Ming and several other factions.
Events from the year 1661 in the Qing dynasty.
Events from the year 1663 in China. Also known as 壬寅 4359 or 4299 to 卯年 4360 or 4300 in the Earthly Branches calendar.
Events from the year 1681 in China.